How Does Fenofibrate Work? Lowering Triglycerides
Fenofibrate, a fibric acid derivative, is a widely prescribed medication for managing high cholesterol and triglyceride levels in the blood. It belongs to a class of drugs known as fibrates, which are used to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by improving lipid profiles. But how does fenofibrate work, and what benefits does it offer in lowering triglycerides?
Mechanism of Action
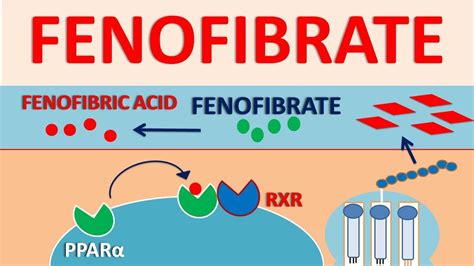
Fenofibrate works by activating a protein called peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-alpha). This protein is a nuclear receptor that plays a crucial role in regulating lipid metabolism, glucose homeostasis, and inflammation. When fenofibrate binds to PPAR-alpha, it triggers a series of downstream effects that ultimately lead to improved lipid profiles.
One of the primary mechanisms by which fenofibrate lowers triglycerides is by increasing the breakdown of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles in the liver. VLDL particles are rich in triglycerides and are produced by the liver to transport lipids from the liver to peripheral tissues. By enhancing the clearance of VLDL particles, fenofibrate reduces the amount of triglycerides in the blood.
Effects on Lipid Metabolism
Fenofibrate has several effects on lipid metabolism that contribute to its triglyceride-lowering properties:
- Increased Lipolysis: Fenofibrate increases the activity of lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme that breaks down triglycerides in VLDL particles. This leads to a reduction in triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in the blood.
- Enhanced Fatty Acid Oxidation: Fenofibrate increases the expression of genes involved in fatty acid oxidation, which promotes the breakdown of fatty acids in the liver and other tissues.
- Reduced Apolipoprotein C-III: Fenofibrate decreases the production of apolipoprotein C-III, a protein that inhibits the activity of lipoprotein lipase. By reducing apolipoprotein C-III levels, fenofibrate enhances the clearance of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins.
- Increased High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL) Cholesterol: Fenofibrate also increases HDL cholesterol levels, which is beneficial for cardiovascular health.
Clinical Benefits
The triglyceride-lowering effects of fenofibrate have been consistently demonstrated in clinical trials. Studies have shown that fenofibrate:
- Reduces Triglyceride Levels: Fenofibrate has been shown to decrease triglyceride levels by 20-50% in patients with hypertriglyceridemia.
- Lowers VLDL Cholesterol: Fenofibrate reduces VLDL cholesterol levels, which is associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Increases HDL Cholesterol: Fenofibrate increases HDL cholesterol levels, which is beneficial for cardiovascular health.
- Improves Insulin Sensitivity: Fenofibrate has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity, which can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fenofibrate is a powerful medication that works by activating PPAR-alpha to improve lipid metabolism and reduce triglyceride levels. Its ability to increase the breakdown of VLDL particles, enhance fatty acid oxidation, and reduce apolipoprotein C-III production makes it an effective treatment for managing high triglycerides. By understanding how fenofibrate works, healthcare professionals can better appreciate its clinical benefits and use it to improve patient outcomes.
What is the primary mechanism by which fenofibrate lowers triglycerides?
+Fenofibrate works by increasing the breakdown of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particles in the liver, which are rich in triglycerides.
What are the effects of fenofibrate on lipid metabolism?
+Fenofibrate increases lipolysis, enhances fatty acid oxidation, reduces apolipoprotein C-III production, and increases HDL cholesterol levels.
What are the clinical benefits of fenofibrate?
+Fenofibrate reduces triglyceride levels, lowers VLDL cholesterol, increases HDL cholesterol, and improves insulin sensitivity, which can help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
To further understand the benefits and risks of fenofibrate, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and guidance on using fenofibrate to manage high triglycerides and improve overall cardiovascular health.