When Do Strep Throat Symptoms Appear? Know The Signs

Strep throat, also known as streptococcal pharyngitis, is a bacterial infection caused by Group A Streptococcus (GAS). It’s a common illness that affects people of all ages, but it’s most prevalent among children and adolescents. One of the most critical aspects of managing strep throat is recognizing its symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of strep throat, exploring when its symptoms appear, the signs to look out for, and what you can do to prevent and treat this infection.
Incubation Period: The Timeline of Symptom Onset
The incubation period of strep throat refers to the time between exposure to the bacteria and the onset of symptoms. Typically, the incubation period for strep throat ranges from 2 to 5 days, with most people developing symptoms within 3 days of exposure. During this time, the bacteria multiply and invade the tissues of the throat, leading to inflammation and the characteristic symptoms of strep throat.
Early Signs and Symptoms: What to Look Out For
The symptoms of strep throat can vary from person to person, but there are some common signs to look out for. These may include:
- Sudden onset of sore throat: A severe, sharp pain in the throat that can make swallowing difficult
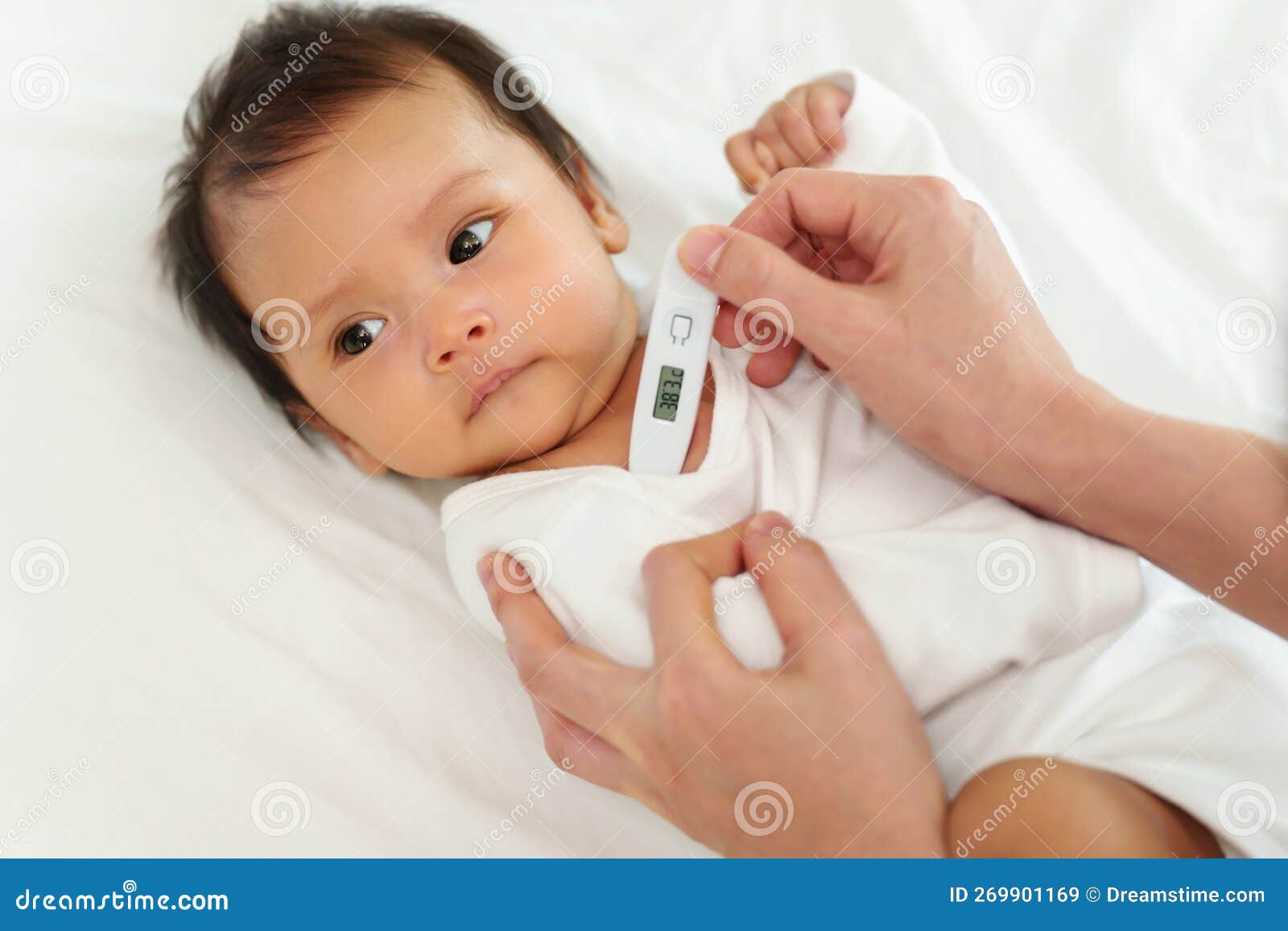
- Fever: A high temperature, often above 101°F (38.3°C)
- White or yellowish patches on the tonsils: These patches can be a sign of bacterial infection
- Swollen, tender lymph nodes in the neck: Enlarged lymph nodes can indicate that the body is fighting an infection
- Headache: A severe headache can accompany the other symptoms of strep throat
- Stomachache: Some people may experience abdominal pain or nausea
- Loss of appetite: The pain and discomfort of strep throat can lead to a decrease in appetite
What to Expect: The Progression of Symptoms
If left untreated, strep throat can lead to complications, such as kidney inflammation or rheumatic fever. It’s essential to recognize the symptoms of strep throat and seek medical attention if you or your child is experiencing any of the following:
- Severe throat pain that lasts for more than 48 hours
- Fever above 103°F (39.4°C)
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- A sore throat accompanied by a rash or other symptoms
Diagnosis and Treatment: What You Need to Know
A healthcare professional can diagnose strep throat using a rapid strep test or a throat culture. If the test is positive, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection. It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication.
Prevention Strategies: Reducing the Risk of Transmission
Strep throat is highly contagious, and it can spread through:
- Direct contact with an infected person’s mucus or saliva
- Indirect contact with contaminated surfaces or objects
- Droplet transmission through coughing or sneezing
To reduce the risk of transmission, practice good hygiene:
- Wash your hands frequently with soap and water
- Avoid close contact with people who have strep throat
- Avoid sharing food, drinks, or personal items
- Cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
How long is someone with strep throat contagious?
+Someone with strep throat is typically contagious for 2-3 weeks, but they can spread the infection to others within 2-5 days of developing symptoms. Antibiotics can reduce the contagious period to 24 hours after starting treatment.
Can strep throat be treated without antibiotics?
+Antibiotics are the most effective treatment for strep throat. Without antibiotics, the infection can lead to complications, and the risk of transmission to others increases. However, over-the-counter pain relievers and home remedies can help alleviate symptoms.
How can I prevent getting strep throat?
+Practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with people who have strep throat, and not sharing personal items can help reduce the risk of transmission. Additionally, washing your hands frequently, covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing, and avoiding touching your face can help prevent the spread of the infection.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of strep throat and seeking medical attention promptly is crucial to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission. By understanding the incubation period, early signs, and symptoms of strep throat, you can take the necessary steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Remember to practice good hygiene, complete the full course of antibiotics, and follow prevention strategies to reduce the risk of transmission.