10 Newborn Heart Rates For Healthy Outcomes
A newborn’s heart rate is a vital indicator of their overall health and well-being. Immediately after birth, a newborn’s heart rate is typically high, ranging from 100 to 160 beats per minute (bpm), due to the transition from the womb to the outside world. This rate gradually slows down as the baby adapts to life outside the uterus. For healthy outcomes, monitoring and understanding newborn heart rates is crucial. Here’s an overview of what to expect and the importance of heart rate monitoring in the first few days and weeks of life.
Immediate Post-Delivery (0-30 minutes)
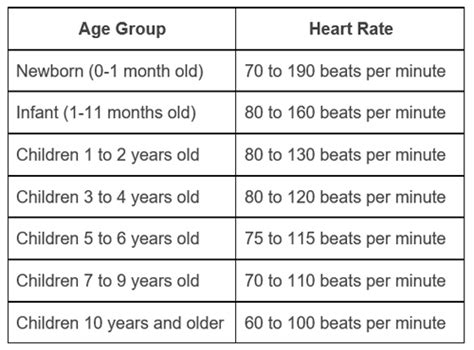
- Average Heart Rate: 100-160 bpm
- Importance: A high heart rate immediately after birth is normal. It indicates the baby’s adaptation to the extrauterine environment. Healthcare providers closely monitor this rate to ensure it remains within a healthy range, signaling good cardiac function and adequate oxygenation.
First Hour (30 minutes - 1 hour)
- Average Heart Rate: 100-150 bpm
- Considerations: By this time, the heart rate may start to decrease slightly as the baby continues to adapt. Monitoring during this period helps in identifying any potential issues early on, such as respiratory distress or cardiac problems.
First 24 Hours
- Average Heart Rate: 90-150 bpm
- Observations: The newborn’s heart rate can fluctuate, especially during feeding, sleeping, and crying. A rate within this range is generally considered normal. Continuous monitoring, especially in the first 24 hours, is critical for detecting any anomalies or signs of infection.
2-3 Days Old
- Average Heart Rate: 80-140 bpm
- Notes: As the baby grows accustomed to life outside the womb, the heart rate tends to stabilize and may decrease. It’s essential to continue monitoring for any significant deviations from the expected range, as these could indicate underlying health issues.
1 Week Old
- Average Heart Rate: 80-120 bpm
- Considerations: By one week, most newborns have a heart rate that falls within a more adult-like range, though still higher than adults. Monitoring at this stage helps in assessing the baby’s overall health, feeding patterns, and response to any treatments if necessary.
Factors Influencing Heart Rate
Several factors can influence a newborn’s heart rate, including:
- Sleep vs. Wakefulness: Heart rates can be slower during sleep and increase during wakefulness.
- Feeding: Nursing or bottle-feeding can cause temporary increases in heart rate.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature, noise, and handling can affect heart rate.
- Emotional State: Crying or distress can significantly increase a newborn’s heart rate.
Monitoring Techniques
Healthcare providers use various methods to monitor a newborn’s heart rate, including:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): For detailed heart activity assessment.
- Pulse Oximetry: Non-invasive method to monitor oxygen saturation and heart rate.
- Auscultation: Listening to the heartbeat with a stethoscope.
Importance of Monitoring
Continuous monitoring of a newborn’s heart rate in the first few days and weeks of life is crucial for:
- Early Detection of Issues: Quickly identifying heart problems, infections, or other health concerns.
- Guiding Treatment: Helping healthcare providers make informed decisions about care and interventions.
- Parental Reassurance: Providing parents with peace of mind and educating them on what to expect and look for in their baby’s health.
Conclusion
A newborn’s heart rate is a critical vital sign that offers insights into their health and adaptation to life outside the womb. Understanding the normal ranges and variations in heart rate at different stages after birth can help parents and healthcare providers ensure the best possible outcomes for newborns. Whether it’s the immediate post-delivery period, the first few days, or the weeks that follow, monitoring heart rate is an essential part of newborn care, helping to detect any potential issues early and supporting healthy development.
What is considered a normal heart rate for a newborn immediately after birth?
+A normal heart rate for a newborn immediately after birth is typically between 100 to 160 beats per minute (bpm). This high rate is due to the baby’s adaptation to the outside world and gradually decreases as the baby grows.
How does feeding affect a newborn’s heart rate?
+Feeding, whether nursing or bottle-feeding, can cause a temporary increase in a newborn’s heart rate. This is a normal response and typically stabilizes after feeding is completed.
Why is continuous monitoring of a newborn’s heart rate important?
+Continuous monitoring of a newborn’s heart rate is important for the early detection of potential health issues, guiding appropriate treatment, and providing reassurance to parents. It helps in ensuring the newborn receives the best possible care.
What methods are used to monitor a newborn’s heart rate?
+Healthcare providers use methods such as electrocardiogram (ECG), pulse oximetry, and auscultation (listening to the heartbeat with a stethoscope) to monitor a newborn’s heart rate. Each method provides valuable information about the baby’s cardiac health.
Can environmental factors affect a newborn’s heart rate?
+What should parents look for in their baby’s heart rate in the first few weeks of life?
+Parents should lookout for any significant deviations from the normal heart rate range, persistent irregularities, or symptoms such as difficulty breathing, pale skin, or lethargy. Consulting with a healthcare provider if there are concerns is essential.