Appendix Removal Surgery
The human body is a complex and intricate system, composed of various organs and structures that work in harmony to maintain overall health and function. One such structure is the appendix, a small, tube-like organ attached to the large intestine. While its function is not entirely understood, the appendix is believed to play a role in the early development of the gut microbiome. However, in some cases, the appendix can become inflamed or infected, leading to a condition known as appendicitis. In such situations, surgical removal of the appendix, also known as an appendectomy, is often necessary to prevent further complications.
Understanding Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a medical emergency that requires prompt attention. It occurs when the appendix becomes blocked, leading to inflammation and potential rupture. The blockage can be caused by various factors, including fecal impaction, foreign bodies, or lymphoid hyperplasia. As the appendix becomes inflamed, it can lead to severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and fever. If left untreated, the appendix can rupture, leading to peritonitis, a potentially life-threatening condition.
Surgical Removal of the Appendix
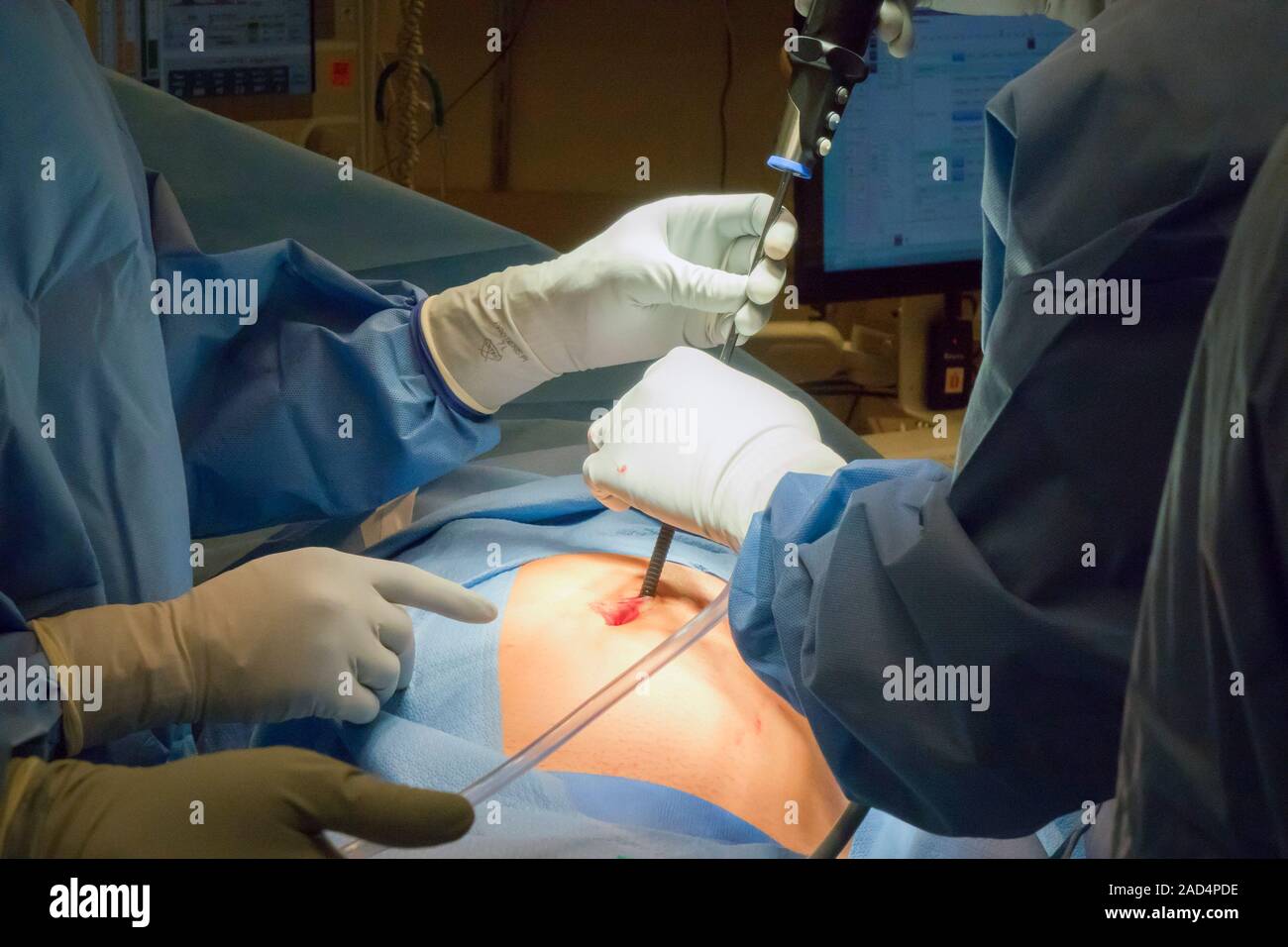
An appendectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the inflamed or infected appendix. The surgery can be performed through an open approach, where a single incision is made in the abdomen, or a laparoscopic approach, which involves several small incisions and the use of a camera and instruments. The laparoscopic approach is generally preferred, as it results in less tissue damage, reduced risk of infection, and faster recovery times.
The surgical procedure typically begins with the administration of general anesthesia, followed by the insertion of a laparoscope and instruments through small incisions in the abdomen. The surgeon then identifies the appendix and carefully dissectes it from surrounding tissues. Once the appendix is freed, it is removed through one of the incisions, and the area is cleaned and irrigated to prevent infection.
Post-Operative Care and Recovery
After the surgery, patients are typically monitored in the hospital for several hours to ensure that there are no complications. Pain management is a priority, and patients may be prescribed pain medication to manage discomfort. The recovery process usually takes several weeks, during which patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting, bending, or strenuous activities.
It is essential to follow the surgeon’s instructions and attend follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and prevent potential complications. Patients can usually return to their normal activities within 2-4 weeks, although this may vary depending on the individual’s overall health and the complexity of the surgery.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, there are potential risks and complications associated with an appendectomy. These may include:
- Infection: Bacterial infections can occur at the surgical site or within the abdomen.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding during or after the surgery can lead to complications.
- Adhesions: The formation of scar tissue can lead to bowel obstruction or other complications.
- Hernia: Weakness in the abdominal wall can lead to hernia formation.
It is crucial to discuss these potential risks and complications with a healthcare provider to understand the benefits and risks of the surgery.
Conclusion
Appendix removal surgery, or appendectomy, is a common procedure performed to treat appendicitis. While the procedure is generally safe, it is essential to understand the potential risks and complications associated with the surgery. By following the surgeon’s instructions and attending follow-up appointments, patients can ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of complications. As medical technology continues to evolve, it is likely that new treatments and procedures will emerge, offering improved outcomes and reduced risks for patients undergoing appendix removal surgery.
FAQs
What are the symptoms of appendicitis?
+Common symptoms of appendicitis include severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, and loss of appetite. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to seek medical attention immediately.
Can appendicitis be treated without surgery?
+In some cases, appendicitis can be treated with antibiotics alone. However, this approach is typically reserved for patients with early-stage appendicitis or those who are not good candidates for surgery. Surgery is often necessary to prevent further complications and ensure proper recovery.
How long does it take to recover from an appendectomy?
+The recovery process for an appendectomy typically takes several weeks. Patients can usually return to their normal activities within 2-4 weeks, although this may vary depending on the individual’s overall health and the complexity of the surgery.
Can I prevent appendicitis?
+While there is no guaranteed way to prevent appendicitis, maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding strenuous activities can help reduce the risk of developing the condition. It is also essential to seek medical attention immediately if you experience any symptoms of appendicitis.