12 Hemoglobin A1c Test Tips For Better Control
Understanding the intricacies of managing diabetes involves a myriad of tests and checks to ensure that blood sugar levels are within a healthy range. One of the most crucial tests for assessing diabetes control over time is the Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test. This test measures the average blood glucose levels over the past 2 to 3 months by analyzing the percentage of glucose that has bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Here are 12 tips to help individuals better understand and utilize the HbA1c test for improved diabetes management:
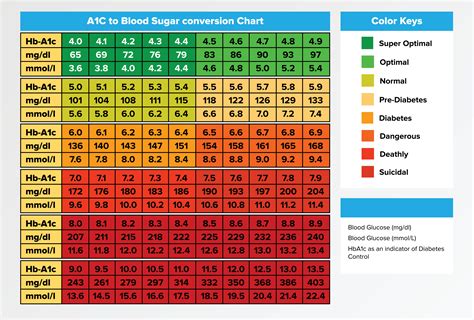
Understand the HbA1c Scale: The HbA1c test results are given as a percentage, which indicates the average blood glucose levels over the preceding 2-3 months. For people without diabetes, the typical range is below 5.7%. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends an HbA1c goal of less than 7% for most adults, though this target may be adjusted based on individual factors such as age, other health conditions, duration of diabetes, life expectancy, resources, and support system.
Recognize the Importance of Regular Testing: Regular HbA1c tests are crucial for people with diabetes. They help in understanding how well the diabetes management plan is working and guide any necessary adjustments to diet, exercise, or medication. The frequency of testing depends on the type of diabetes and how well-controlled it is. Generally, the test should be done at least twice a year in people who are meeting treatment goals and have stable glycemic control. More frequent testing (every 3 months) is recommended for those whose therapy has changed or who are not meeting their treatment goals.
Preparation is Key: Unlike some other blood tests, the HbA1c does not require fasting. However, it’s essential to follow any specific instructions provided by the healthcare provider or laboratory. Certain conditions, such as red blood cell disorders or recent blood transfusions, can affect the test results, so it’s crucial to discuss these factors with a healthcare provider.
Understanding Variability: HbA1c results can sometimes vary between different laboratories due to differences in testing equipment and techniques. If comparing results from different labs, it’s essential to consider this potential variability. Also, lifestyle changes, especially those made close to the time of the test, may not be fully reflected in the HbA1c level, as this test averages glucose levels over a longer period.
Using HbA1c in Context: The HbA1c is a powerful tool but should be interpreted in the context of the individual’s overall health, symptoms, and other glucose monitoring data, such as those from a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) or self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG). Symptoms such as polyuria (frequent urination), polydipsia (excessive thirst), and unexplained weight loss can indicate high blood glucose levels and should be evaluated in conjunction with HbA1c results.
Lifestyle Adjustments: For those looking to lower their HbA1c levels, adopting healthier lifestyle habits can make a significant difference. These include eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars and saturated fats, increasing physical activity (aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week), maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress effectively.
Medication Adherence: For individuals with diabetes who are on medication, adhering to the prescribed treatment plan is crucial. Medications should be taken as directed, and any questions or concerns about side effects, dosages, or potential interactions with other medications should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): These tools provide detailed information on daily glucose patterns and can help identify specific times when glucose levels are high or low, which can inform adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication. They are particularly useful for making timely adjustments to manage blood glucose levels more effectively.
Setting Realistic Goals: It’s essential to work with a healthcare provider to set realistic HbA1c targets based on individual health needs and circumstances. Achieving these goals can help motivate individuals to continue making healthy lifestyle choices and adhering to their diabetes management plan.
Addressing Barriers to Care: Some individuals may face challenges in accessing regular HbA1c testing, such as lack of health insurance, high costs of tests or medications, or difficulty in getting to a healthcare provider. Addressing these barriers through patient assistance programs, community health clinics, or telehealth services can help improve diabetes management.
Staying Informed and Connected: Continuous education and support are vital for effective diabetes management. This includes staying updated on the latest research and treatments, participating in diabetes education programs, and connecting with others who have diabetes through support groups or online forums.
Embracing Technology and Tools: Leveraging technology, such as mobile apps for tracking blood glucose levels, medication adherence, and lifestyle habits, can make managing diabetes more manageable and efficient. Devices like smart insulin pens and automated insulin dosing systems can also simplify diabetes care.
In conclusion, the HbA1c test is a valuable tool for assessing long-term glucose control in individuals with diabetes. By understanding how to interpret HbA1c results, making informed lifestyle choices, adhering to medication regimens, and leveraging available tools and technologies, individuals can work towards better control of their diabetes and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. Regular communication with a healthcare provider is key to tailoring the diabetes management plan to meet individual needs and goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Hemoglobin A1c test in diabetes management?
+The Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test is significant because it provides a snapshot of average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months, helping individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers assess the effectiveness of their diabetes management plan and make informed decisions about adjustments to diet, exercise, or medication.
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How often should I get an HbA1c test if I have diabetes?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The frequency of HbA1c testing depends on the type of diabetes and how well-controlled it is. Generally, testing should be done at least twice a year for those meeting treatment goals and having stable glycemic control. For those whose therapy has changed or who are not meeting their treatment goals, testing every 3 months is recommended.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>Can lifestyle changes affect my HbA1c levels?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Yes, adopting healthier lifestyle habits such as eating a balanced diet, increasing physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing stress can significantly lower HbA1c levels and improve overall diabetes management.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How does the HbA1c test account for variability in red blood cell lifespan?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>The HbA1c test averages blood glucose levels over the lifespan of red blood cells, which is typically about 120 days. However, conditions affecting red blood cell lifespan, such as recent blood transfusions or certain blood disorders, can influence HbA1c results. It's crucial to discuss these factors with a healthcare provider for accurate interpretation of test results.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>What role does medication adherence play in managing HbA1c levels?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Medication adherence is critical for managing diabetes and achieving target HbA1c levels. Taking medications as prescribed and discussing any concerns or questions with a healthcare provider can help in maintaining good glycemic control.</p>
</div>
</div>
<div class="faq-item">
<div class="faq-question">
<h3>How can I lower my HbA1c levels naturally?</h3>
<span class="faq-toggle">+</span>
</div>
<div class="faq-answer">
<p>Natural ways to lower HbA1c levels include adopting a healthy diet low in added sugars and saturated fats, engaging in regular physical activity, losing weight if needed, and managing stress through techniques like yoga or meditation. These lifestyle changes can significantly impact blood glucose control and overall health.</p>
</div>
</div>
</div>