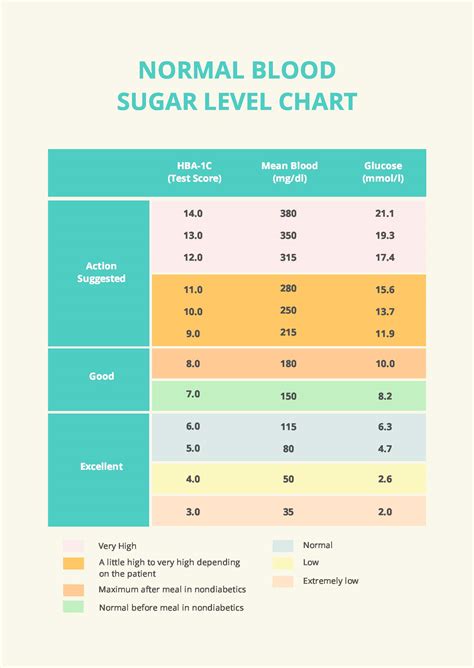
Amlodipine 2.5 Mg: Effective Blood Pressure Control

Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a pervasive health issue affecting millions worldwide. It’s a condition where the force of blood against artery walls is consistently too high, leading to potential heart damage, stroke, and other serious health problems. Managing hypertension is crucial, and one of the most commonly prescribed medications for this purpose is Amlodipine, particularly in its 2.5 mg dosage. This article delves into the specifics of Amlodipine 2.5 mg, its role in blood pressure control, its effects, and considerations for its use.
Understanding Amlodipine
Amlodipine belongs to a class of drugs known as calcium channel blockers. These medications work by relaxing blood vessels so blood can flow more easily, thereby reducing blood pressure. Amlodipine is specifically a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker, which means it primarily affects the blood vessels rather than the heart muscle itself. This distinction is important because it influences the drug’s side effect profile and its suitability for certain patients.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of Amlodipine involves the inhibition of the influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. By blocking these calcium channels, Amlodipine prevents calcium from entering the cells of the heart and blood vessel walls, leading to lower blood pressure. This effect is primarily seen in the peripheral arteries, where the reduction in vascular resistance leads to a lowering of blood pressure without significantly affecting cardiac output or heart rate, making it an effective option for patients with hypertension.
Efficacy of Amlodipine 2.5 Mg
The 2.5 mg dosage of Amlodipine is often considered a starting point for many patients, especially those who are older or have certain medical conditions that may make them more susceptible to the effects of the medication. Studies have shown that Amlodipine 2.5 mg is effective in lowering blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Its efficacy is comparable to other antihypertensive drugs, but its unique mechanism of action and side effect profile make it a favorable choice for many patients. The dosage can be titrated up to 10 mg based on the patient’s response and tolerability, allowing for personalized management of hypertension.
Side Effects and Considerations
While Amlodipine is generally well-tolerated, like all medications, it can cause side effects. Common side effects include edema (swelling of the legs and ankles), dizziness, headache, and palpitations. These side effects are often mild and transient but can be more severe in some cases. It’s also important to note that Amlodipine can interact with other medications, including certain antifungals, anti-seizure drugs, and macrolide antibiotics, which can increase its levels in the blood and potentially exacerbate side effects.
Combination Therapy
Amlodipine is often used in combination with other antihypertensive medications, such as ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, or diuretics. These combination therapies can provide a more significant reduction in blood pressure than any single drug alone and can also help mitigate side effects by allowing for lower doses of each medication. The choice of combination depends on the patient’s specific condition, other health issues, and how well they tolerate the medications.
Lifestyle Modifications
While Amlodipine 2.5 mg can be an effective tool in managing hypertension, it’s essential to remember that lifestyle modifications are also crucial. These include adopting a healthy diet, reducing sodium intake, increasing physical activity, losing weight if necessary, limiting alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking. These changes not only complement the effects of Amlodipine but also contribute to overall cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Amlodipine 2.5 mg is a valuable medication for controlling blood pressure. Its efficacy, safety profile, and versatility in both monotherapy and combination regimens make it a popular choice among healthcare providers. However, like any treatment for hypertension, it should be part of a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes. By understanding how Amlodipine works, its potential side effects, and the importance of combining it with healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can better manage their hypertension and reduce their risk of cardiovascular disease.
FAQ Section
What is the primary mechanism of action of Amlodipine?
+Amlodipine works by inhibiting the influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle, leading to the relaxation of blood vessels and a reduction in blood pressure.
What are common side effects of Amlodipine?
+Common side effects include edema, dizziness, headache, and palpitations. These are generally mild but can be more severe in some cases.
Can Amlodipine be used with other medications for hypertension?
+Yes, Amlodipine can be used in combination with other antihypertensive medications. The choice of combination depends on the patient’s specific condition and response to the medication.
How does lifestyle modification complement Amlodipine in managing hypertension?
+Lifestyle modifications such as a healthy diet, regular physical activity, weight loss, and smoking cessation are crucial. They not only enhance the efficacy of Amlodipine but also contribute to overall cardiovascular health.
What is the starting dosage of Amlodipine for hypertension, and how can it be adjusted?
+The starting dosage is often 2.5 mg, which can be titrated up to 10 mg based on the patient’s response and tolerability. The adjustment should be made under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Can Amlodipine interact with other medications?
+Yes, Amlodipine can interact with certain medications, including antifungals, anti-seizure drugs, and macrolide antibiotics, which can increase its levels in the blood. It’s essential to discuss all medications with a healthcare provider.