Normal Blood Sugar Numbers
Blood sugar levels are a crucial aspect of our health, and understanding what constitutes normal blood sugar numbers is vital for maintaining overall well-being. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the cells in our body. It is obtained from the food we eat and is regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas.
The measurement of blood sugar levels is typically done using a glucose meter, which provides a reading in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). The American Diabetes Association (ADA) has established guidelines for normal blood sugar levels, which vary depending on the time of day and when the last meal was consumed.
Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
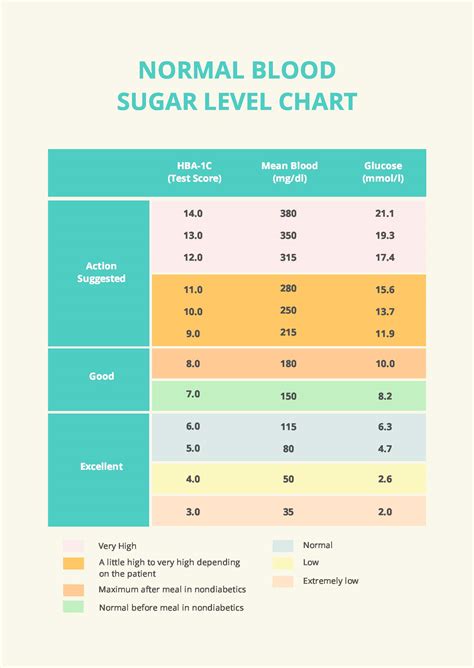
Fasting blood sugar levels are measured after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. Normal fasting blood sugar levels are between 70 mg/dL and 99 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L to 5.5 mmol/L). Levels within this range indicate that the body is efficiently regulating blood glucose levels.
Postprandial (After Meal) Blood Sugar Levels
Postprandial blood sugar levels are measured 1-2 hours after eating a meal. Normally, blood sugar levels should not exceed 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) 2 hours after a meal. This threshold is important because consistently high postprandial glucose levels can lead to complications such as insulin resistance and diabetes.
Random Blood Sugar Levels
Random blood sugar levels can be measured at any time of the day, regardless of when the last meal was consumed. These levels can vary widely but should typically be below 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L). However, the interpretation of random blood glucose levels must consider the timing of the last meal and other individual factors.
Importance of Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Monitoring blood sugar levels is crucial, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing diabetes. It helps in managing the condition, preventing complications, and maintaining quality of life. The frequency of monitoring blood sugar levels can vary depending on the individual’s health status and the type of diabetes (Type 1, Type 2, or gestational diabetes).
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can affect blood sugar levels, including diet, physical activity, stress levels, certain medications, and sleep patterns. A diet high in sugars and refined carbohydrates can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity, thereby lowering blood sugar levels. Stress can cause the release of hormones like cortisol, which can increase blood sugar levels. Some medications, such as steroids, can raise blood sugar levels as a side effect. Adequate sleep is also crucial, as lack of sleep can affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
Maintaining Normal Blood Sugar Levels
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels requires a combination of a healthy diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and adequate sleep. Eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and salt, and high in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, along with muscle-strengthening activities on all major muscle groups at least twice a week, as recommended by health guidelines, can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and overall health. Managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can also contribute to maintaining normal blood sugar levels.
Addressing Abnormal Blood Sugar Levels
If blood sugar levels are consistently outside the normal range, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. Abnormal blood sugar levels can indicate an underlying health issue, such as diabetes or prediabetes, which requires medical attention. A healthcare provider can offer personalized advice, prescribe necessary medications, and help develop a plan to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
Technology and Blood Sugar Management
Advancements in technology have made managing blood sugar levels more accessible and convenient. Continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGMS) provide real-time data on glucose levels throughout the day, enabling more precise management of diabetes. Mobile apps can help track diet, physical activity, and medication adherence, offering a holistic approach to blood sugar control.
Implications of High Blood Sugar Levels
High blood sugar levels over an extended period can lead to serious health complications, including cardiovascular diseases, nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney damage (nephropathy), and vision problems (retinopathy). Therefore, early detection and management of abnormal blood sugar levels are critical to preventing these complications.
Conclusion
Normal blood sugar numbers are a critical indicator of our metabolic health. Maintaining these levels within the recommended range through a combination of diet, exercise, and other lifestyle modifications is essential for preventing diabetes and its complications. Understanding what constitutes normal blood sugar levels and taking proactive steps to manage them can significantly contribute to overall health and well-being.
What are normal blood sugar levels after eating?
+Normally, blood sugar levels should not exceed 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) 2 hours after a meal. However, this can vary slightly from person to person and depends on factors such as the type of meal consumed and individual health status.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on your health status and the type of diabetes you have. For individuals with Type 1 diabetes or those taking insulin, it may be necessary to check blood sugar levels multiple times a day. For those with Type 2 diabetes, the frequency can vary based on the treatment plan and the healthcare provider's recommendations.
What can cause high blood sugar levels?
+Several factors can cause high blood sugar levels, including consuming high-sugar or high-carbohydrate meals, lack of physical activity, stress, certain medications, and inadequate sleep. Understanding these factors can help in managing and preventing high blood sugar levels.
How can I lower my blood sugar levels naturally?
+Lowering blood sugar levels naturally can be achieved through a combination of a balanced diet low in added sugars and refined carbohydrates, regular physical activity, stress management techniques, and adequate sleep. Drinking plenty of water and incorporating fiber-rich foods into your diet can also help regulate blood sugar levels.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar levels?
+Symptoms of high blood sugar levels can include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, slow healing of cuts and wounds, and frequent infections. If you are experiencing these symptoms, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In conclusion, understanding and managing blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of health management. By knowing what constitutes normal blood sugar numbers and taking steps to maintain them, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing diabetes and its associated complications, leading to a healthier and more fulfilling life.