Understanding blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining good health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar levels, also known as glucose levels, indicate the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. It is obtained from the food we eat and is regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Here, we will delve into normal blood sugar ranges, factors that influence these levels, and how to manage them effectively.
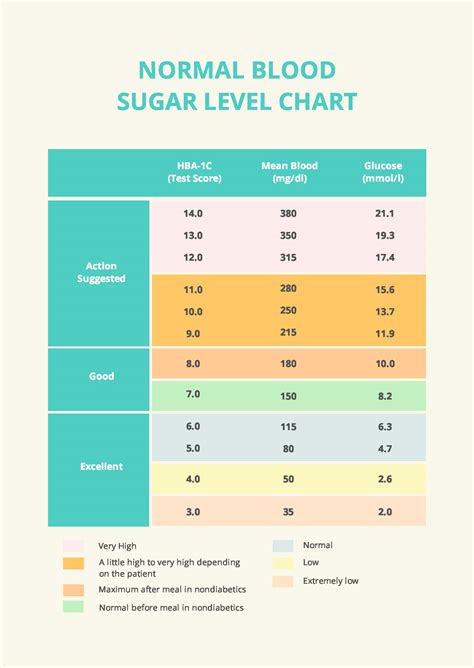
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges
Normal blood sugar ranges vary slightly depending on the time of day, the last time you ate, and your physical activity level. Generally, for individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are as follows:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (before eating or drinking in the morning): Less than 100 mg/dL.
- After Eating (postprandial): Less than 140 mg/dL.
- Before Meals: 70 to 130 mg/dL.
For people with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following targets:
- Before Meals: 80 to 130 mg/dL for many adults.
- After Eating (1-2 hours after beginning of meal): Less than 180 mg/dL.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: The types and amounts of food you eat, particularly carbohydrates, can significantly affect blood sugar levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: Certain medications, including those for diabetes, can influence blood sugar levels.
- Stress and Sleep: High levels of stress and lack of quality sleep can raise blood sugar levels.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menstruation, can affect blood sugar levels.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Effective management of blood sugar levels involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, for those with diabetes, adherence to medication regimens. Key strategies include:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, can improve insulin sensitivity and help lower blood sugar levels.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar: Regularly checking blood sugar levels can help identify patterns and make informed decisions about diet and physical activity.
- Stress Management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can help manage stress and its impact on blood sugar levels.
- Adequate Sleep: Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for overall health and can help regulate blood sugar levels.
Understanding Blood Sugar Testing
Blood sugar testing is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. It involves using a glucometer to measure the glucose levels in a blood sample. There are several types of blood sugar tests, including:
- Fasting Plasma Glucose Test (FPG): Measures blood glucose levels after an overnight fast.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Measures blood glucose levels after consuming a sugary drink.
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Test: Provides an average of blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months.
Technology and Blood Sugar Management
Advancements in technology have significantly improved the management of blood sugar levels. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, for example, provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night, offering valuable insights into glucose patterns and trends. Moreover, mobile applications and online platforms can help track diet, physical activity, and medication adherence, facilitating more effective blood sugar management.
Conclusion
Maintaining normal blood sugar ranges is vital for overall health and preventing complications associated with diabetes. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels and implementing effective management strategies, individuals can take proactive steps towards healthier living. Whether through dietary adjustments, increased physical activity, or the use of technology, managing blood sugar levels is within reach for everyone.
What are the normal blood sugar ranges for someone without diabetes?
+For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar ranges are less than 100 mg/dL when fasting and less than 140 mg/dL after eating.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels if I have diabetes?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels can vary depending on the type of diabetes and the treatment plan. Generally, it is recommended to check levels at least four times a day, including before meals and before bedtime.
What are the benefits of using a continuous glucose monitoring system?
+Continuous glucose monitoring systems provide real-time glucose readings, helping individuals understand their glucose patterns, make informed decisions about their diet and activity, and potentially reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.