Abo Rh System: Determine Compatibility Easily
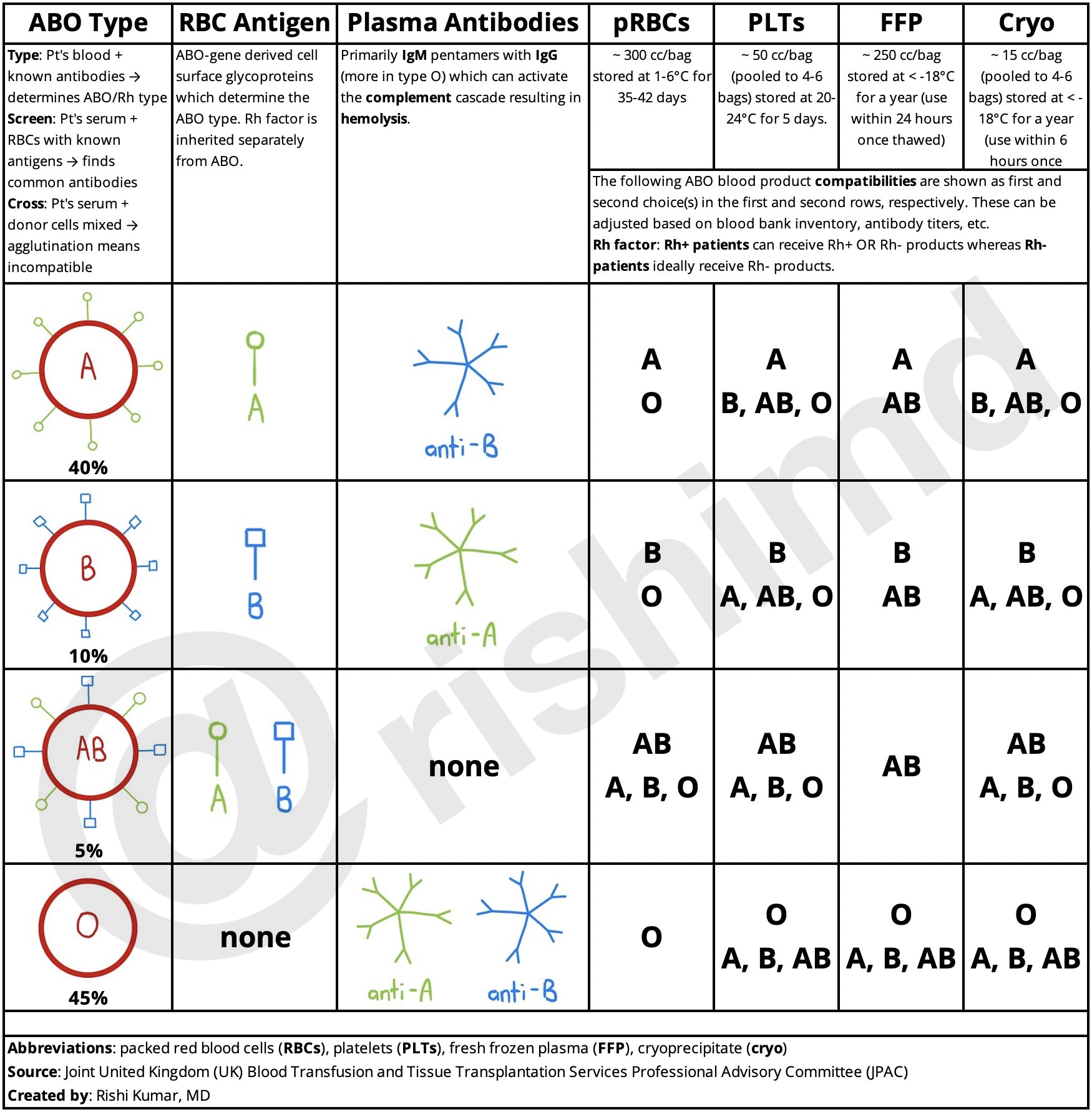
The ABO blood group system, also known as the ABO Rh system, is one of the most important blood types in human medicine. It determines the compatibility of blood transfusions between individuals, which is crucial for preventing adverse reactions. The ABO Rh system consists of two main components: the ABO blood group and the Rh blood type.
Understanding the ABO Blood Group
The ABO blood group is classified into four main categories: A, B, AB, and O. These categories are determined by the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. Antigens are substances that can trigger an immune response, and in the case of blood transfusions, they can cause the recipient’s immune system to react against the donated blood.
- Type A: Individuals with type A blood have the A antigen on their red blood cells and B antibodies in their plasma.
- Type B: Those with type B blood have the B antigen on their red blood cells and A antibodies in their plasma.
- Type AB: People with type AB blood have both A and B antigens on their red blood cells and no A or B antibodies in their plasma.
- Type O: Individuals with type O blood have no A or B antigens on their red blood cells and both A and B antibodies in their plasma.
Understanding the Rh Blood Type
The Rh blood type is classified as either Rh-positive (Rh+) or Rh-negative (Rh-). The Rh factor is another antigen that can be present or absent on the surface of red blood cells. If an individual has the Rh antigen, they are considered Rh-positive, while those without it are considered Rh-negative.
Determining Compatibility
Determining compatibility between blood donors and recipients is crucial to prevent adverse reactions. The following rules apply:
- ABO Compatibility: The recipient’s immune system will react against any ABO blood type that is not compatible with their own. For example, an individual with type A blood can receive blood from a type A or type O donor, but not from a type B or type AB donor.
- Rh Compatibility: If the recipient is Rh-negative, they should only receive blood from an Rh-negative donor to prevent the formation of Rh antibodies. If the recipient is Rh-positive, they can receive blood from either an Rh-positive or Rh-negative donor.
Consequences of Incompatibility
Receiving incompatible blood can lead to severe health complications, including:
- Hemolysis: The destruction of red blood cells, which can cause anemia, jaundice, and other symptoms.
- Allergic Reactions: Mild to severe allergic reactions can occur, ranging from itching and rash to anaphylaxis.
- Kidney Damage: In severe cases, incompatible blood can cause kidney damage or failure.
Best Practices for Blood Transfusions
To ensure safe and compatible blood transfusions:
- Verify Blood Type: Confirm the blood type of both the donor and recipient before transfusion.
- Use Cross-Matching: Perform cross-matching tests to verify compatibility between the donor and recipient.
- Follow Proper Protocols: Adhere to established protocols for blood storage, handling, and transfusion to minimize the risk of contamination or mix-ups.
By understanding the ABO Rh system and following proper protocols, healthcare professionals can ensure safe and compatible blood transfusions, reducing the risk of adverse reactions and saving lives.
It's essential to remember that blood type is just one aspect of compatibility. Other factors, such as the presence of other antibodies or underlying medical conditions, can also impact the safety of blood transfusions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the rarest blood type in the ABO Rh system?
+The rarest blood type in the ABO Rh system is AB negative, which is found in less than 1% of the population.
Can an Rh-negative individual receive blood from an Rh-positive donor?
+No, an Rh-negative individual should not receive blood from an Rh-positive donor, as this can lead to the formation of Rh antibodies and increase the risk of complications during future pregnancies or transfusions.
How is blood type determined in newborns?
+Blood type is determined by inherited traits from an individual's parents. Newborns can have their blood type determined through a simple blood test, which can help identify potential compatibility issues for future transfusions or medical procedures.
By understanding the complexities of the ABO Rh system and following proper protocols, healthcare professionals can ensure safe and compatible blood transfusions, ultimately saving lives and improving patient outcomes.



