12 Cephalexin Uses To Treat Infections
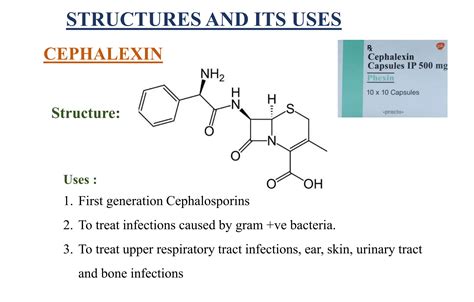
Cephalexin, a cephalosporin antibiotic, has been widely used to treat various bacterial infections. Its broad-spectrum activity makes it an effective option against a range of pathogens. Here, we delve into 12 significant uses of cephalexin in treating infections, exploring its applications, efficacy, and the importance of responsible antibiotic use.
1. Respiratory Tract Infections
Cephalexin is commonly prescribed for respiratory tract infections such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and streptococcal pharyngitis. Its ability to penetrate into respiratory tissues and fluids makes it effective against such infections.
2. Skin and Soft Tissue Infections
It’s used to treat skin and soft tissue infections like impetigo, folliculitis, and cellulitis, which are often caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. Cephalexin’s efficacy in these cases is due to its ability to inhibit cell wall synthesis in bacteria.
3. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Cephalexin is effective against UTIs caused by bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, and Proteus mirabilis. Its use in these infections is supported by its pharmacokinetic properties, which allow for high concentrations in the urine.
4. Bone and Joint Infections
Osteomyelitis and septic arthritis, infections of the bone and joints, respectively, can be treated with cephalexin, especially when caused by susceptible organisms. The drug’s penetration into bone and joint tissues contributes to its effectiveness in these conditions.
5. Genital Infections
Cephalexin can be used for the treatment of certain genital infections, such as those caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae, though resistance patterns must be considered. It’s crucial to follow local resistance guidelines when treating such infections.
6. Dental Infections
For dental infections such as abscesses and periapical infections, cephalexin may be prescribed due to its coverage of oral pathogens. Its use can help manage symptoms and prevent the spread of infection.
7. Osteitis and Periostitis
Infections involving the bone and its surrounding tissue, like osteitis and periostitis, can be managed with cephalexin. The drug’s pharmacodynamics support its use in these conditions.
8. Septicemia
Cephalexin might be considered for the treatment of septicemia (blood infections) when the causative organism is known to be susceptible. However, the choice of antibiotic must be guided by culture and sensitivity results due to the potential for resistance.
9. Meningitis
Though less common, cephalexin can be used in the treatment of bacterial meningitis caused by susceptible strains, often in combination with other antibiotics to ensure broad coverage.
10. Prostatitis
For chronic bacterial prostatitis, cephalexin has been used due to its ability to achieve therapeutic levels in the prostate tissue. The treatment duration is typically prolonged to ensure complete eradication of the infecting organism.
11. Otitis Media and Otitis Externa
Cephalexin is effective against middle ear infections (otitis media) and outer ear infections (otitis externa), making it a valuable option for treating these common conditions, especially in pediatric and adult populations.
12. Preventive Use in Surgery
Cephalexin can be administered prophylactically before certain surgical procedures to prevent surgical site infections, particularly in operations where the risk of contamination is high. Its use in this context is based on its spectrum of activity and pharmacokinetic properties.
Key Considerations
- Antibiotic Resistance: The increasing prevalence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is a concern. Cephalexin’s efficacy can be compromised in areas with high resistance rates, underscoring the need for antibiotic stewardship.
- Side Effects and Allergies: While generally well-tolerated, cephalexin can cause side effects and allergic reactions. Patients should be monitored for any adverse effects, and alternative treatments considered if necessary.
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Cephalexin is typically considered safe during pregnancy and breastfeeding, but its use should be guided by a healthcare professional, weighing the benefits against potential risks.
Conclusion
Cephalexin remains a versatile and effective antibiotic for treating a wide range of bacterial infections. Its application, however, must be guided by principles of antimicrobial stewardship to preserve its efficacy and mitigate the development of resistance. Always consult a healthcare professional for the appropriate use of cephalexin or any antibiotic, as they can provide personalized advice based on the specific infection, local resistance patterns, and patient health status.
What is cephalexin used for?
+Cephalexin is used to treat various bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, skin and soft tissue infections, urinary tract infections, and more.
How does cephalexin work?
+Cephalexin works by inhibiting the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall, leading to the death of the bacteria. It is effective against a broad spectrum of Gram-positive and some Gram-negative bacteria.
What are the common side effects of cephalexin?
+Common side effects of cephalexin include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Allergic reactions can also occur, ranging from mild rash to severe anaphylaxis, though these are less common.
Can cephalexin be used in pregnant or breastfeeding women?
+Cephalexin is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before taking any medication in these situations to discuss potential risks and benefits.
How can antibiotic resistance be prevented?
+Antibiotic resistance can be prevented by using antibiotics judiciously, completing the full course of prescribed antibiotics, not sharing antibiotics, and practicing good hygiene to prevent the spread of infections.