12 Diabetic Blood Sugar Levels Tips For Better Control
Living with diabetes requires a deep understanding of how to manage blood sugar levels effectively. It’s a delicate balance that, when achieved, can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals with diabetes. Here, we’ll delve into 12 essential tips for better controlling diabetic blood sugar levels, exploring the nuances of each and how they contribute to overall diabetes management.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
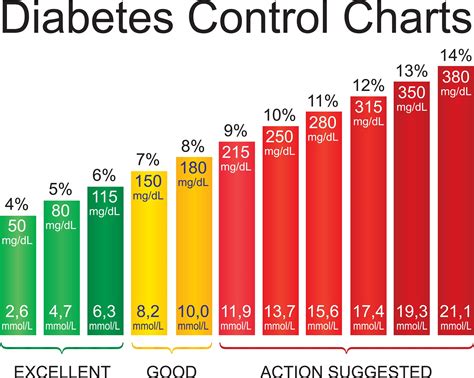
Before diving into the tips, it’s crucial to understand what blood sugar levels are and why they’re so important for individuals with diabetes. Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary energy source for cells in the body. In individuals with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or can’t effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes), leading to high blood sugar levels. Monitoring and controlling these levels is key to preventing complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
Tip 1: Develop a Personalized Diet Plan
A well-planned diet is foundational for managing blood sugar levels. Working with a dietitian or healthcare provider to develop a personalized meal plan can help ensure that dietary needs are met without causing spikes in blood sugar. This plan should consider the glycemic index of foods, portion sizes, and the balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Tip 2: Stay Hydrated
Water is essential for the body, and its importance cannot be overstated for individuals with diabetes. Staying hydrated helps the kidneys to flush out excess glucose through urine, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. It’s recommended to drink at least eight glasses of water a day, though this can vary based on activity level and climate.
Tip 3: Exercise Regularly
Physical activity is another critical component of diabetes management. Exercise not only helps lower blood sugar levels but also improves insulin sensitivity, meaning the body can more effectively use the insulin it produces. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent options, but it’s essential to discuss any new exercise regimen with a healthcare provider to ensure safety.
Tip 4: Monitor Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels provides valuable insights into how the body responds to different foods, activities, and medications. This data can be used to make informed decisions about diet and exercise, ensuring that blood sugar levels remain within a healthy range. The frequency of monitoring will depend on the type of diabetes and the individual’s specific situation.
Tip 5: Get Enough Sleep
Sleep plays a significant role in glucose regulation and insulin sensitivity. Lack of quality sleep or insufficient sleep duration can lead to increased blood sugar levels and decreased insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to support glucose metabolism and overall health.
Tip 6: Manage Stress
Chronic stress can have a detrimental effect on blood sugar levels, as it triggers the release of hormones like cortisol, which can cause blood sugar to rise. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help mitigate this effect and support better glucose control.
Tip 7: Limit Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels, and its effects can vary greatly depending on the type of alcohol consumed, the amount, and the individual’s health status. For those with diabetes, it’s crucial to limit alcohol intake and always consume it with food to avoid hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Tip 8: Quit Smoking
Smoking is harmful for everyone, but it’s especially dangerous for individuals with diabetes. Smoking can increase the risk of complications from diabetes, such as heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce these risks and improve overall health.
Tip 9: Be Mindful of Medications
For many individuals with diabetes, medication is a part of their daily routine. It’s essential to take medications as prescribed and to be aware of potential side effects, including how they might affect blood sugar levels. Never adjust medications without consulting a healthcare provider, as this can lead to serious health issues.
Tip 10: Stay Up-to-Date with Healthcare Appointments
Regular check-ins with healthcare providers are vital for managing diabetes effectively. These visits provide an opportunity to monitor progress, adjust treatment plans as necessary, and catch any potential issues early. Keeping a log of blood sugar levels, medications, and any symptoms can be incredibly helpful during these appointments.
Tip 11: Learn to Recognize Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
Understanding the signs and symptoms of both low (hypoglycemia) and high (hyperglycemia) blood sugar is critical for prompt intervention. Hypoglycemia symptoms include shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, and irritability, while hyperglycemia can lead to thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Knowing how to treat these conditions can prevent serious complications.
Tip 12: Build a Support Network
Living with diabetes can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Building a support network of family, friends, and support groups can provide emotional support, practical help, and valuable insights from others who are going through similar experiences. This network can play a significant role in maintaining motivation and adherence to diabetes management plans.
Conclusion
Managing diabetic blood sugar levels is a multifaceted endeavor that requires attention to diet, exercise, medication, and mental well-being. By incorporating these 12 tips into daily life, individuals with diabetes can better control their blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. It’s a journey that requires patience, dedication, and support, but with the right approach, it’s possible to thrive with diabetes.
FAQ Section
What are normal blood sugar levels?
+For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 to 140 mg/dL. However, these targets can vary slightly for people with diabetes, depending on their specific health status and treatment goals.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes and the individual’s health status. Generally, those with Type 1 diabetes or those taking insulin may need to monitor their levels more frequently than those with Type 2 diabetes who are managing their condition with diet and exercise.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can include increased thirst and urination, feeling tired, blurred vision, cuts or wounds that are slow to heal, and tingling or numbness in the hands and feet. If left untreated, hyperglycemia can lead to serious complications.



