When Do High Sugar Levels Become Dangerous? Know Now
High sugar levels, also known as hyperglycemia, can be a serious health concern if left untreated or poorly managed. The body’s primary source of energy is glucose, a type of sugar found in the bloodstream. However, when glucose levels exceed the normal range, it can lead to a range of complications, from mild to life-threatening. In this article, we will delve into the world of high sugar levels, exploring the dangers, symptoms, and consequences of uncontrolled hyperglycemia.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
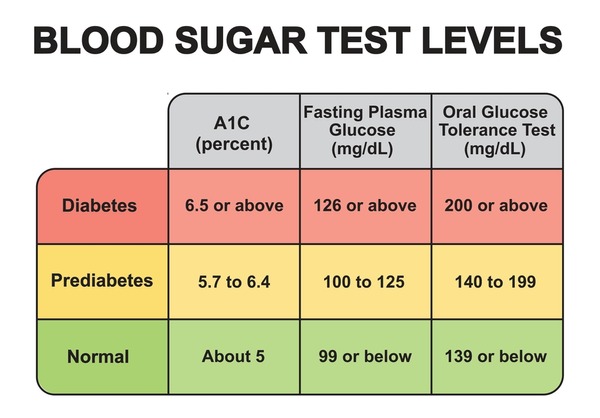
To grasp the concept of high sugar levels, it’s essential to understand how blood sugar works. When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream. The pancreas, an organ located behind the stomach, produces insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels. Insulin facilitates the entry of glucose into cells, where it’s used for energy production, growth, and repair. In a healthy individual, blood sugar levels typically range from 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL).
The Dangers of High Sugar Levels
Prolonged periods of high sugar levels can lead to a range of health problems, including:
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA): A life-threatening condition that occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, toxic acids that can poison the body. DKA is often triggered by uncontrolled hyperglycemia, particularly in individuals with type 1 diabetes.
- Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome (HHNS): A condition characterized by extremely high blood sugar levels, often above 600 mg/dL. HHNS can cause seizures, coma, and even death if left untreated.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy): High sugar levels can damage the nerves, leading to numbness, tingling, and pain in the hands and feet.
- Kidney Damage (Nephropathy): Uncontrolled hyperglycemia can damage the kidneys, increasing the risk of kidney failure and end-stage renal disease.
- Blindness (Retinopathy): High sugar levels can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision loss and blindness.
Symptoms of High Sugar Levels
Recognizing the symptoms of high sugar levels is crucial for prompt treatment and prevention of complications. Common symptoms include:
- Increased Thirst and Urination: High sugar levels can lead to excessive thirst and urination, as the body tries to flush out excess glucose.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Uncontrolled hyperglycemia can cause fatigue, weakness, and a lack of energy.
- Blurred Vision: High sugar levels can cause blurry vision, double vision, or even vision loss.
- Slow Healing of Cuts and Wounds: Poor blood sugar control can impede the healing process, increasing the risk of infections.
- Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet: Nerve damage caused by high sugar levels can lead to numbness, tingling, or pain in the extremities.
When Do High Sugar Levels Become Dangerous?
High sugar levels become dangerous when they exceed 250 mg/dL for an extended period. However, the exact threshold may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, health status, and medications. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine a safe blood sugar range.
Managing High Sugar Levels
Fortunately, high sugar levels can be managed and controlled with the right treatment plan. This may include:
- Medications: Oral medications or insulin therapy can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Lifestyle Changes: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help control hyperglycemia.
- Monitoring: Regular blood sugar monitoring can help identify patterns and trends, enabling prompt adjustments to the treatment plan.
FAQ Section
What are the symptoms of high sugar levels?
+Common symptoms of high sugar levels include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, and tingling or numbness in hands and feet.
How can I manage high sugar levels?
+High sugar levels can be managed with medications, lifestyle changes, and monitoring. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and stress management can help control hyperglycemia.
What are the dangers of high sugar levels?
+Prolonged periods of high sugar levels can lead to a range of health problems, including diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperglycemic hyperosmolar nonketotic syndrome, nerve damage, kidney damage, and blindness.
When do high sugar levels become dangerous?
+High sugar levels become dangerous when they exceed 250 mg/dL for an extended period. However, the exact threshold may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, health status, and medications.
How often should I monitor my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of blood sugar monitoring depends on individual factors, such as the type of diabetes, medications, and lifestyle. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best monitoring schedule for your needs.
Conclusion
High sugar levels can be a serious health concern if left untreated or poorly managed. Recognizing the symptoms, understanding the dangers, and managing hyperglycemia with the right treatment plan can help prevent complications and ensure optimal health. By monitoring blood sugar levels, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can take control of their health and mitigate the risks associated with high sugar levels. Remember, knowledge is power, and being informed about high sugar levels is the first step towards a healthier, happier life.



