10+ Blood Sugar Checks To Confirm Diabetes Fast
When it comes to diagnosing diabetes, one of the most critical steps is confirming the presence of high blood sugar levels through multiple checks. The American Diabetes Association recommends that a diagnosis of diabetes be confirmed through one of the following methods: a fasting plasma glucose test, an oral glucose tolerance test, or a random plasma glucose test, with a confirmatory test on a separate day if the initial test is abnormal. Here, we’ll explore over 10 different methods and considerations for confirming diabetes, emphasizing the importance of thorough and repeated testing to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning.
1. Fasting Plasma Glucose (FPG) Test
This test measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. A level of 126 mg/dL or higher on two separate occasions confirms diabetes.
2. Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
During this test, blood glucose levels are measured after an overnight fast and then again 2 hours after consuming a glucose-rich drink. A 2-hour level of 200 mg/dL or higher confirms diabetes.
3. Random Plasma Glucose Test
This test can be taken at any time and does not require fasting. Blood glucose levels of 200 mg/dL or higher, accompanied by symptoms such as increased thirst and urination, confirm diabetes.
4. Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test
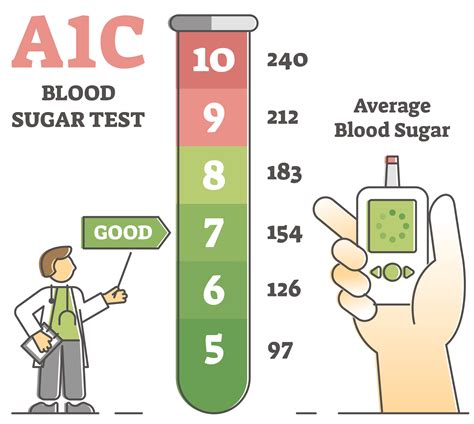
This blood test provides information on average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. An HbA1c level of 6.5% or higher confirms diabetes.
5. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM devices track glucose levels throughout the day and night, providing a detailed picture of glucose levels. This can be particularly useful for confirming patterns of high blood sugar.
6. Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG)
Using a glucometer at home to check blood glucose levels multiple times a day can provide valuable data to confirm diabetes and monitor the effectiveness of treatment.
7. Glycated Albumin Test
For individuals who have conditions affecting hemoglobin, such as anemia, a glycated albumin test can provide an alternative measure of average blood glucose control over the past 2 weeks.
8. 1,5-Anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) Test
This test measures a substance in the blood that decreases when blood glucose levels are high. It can be used to assess glycemic control over a short period.
9. Fructosamine Test
Similar to the HbA1c test, fructosamine measures average blood glucose levels but over a shorter period (about 2-3 weeks). It can be an alternative for people with certain blood disorders.
10. Urine Tests
While not as accurate for diagnosing diabetes, urine tests can detect ketones (produced when the body breaks down fat for energy instead of glucose) or glucose in the urine, which can indicate high blood glucose levels.
Additional Considerations
- Multiple Confirmatory Tests: It’s crucial to use more than one test method on different days to confirm the diagnosis, as recommended by clinical guidelines.
- Symptom Evaluation: Alongside these tests, healthcare providers evaluate symptoms such as polyuria (frequent urination), polydipsia (excessive thirst), and polyphagia (increased appetite).
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A thorough medical history and physical examination are also essential components of the diagnostic process.
- Lifestyle and Genetic Factors: Understanding an individual’s lifestyle, including diet and physical activity level, as well as genetic predispositions, can provide a more comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment planning.
FAQ Section
How often should blood sugar checks be performed to confirm diabetes?
+Blood sugar checks should be performed multiple times and on different days, using more than one method, to confirm a diagnosis of diabetes accurately.
What is the role of the HbA1c test in confirming diabetes?
+The HbA1c test provides a measure of average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months and is a crucial tool for confirming diabetes, with levels of 6.5% or higher indicating diabetes.
Can urine tests alone confirm diabetes?
+No, urine tests are not definitive for diagnosing diabetes. They can detect ketones or glucose in the urine but should be used in conjunction with blood glucose tests for a confirmed diagnosis.
Confirming diabetes through multiple blood sugar checks and tests is a critical step in managing the condition effectively. By understanding the various methods available and their applications, individuals can work closely with healthcare providers to ensure an accurate diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan.