10+ Elevated B12 Reasons Explained

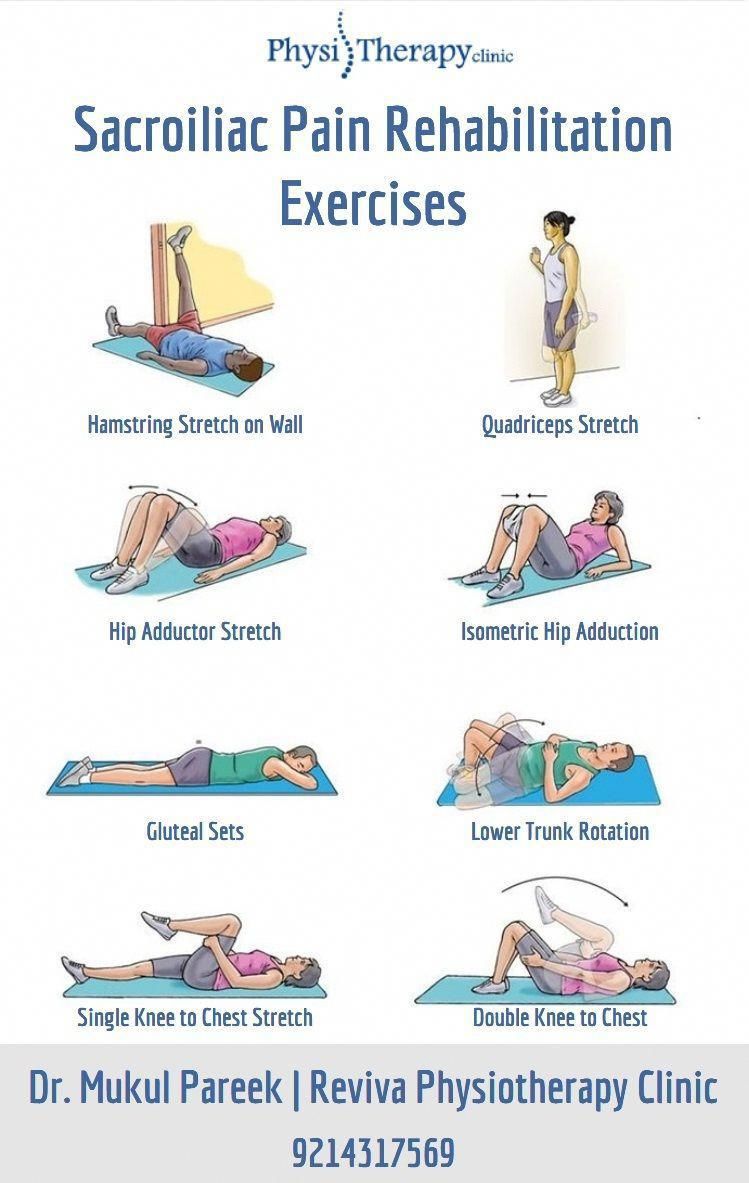
Vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient that plays a central role in various bodily functions, including the production of red blood cells, the maintenance of the nervous system, and the synthesis of DNA. An elevated level of vitamin B12, also known as hypercobalaminemia or hypervitaminosis B12, in the blood can have several implications, some of which may be beneficial, while others could indicate underlying health issues. Let’s delve into the reasons behind elevated B12 levels and explore the complexities surrounding this condition.
1. Dietary Intake
Consuming large amounts of vitamin B12 through diet or supplements can lead to elevated levels in the blood. Vitamin B12 is found naturally in animal products, such as meat, fish, and dairy products. Vegetarians and vegans, who might have lower levels due to their diet, sometimes take high doses of B12 supplements, potentially resulting in higher-than-normal blood levels.
2. Supplementation
The use of vitamin B12 supplements, especially in high doses, is a common cause of elevated B12 levels. This is particularly true for individuals who do not have a dietary deficiency but are taking supplements for energy boosts or to prevent deficiency, as the body can only use so much B12 at a time.
