What's Mcg To Iu Vitamin D? Easy Conversion
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining strong bones, immune function, and overall health. When it comes to measuring vitamin D intake, two common units of measurement are micrograms (mcg) and International Units (IU). Understanding the conversion between these units is vital for ensuring adequate vitamin D supplementation and avoiding excessive intake.
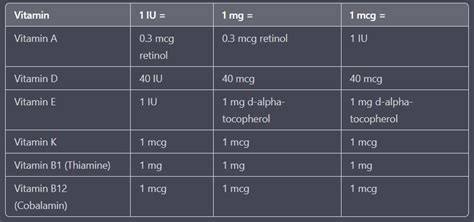
The conversion rate between micrograms and International Units for vitamin D is as follows: 1 microgram (mcg) of vitamin D is equivalent to 40 International Units (IU). This conversion factor applies to both vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol), which are the two primary forms of vitamin D used in dietary supplements.
To convert mcg to IU for vitamin D, you can use the following simple formula:
IU = mcg x 40
For example, if a vitamin D supplement contains 2.5 mcg of vitamin D3, the equivalent dosage in IU would be:
IU = 2.5 mcg x 40 = 100 IU
Conversely, to convert IU to mcg, you can use the inverse formula:
mcg = IU / 40
For instance, if a multivitamin contains 2000 IU of vitamin D, the equivalent dosage in mcg would be:
mcg = 2000 IU / 40 = 50 mcg
It’s essential to note that the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for vitamin D varies based on factors such as age, sex, and overall health status. The Institute of Medicine recommends the following daily intake levels for vitamin D:
- Infants 0-12 months: 400 IU (10 mcg)
- Children 1-18 years: 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults 19-50 years: 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults 51-70 years: 600 IU (15 mcg)
- Adults over 70 years: 800 IU (20 mcg)
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women: 600 IU (15 mcg)
When selecting a vitamin D supplement, it’s crucial to choose a product that provides the recommended amount of vitamin D in IU or mcg. Be sure to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen, as excessive intake of vitamin D can cause adverse effects.
In terms of food sources, few foods are naturally rich in vitamin D. However, some examples of vitamin D-rich foods and their approximate IU content per serving are:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines): 600 IU (15 mcg) per 3-ounce serving
- Fortified dairy products (milk, cheese, yogurt): 100 IU (2.5 mcg) per cup
- Fortified cereals: 40 IU (1 mcg) per serving
- Mushrooms (shiitake, portobello): 100 IU (2.5 mcg) per 3-ounce serving
In conclusion, understanding the conversion between mcg and IU for vitamin D is vital for ensuring adequate supplementation and avoiding excessive intake. By using the conversion formula and being aware of the recommended dietary allowance, you can make informed decisions about your vitamin D intake and maintain optimal health.
Key Takeaway:
1 microgram (mcg) of vitamin D is equivalent to 40 International Units (IU). Use the conversion formula IU = mcg x 40 to convert between units and ensure adequate vitamin D supplementation.
What is the recommended daily intake of vitamin D?
+The recommended daily intake of vitamin D varies based on factors such as age, sex, and overall health status. The Institute of Medicine recommends 600 IU (15 mcg) per day for adults 19-50 years and 800 IU (20 mcg) per day for adults over 70 years.
What foods are naturally rich in vitamin D?
+Few foods are naturally rich in vitamin D. However, examples of vitamin D-rich foods include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), fortified dairy products, and mushrooms (shiitake, portobello).
What are the risks of excessive vitamin D intake?
+Excessive intake of vitamin D can cause adverse effects, including nausea, vomiting, and weakness. It can also lead to more serious health problems, such as kidney stones and hardening of arteries. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen.
By following these guidelines and being mindful of the conversion between mcg and IU, you can ensure adequate vitamin D intake and maintain optimal health. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen, and always choose a high-quality supplement that provides the recommended amount of vitamin D.