12+ Low Bun Blood Test Results Explained
Elevated bun blood test results can be a cause for concern, but understanding what these results mean is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. The BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen) test is a common diagnostic tool used to assess kidney function and detect potential kidney problems. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of BUN blood tests, exploring what a 12+ result means, its possible causes, and the necessary steps to take if you receive such a result.
What is a BUN Test?
The BUN test measures the level of urea nitrogen in the blood. Urea is a waste product produced by the body’s metabolic processes, and the kidneys are responsible for filtering it out of the blood. When kidney function is impaired, urea can build up in the blood, leading to elevated BUN levels. The test is often used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools, such as the creatinine test, to evaluate kidney function and detect potential kidney disease.
Interpreting BUN Test Results
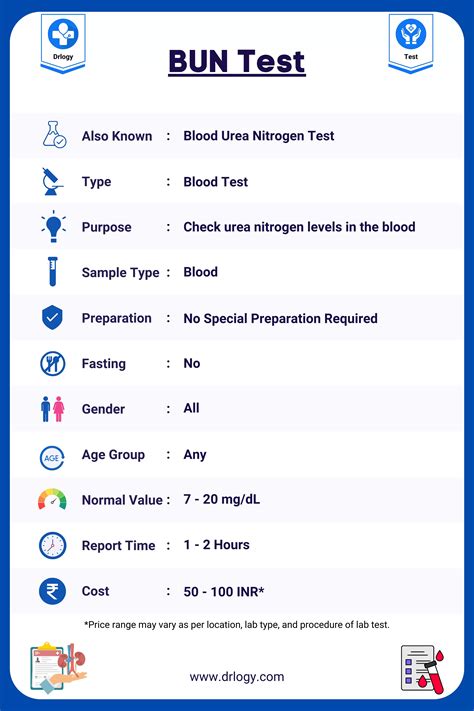
BUN test results are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Normal BUN levels typically range from 6 to 24 mg/dL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual’s age, sex, and overall health. A result of 12+ mg/dL is considered slightly elevated, but it’s essential to consider this result in the context of other diagnostic tests and medical evaluations.
Possible Causes of Elevated BUN Levels
There are several possible causes of elevated BUN levels, including:
- Dehydration: Inadequate fluid intake or excessive fluid loss can cause a rise in BUN levels.
- Kidney Disease: Conditions such as kidney failure, kidney stones, or glomerulonephritis can impair kidney function, leading to elevated BUN levels.
- Heart Failure: Reduced blood flow to the kidneys can cause a buildup of urea in the blood.
- High-Protein Diet: Consuming a diet high in protein can increase urea production, leading to elevated BUN levels.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics and diuretics, can affect kidney function and cause elevated BUN levels.
What to Do If You Receive a 12+ BUN Test Result
If you receive a BUN test result of 12+ mg/dL, it’s essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of the elevation. Your healthcare provider may order additional tests, such as:
- Creatinine Test: To evaluate kidney function and detect potential kidney disease.
- Urinalysis: To check for protein, blood, or other abnormalities in the urine.
- Imaging Tests: Such as ultrasound or CT scans, to visualize the kidneys and detect potential abnormalities.
FAQ Section
What is a normal BUN test result?
+A normal BUN test result typically ranges from 6 to 24 mg/dL, but this can vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's age, sex, and overall health.
What causes elevated BUN levels?
+Elevated BUN levels can be caused by dehydration, kidney disease, heart failure, high-protein diet, and certain medications.
What should I do if I receive a 12+ BUN test result?
+If you receive a BUN test result of 12+ mg/dL, it's essential to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause of the elevation. Your healthcare provider may order additional tests to evaluate kidney function and detect potential kidney disease.
Conclusion
Elevated BUN levels can be a cause for concern, but understanding what these results mean is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. A BUN test result of 12+ mg/dL is considered slightly elevated, but it’s essential to consider this result in the context of other diagnostic tests and medical evaluations. By consulting with your healthcare provider and undergoing additional testing, you can determine the underlying cause of the elevation and take the necessary steps to maintain optimal kidney function and overall health.