12 Lactic Acid Elevated Fixes For Faster Recovery

Elevated lactic acid levels in the body can be a significant impediment to athletic performance and overall health. Lactic acid buildup occurs when the body’s demand for oxygen exceeds its supply, leading to anaerobic metabolism and the production of lactic acid. While some lactic acid is normal, excessively high levels can cause muscle fatigue, soreness, and decreased endurance. Fortunately, there are several strategies that can help mitigate elevated lactic acid levels and promote faster recovery.
Understanding Lactic Acid
Before diving into the fixes, it’s essential to understand what lactic acid is and how it affects the body. Lactic acid, or lactate, is a naturally occurring compound that is produced when the body breaks down glucose for energy. During intense exercise, the body’s demand for oxygen increases, and when the oxygen supply is limited, the body resorts to anaerobic metabolism, resulting in the production of lactic acid. Elevated lactic acid levels can lead to muscle fatigue, decreased performance, and delayed recovery.
1. Proper Hydration
Adequate hydration is crucial for flushing out lactic acid from the muscles. Drinking plenty of water before, during, and after exercise can help reduce lactic acid buildup and promote faster recovery. Aim to drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day, and consider increasing your intake during intense training periods.
2. Post-Exercise Nutrition
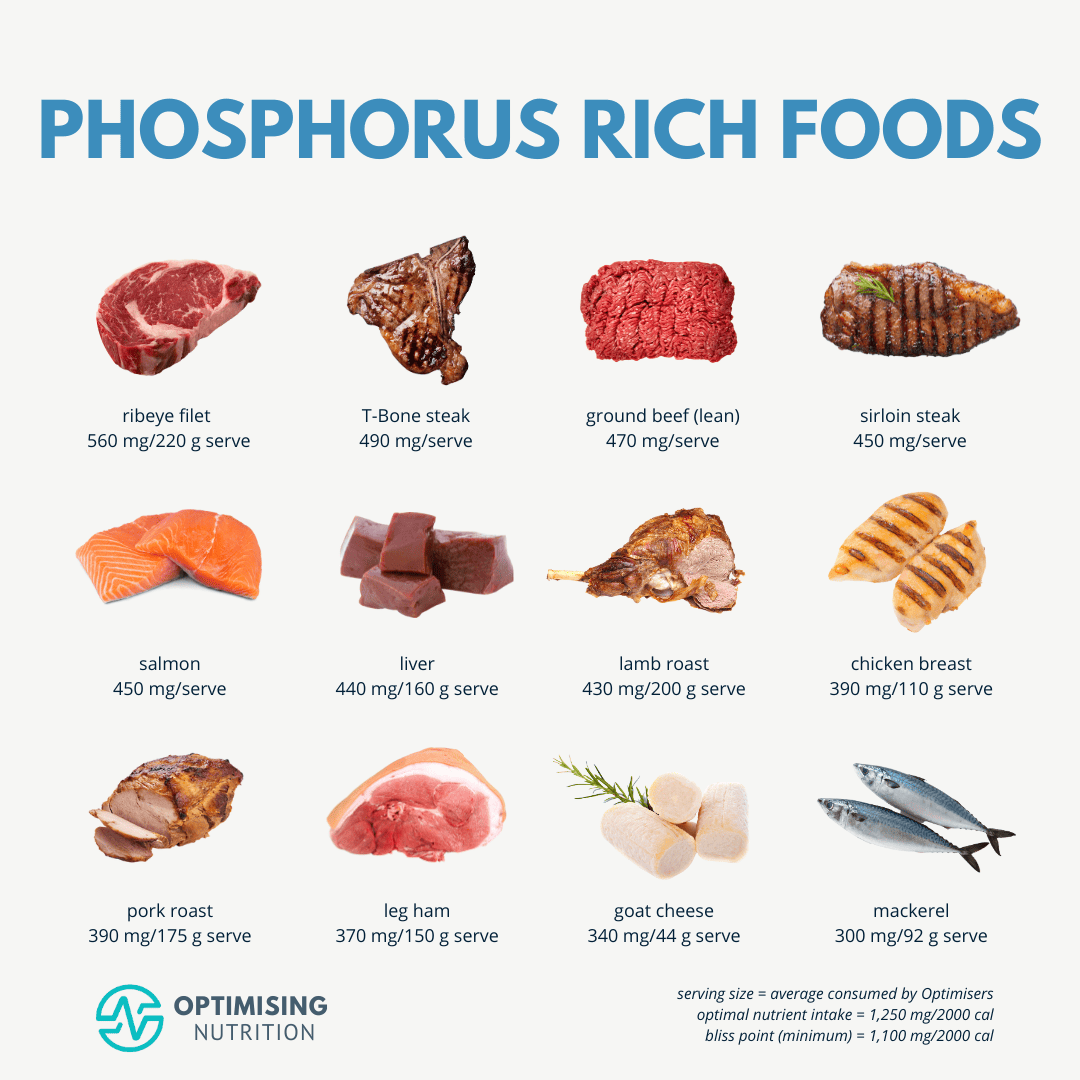
Consuming the right nutrients after exercise can help reduce lactic acid levels and promote recovery. Focus on foods that are rich in antioxidants, such as berries, leafy greens, and other fruits and vegetables. Additionally, include protein-rich foods like lean meats, fish, and eggs to help repair and rebuild muscle tissue.
