25 Mg Metoprolol
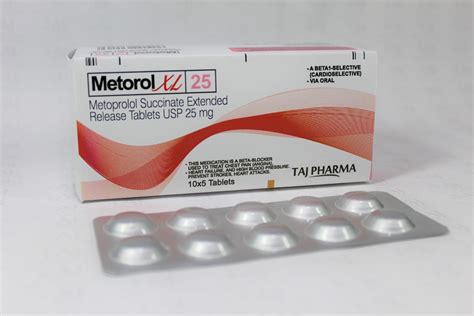
Metoprolol, a medication known for its effectiveness in managing various cardiovascular conditions, is often prescribed in different dosages, including 25 mg, to cater to the specific needs of patients. This beta-blocker works by slowing the heart rate and reducing the force of the heart’s muscular contractions, which in turn lowers blood pressure and increases oxygen supply to the heart.
Introduction to Metoprolol
Metoprolol is a selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor blocker, which means it primarily affects the heart, with less impact on the airways compared to non-selective beta-blockers. This selectivity reduces the risk of bronchospasm (tightening of the airway muscles), making it a safer option for patients with respiratory issues such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Uses of Metoprolol
The medication is used for several purposes, including:
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure): To lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney problems.
- Angina Pectoris (Chest Pain): By reducing the heart’s workload, metoprolol helps decrease the frequency of angina attacks and improves exercise tolerance.
- Heart Attack (Myocardial Infarction): Metoprolol can be prescribed to reduce the risk of death and another heart attack in patients who have had a heart attack.
- Heart Failure: In combination with other medications, metoprolol is used to improve survival and reduce hospitalizations due to worsening heart failure.
- Atrial Fibrillation/Flutter: To control heart rate in patients with these irregular heartbeat conditions.
Dosage: 25 Mg Metoprolol
The dosage of metoprolol can vary widely depending on the condition being treated. A 25 mg dose is on the lower end of the spectrum and may be prescribed for:
- Initial Treatment: For certain conditions, such as hypertension, a low dose like 25 mg once daily may be started to gauge the patient’s response and tolerance to the medication.
- Maintenance Therapy: For some patients, especially the elderly or those with certain health conditions, a lower maintenance dose of 25 mg daily may be appropriate to minimize side effects while still providing therapeutic benefits.
- Pediatric Patients: In children, metoprolol dosing is based on body weight, and a 25 mg dose might be appropriate for smaller children.
Side Effects and Precautions
Common side effects of metoprolol include fatigue, dizziness, depression, and shortness of breath. More serious side effects can include worsening heart failure, bronchospasm, and bradycardia (abnormally slow heart rate). It’s essential for patients to discuss their medical history, including any previous heart conditions, respiratory issues, or allergies, with their healthcare provider before starting metoprolol.
Interaction with Other Medications
Metoprolol can interact with a variety of medications, including other beta-blockers, certain antidepressants, and over-the-counter cough, cold, and allergy medicines. Patients should provide their healthcare provider with a comprehensive list of all prescription and non-prescription medications they are taking.
FAQ Section
What is the primary use of metoprolol 25 mg?
+Metoprolol 25 mg is primarily used for managing hypertension (high blood pressure), angina pectoris (chest pain), and for patients who have had a heart attack. The dose might be adjusted based on the patient's response and medical condition.
How does metoprolol affect the heart rate?
+Metoprolol slows the heart rate by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, and by slowing the electrical conduction in the heart. This action reduces the heart's workload and its demand for oxygen, which is particularly beneficial for patients with angina or heart failure.
Can metoprolol be used in patients with asthma or COPD?
+While metoprolol is a beta-1 selective blocker, which makes it safer for patients with respiratory conditions compared to non-selective beta-blockers, it should still be used with caution in patients with asthma or COPD. The decision to use metoprolol in these patients should be made by a healthcare provider, considering the benefits versus the potential risks.
How long does it take for metoprolol to start working?
+Metoprolol can start to lower blood pressure within a few hours of the first dose, but its full effects may take several weeks to develop. Patients should continue to take the medication as directed and follow up with their healthcare provider for adjustments to their treatment plan as needed.
In conclusion, metoprolol 25 mg, while a lower dose, plays a critical role in the management of various cardiovascular conditions. Its selective beta-1 adrenergic receptor blockade makes it a preferred choice for many patients, including those with respiratory conditions. As with any medication, it’s crucial for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the appropriate dosage and to monitor for any side effects or interactions with other medications.