What Causes Shingles Reaction? Vaccine Side Effects Guide
The shingles reaction, also known as herpes zoster, is a viral infection that causes a painful rash, often accompanied by fever, headache, and fatigue. It is estimated that approximately 1 in 3 people in the United States will develop shingles in their lifetime, with the risk increasing significantly after the age of 50. But what causes this reaction, and how can the shingles vaccine help prevent it? In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes of shingles, the benefits and risks of the shingles vaccine, and provide a detailed overview of potential vaccine side effects.
Understanding Shingles: Causes and Risk Factors
Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, which is the same virus that causes chickenpox. After a person recovers from chickenpox, the virus can remain dormant in the body for years, hiding in the nerve cells. In some cases, the virus can reactivate, traveling down the nerve fibers to the skin, where it causes the characteristic shingles rash. The exact reason for the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus is not fully understood, but several factors can increase the risk, including:
- Age: The risk of developing shingles increases with age, especially after 50.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with cancer, HIV/AIDS, or taking immunosuppressive drugs, are more susceptible to shingles.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can trigger the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus.
The Shingles Vaccine: Protection Against Herpes Zoster
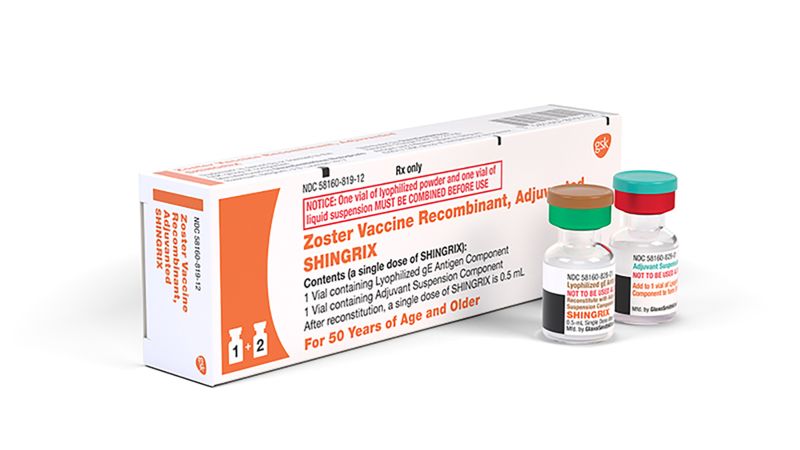
The shingles vaccine, known as Shingrix, is a recombinant vaccine that provides strong protection against shingles and postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), a common complication of shingles. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that healthy adults 50 years and older get two doses of Shingrix, two to six months apart. The vaccine works by introducing a piece of the virus’s genetic material to the body, which stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies that can fight the virus.
Vaccine Side Effects: What to Expect
While the shingles vaccine is generally safe, it can cause side effects, some of which may be similar to the symptoms of other conditions. Common side effects include:
- Pain, Redness, or Swelling at the Injection Site: These are the most common side effects, experienced by about 80% of vaccine recipients.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or exhausted after receiving the vaccine.
- Headache: Mild to moderate headaches can occur.
- Muscle or Joint Pain: Some people may experience muscle or joint pain.
- Fever: A low-grade fever can occur in some individuals.
Rare but Serious Side Effects
While rare, the shingles vaccine can cause more serious side effects, including:
- Allergic Reactions: Although extremely rare, allergic reactions to the vaccine can occur. Symptoms may include hives, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS): A condition in which the immune system damages nerve cells, leading to muscle weakness and sometimes paralysis.
FAQ Section
Who should get the shingles vaccine?
+The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that healthy adults 50 years and older get two doses of Shingrix, two to six months apart.
Can the shingles vaccine cause shingles?
+No, the shingles vaccine cannot cause shingles. The vaccine contains a piece of the virus's genetic material, not the live virus, so it cannot infect you with shingles.
How long does the shingles vaccine protection last?
+Studies have shown that the shingles vaccine provides strong protection against shingles and PHN for at least the first four years after vaccination. Ongoing studies are looking at how long protection lasts.
Conclusion
The shingles vaccine offers a powerful tool in preventing the shingles reaction and its complications, particularly in older adults and those with weakened immune systems. While side effects can occur, they are generally mild and temporary. By understanding the causes of shingles and the benefits and risks of the vaccine, individuals can make informed decisions about their health. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best approach for your specific situation, especially if you have concerns about the vaccine or potential side effects.