3. Active Recovery
Active recovery techniques, such as light cardio and stretching, can help promote blood flow and reduce lactic acid buildup. Engage in low-intensity activities like cycling, swimming, or yoga to help your body recover from intense exercise.
4. Foam Rolling and Self-Myofascial Release
Foam rolling and self-myofascial release can help reduce muscle tension and promote blood flow, which can aid in the removal of lactic acid. Focus on areas that feel tight or sore, and spend 10-15 minutes per day on foam rolling and self-myofascial release exercises.
5. Contrast Water Therapy
Contrast water therapy involves alternating between hot and cold water to promote blood flow and reduce inflammation. This technique can help reduce lactic acid levels and promote faster recovery. Spend 10-15 minutes in a hot shower or bath, followed by 5-10 minutes in a cold shower or bath.
6. Compression Garments
Compression garments, such as tights and sleeves, can help improve blood flow and reduce lactic acid buildup. Wear compression garments during and after exercise to promote faster recovery.
7. Electrolyte Replenishment
Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, play a crucial role in maintaining proper muscle function. Replenishing electrolytes after exercise can help reduce lactic acid levels and promote faster recovery. Consider using electrolyte-rich beverages or supplements during and after intense exercise.
8. Massage Therapy
Massage therapy can help reduce muscle tension and promote blood flow, which can aid in the removal of lactic acid. Schedule a massage after intense exercise to promote faster recovery.
9. Rest and Recovery
Adequate rest and recovery are essential for allowing the body to remove lactic acid and repair muscle tissue. Ensure you get 7-9 hours of sleep per night and take rest days as needed.
10. Nutritional Supplements
Certain nutritional supplements, such as beta-alanine and branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), can help reduce lactic acid levels and promote faster recovery. Consult with a healthcare professional before adding any supplements to your routine.
11. Breathing Exercises
Deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress and promote relaxation, which can aid in the removal of lactic acid. Practice deep breathing exercises after exercise to promote faster recovery.
12. Gradual Progression
Gradually increasing exercise intensity and duration can help the body adapt to the demands of exercise and reduce lactic acid buildup. Avoid sudden increases in exercise intensity or duration, and focus on gradual progression to promote faster recovery.
What are the symptoms of elevated lactic acid levels?
+Symptoms of elevated lactic acid levels include muscle fatigue, soreness, and decreased endurance. In severe cases, elevated lactic acid levels can lead to muscle cramping, weakness, and decreased athletic performance.
How can I measure my lactic acid levels?
+Can I reduce lactic acid levels through diet alone?
+While a balanced diet that includes antioxidant-rich foods and protein can help reduce lactic acid levels, it is not the only factor. Adequate hydration, proper training, and recovery techniques are also essential for managing lactic acid levels.
In conclusion, elevated lactic acid levels can be a significant obstacle to athletic performance and overall health. However, by implementing the strategies outlined above, individuals can reduce lactic acid levels, promote faster recovery, and improve overall performance. Remember to always prioritize proper hydration, nutrition, and recovery techniques to manage lactic acid levels and achieve optimal athletic performance.