12+ Cbc Abbreviations To Know Fast
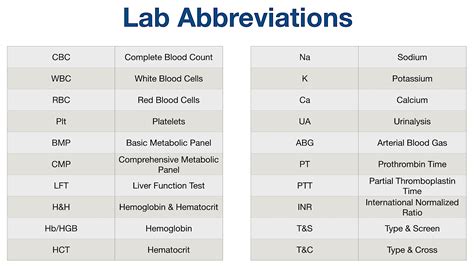
Understanding medical abbreviations is crucial for both healthcare professionals and individuals seeking to comprehend their medical records or communicate effectively with their healthcare providers. CBC, which stands for Complete Blood Count, is a common blood test used to evaluate overall health and diagnose a range of disorders, including infections, inflammation, and anemia. Here are key CBC abbreviations to know, along with their meanings:
- WBC - White Blood Cell count: Measures the number of white blood cells in the blood, which fight infections.
- RBC - Red Blood Cell count: Indicates the number of red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
- HGB or Hb - Hemoglobin: The protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body.
- HCT or Hct - Hematocrit: Represents the proportion of blood volume made up by red blood cells.
- MCV - Mean Corpuscular Volume: The average volume of red blood cells, which helps in diagnosing types of anemia.
- MCH - Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin: The average amount of hemoglobin in a single red blood cell.
- MCHC - Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration: The average concentration of hemoglobin in a given volume of red blood cells.
- RDW - Red Cell Distribution Width: Measures the variation in the size of red blood cells, useful in identifying iron deficiency anemia and other conditions.
- PLT - Platelet count: Indicates the number of platelets, which are vital for blood clotting.
- MPV - Mean Platelet Volume: The average size of platelets, which can help diagnose certain conditions related to platelet production or function.
- NEU or NEUT - Neutrophils: A type of white blood cell important for fighting infections, especially bacterial and fungal.
- LYM or LYMPH - Lymphocytes: Another type of white blood cell crucial for immune responses, including both B cells and T cells.
Understanding these abbreviations and their implications can significantly enhance your ability to interpret the results of a Complete Blood Count (CBC) and engage in more informed discussions about health with medical professionals. Remember, while knowledge of these terms is useful, the interpretation of CBC results should always be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as the significance of any given value can depend on numerous individual factors, including the patient’s medical history, current symptoms, and the presence of any ongoing treatments.



