3Rd Degree Av Block Treatment
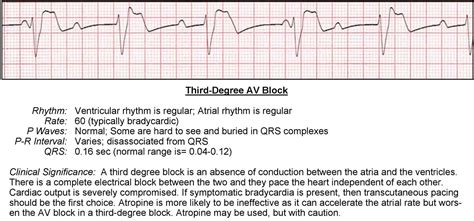
Third-degree atrioventricular (AV) block, also known as complete heart block, is a serious cardiac condition where there is a complete disruption in the electrical conduction pathway between the atria and ventricles. This results in the atria and ventricles beating independently of each other, leading to a potentially life-threatening situation if left untreated. The treatment of third-degree AV block often requires immediate medical attention, and the approach can vary depending on the severity of symptoms, the underlying cause, and the overall health of the patient.
Understanding Third-Degree AV Block
To grasp the treatment, it’s essential to understand the condition. Third-degree AV block is characterized by the complete blockage of electrical signals from the atria to the ventricles. This means that the atria and ventricles contract independently, which can lead to a significant reduction in cardiac output. Symptoms can range from mild, such as fatigue or dizziness, to severe, including syncope (fainting) or even heart failure.
Immediate Treatment Goals
The immediate goal in treating third-degree AV block is to ensure the patient’s safety and stabilize their heart rhythm. This often involves:
- Monitoring: Close monitoring of the patient’s cardiac rhythm and overall clinical status.
- Atropine: Administration of atropine can be considered to try to increase the heart rate, especially in patients with symptomatic bradycardia (slow heart rate).
- Pacing: Temporary pacing may be necessary to ensure an adequate heart rate until a more definitive treatment can be established.
Definitive Treatment: Pacemaker Implantation
The definitive treatment for third-degree AV block, especially in symptomatic patients or those with a high risk of complications, is the implantation of a permanent pacemaker. A pacemaker is a small device that is implanted under the skin, typically near the collarbone, and has leads that are guided to the heart. The pacemaker works by generating electrical impulses that cause the heart muscle to contract, thereby maintaining an adequate heart rate and ensuring proper synchronization between the atria and ventricles.
Types of Pacemakers
There are various types of pacemakers, and the choice depends on the patient’s specific needs and the nature of their heart block. The most common types include:
- Single-Chamber Pacemakers: These have one lead that connects to either the atria or the ventricles.
- Dual-Chamber Pacemakers: These have two leads, one connecting to the atria and the other to the ventricles, allowing for more physiological pacing that mimics the natural heartbeat.
- Biventricular Pacemakers (Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy - CRT): These are used in patients with heart failure who also have evidence of ventricular dyssynchrony (the ventricles do not contract in a coordinated manner).
Lifestyle Adjustments and Follow-Up
After pacemaker implantation, patients typically undergo a period of recovery and are provided with instructions on how to manage their new device. This includes understanding how to monitor their pacemaker, recognizing signs that may indicate a problem, and scheduling regular follow-up appointments with their healthcare provider. Lifestyle adjustments might also be recommended to optimize heart health, such as managing blood pressure, maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking.
Complications and Risks
While pacemaker implantation is a relatively safe procedure, there are risks and potential complications, including infection, bleeding, and damage to the heart or lungs. Additionally, there can be issues related to the pacemaker itself, such as battery depletion or lead malfunction, which may require additional procedures.
Conclusion
Third-degree AV block is a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention. The treatment, particularly pacemaker implantation, has significantly improved outcomes for patients with this condition. Understanding the condition, its treatment options, and the importance of follow-up care is crucial for managing third-degree AV block effectively and improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
What are the symptoms of third-degree AV block?
+Symptoms can range from mild, such as fatigue or dizziness, to severe, including fainting (syncope) or heart failure. The severity of symptoms can vary greatly among individuals.
Is a pacemaker implantation a risky procedure?
+Like any medical procedure, pacemaker implantation carries risks, including infection, bleeding, and potential damage to the heart or lungs. However, for most patients, the benefits of improved heart function and reduced symptoms outweigh these risks.
Can lifestyle changes help manage third-degree AV block after pacemaker implantation?
+Yes, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, managing stress, and avoiding smoking, can help optimize heart health and reduce the risk of complications.