3. Liver Disease
Certain liver diseases, such as liver cancer or cirrhosis, can lead to elevated vitamin B12 levels. The liver stores vitamin B12, and when it is diseased, it may release excess amounts of the vitamin into the bloodstream.
4. Kidney Disease
Kidney disease can impair the body’s ability to effectively remove waste and excess substances, including vitamins. As a result, individuals with kidney disease may experience elevated levels of vitamin B12 due to reduced excretion.
5. Myeloproliferative Disorders
Myeloproliferative disorders, such as polycythemia vera or chronic myeloid leukemia, are conditions where the bone marrow overproduces blood cells. These disorders can lead to increased levels of vitamin B12 because the bone marrow releases more transcobalamin I, a protein that binds to vitamin B12, into the bloodstream.
6. Infectious Diseases
Certain infectious diseases, including bacterial overgrowth in the gut, can lead to elevated B12 levels. Some bacteria can produce vitamin B12, and an overgrowth can result in the vitamin being absorbed into the bloodstream in excessive amounts.
7. Medications
Some medications can increase vitamin B12 levels. For example, certain antibiotics can alter the gut microbiome, potentially leading to the overproduction of vitamin B12 by bacteria. Additionally, medications used to treat conditions like diabetes or seizures can also affect vitamin B12 metabolism.
8. Genetic Disorders
Rare genetic disorders can affect the body’s ability to metabolize or use vitamin B12 efficiently, leading to elevated levels. These disorders often involve defects in the transport or utilization of vitamin B12 within the body.
9. Increased Absorption
In some cases, the body may absorb vitamin B12 more efficiently than usual, leading to elevated levels. This increased absorption can be due to various factors, including changes in gut health or the presence of certain medical conditions.
10. Analytical Errors
Lastly, elevated vitamin B12 levels can sometimes be the result of laboratory errors. The measurement of vitamin B12 in the blood requires precise techniques, and mistakes during sample collection, processing, or analysis can lead to inaccurate results.
11. Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders, such as pernicious anemia, can initially present with elevated B12 levels due to the body’s immune response affecting the absorption of the vitamin. However, over time, this condition typically leads to a deficiency.
Additional Considerations
It’s essential to understand that while vitamin B12 is crucial for health, excessively high levels can sometimes indicate underlying issues that require medical attention. If you’re concerned about your vitamin B12 levels or are experiencing symptoms that might be related to an imbalance, consulting with a healthcare provider is the best course of action. They can provide personalized advice and help diagnose any potential issues through comprehensive testing and evaluation.
Practical Applications and Future Trends
The management and understanding of elevated vitamin B12 levels are evolving. As research continues to uncover the complexities of vitamin B12 metabolism and its role in human health, new diagnostic tools and therapeutic approaches are being developed. For instance, personalized nutrition and targeted supplementation based on genetic profiles are areas of growing interest. Additionally, the role of vitamin B12 in neurological health and disease prevention is under intensive study, with potential implications for the management of neurodegenerative diseases and cognitive health.
Conclusion
Elevated vitamin B12 levels can result from a wide range of factors, from dietary habits and supplementation to underlying medical conditions. Understanding the reasons behind these elevations is crucial for interpreting their significance and for guiding appropriate management strategies. As our knowledge of vitamin B12 and its interactions within the human body expands, so too will our ability to leverage this knowledge for improved health outcomes and disease prevention.
FAQ Section
What are the common symptoms of elevated vitamin B12 levels?
+Elevated vitamin B12 levels may not always present with noticeable symptoms, but when they do, they can include weakness, fatigue, and in rare cases, neurological symptoms. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and advice.
How is elevated vitamin B12 diagnosed?
+Can elevated vitamin B12 levels be treated?
+Treatment depends on the underlying cause. For instance, if the elevation is due to excessive supplementation, reducing or stopping the supplement may resolve the issue. For elevations caused by medical conditions, treating the underlying disease is crucial. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
What are the potential risks of very high vitamin B12 levels?
+Very high levels of vitamin B12 can sometimes indicate serious health issues, such as liver or kidney disease, and certain types of cancer. While vitamin B12 toxicity is rare, it’s crucial to address the underlying cause of the elevation to prevent potential complications.