Arthroscopic Surgery Knee: Minimally Invasive Relief
The advent of arthroscopic surgery has revolutionized the field of orthopedics, offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgery for various knee conditions. This advanced surgical technique has gained widespread acceptance among orthopedic surgeons and patients alike, due to its numerous benefits, including reduced recovery time, less post-operative pain, and minimal scarring. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the world of arthroscopic knee surgery, exploring its indications, procedure, benefits, and potential complications.
Evolution of Arthroscopic Surgery
The concept of arthroscopy, which involves the insertion of a small camera and surgical instruments through tiny incisions, has been around for several decades. However, it wasn’t until the 1980s that arthroscopic surgery gained popularity as a diagnostic and therapeutic tool for knee conditions. Since then, significant advancements in technology and surgical techniques have expanded the scope of arthroscopic procedures, enabling surgeons to address a wide range of knee problems, from meniscal tears and ligament sprains to cartilage defects and early arthritis.
Indications for Arthroscopic Knee Surgery
Arthroscopic surgery is often recommended for patients with knee conditions that have not responded to conservative treatments, such as physical therapy, medication, or injections. The most common indications for arthroscopic knee surgery include:
- Meniscal tears: Tears in the meniscus, a cartilage structure that cushions the joint, can cause pain, locking, or catching sensations in the knee.
- Ligament sprains: Injuries to the ligaments, such as the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or medial collateral ligament (MCL), can lead to knee instability and pain.
- Cartilage defects: Damage to the articular cartilage, which covers the ends of bones, can cause knee pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
- Loose bodies: Small fragments of bone or cartilage can break off and float in the joint, causing pain and mechanical symptoms.
The Arthroscopic Procedure
Arthroscopic knee surgery is typically performed on an outpatient basis, under regional or general anesthesia. The procedure involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The patient is positioned on the operating table, and the knee is cleaned and draped in a sterile manner.
- Portal creation: The surgeon creates two to three small incisions, called portals, around the knee joint.
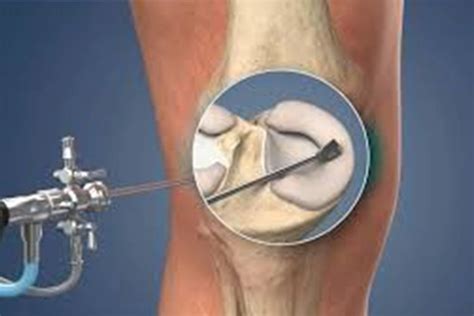
- Camera insertion: An arthroscope, a small camera with a light source, is inserted through one of the portals, allowing the surgeon to visualize the inside of the knee joint on a monitor.
- Instrument insertion: Surgical instruments, such as probes, forceps, and shavers, are inserted through the other portals to perform the necessary repairs.
- Procedure: The surgeon performs the required procedure, such as meniscal repair, ligament reconstruction, or cartilage debridement.
- Closure: The portals are closed with sutures or staples, and the knee is dressed with a sterile bandage.
Benefits of Arthroscopic Knee Surgery
Arthroscopic knee surgery offers numerous benefits, including:
- Minimally invasive: Small incisions result in less tissue damage and trauma.
- Reduced recovery time: Patients can often return to their normal activities within a few weeks.
- Less post-operative pain: The minimally invasive nature of the procedure reduces post-operative pain and discomfort.
- Minimal scarring: The small incisions result in minimal scarring.
Potential Complications
While arthroscopic knee surgery is generally a safe procedure, potential complications can occur, including:
- Infection: As with any surgical procedure, there is a small risk of infection.
- Nerve damage: Injury to the nerves surrounding the knee joint can occur, resulting in numbness, tingling, or weakness.
- Bleeding: Excessive bleeding can occur, requiring blood transfusions or additional surgery.
Post-Operative Rehabilitation
A well-structured rehabilitation program is essential to ensure a successful outcome after arthroscopic knee surgery. The rehabilitation process typically involves:
- Pain management: Controlling post-operative pain with medication and other modalities.
- Range of motion exercises: Gentle exercises to maintain knee mobility and prevent stiffness.
- Strengthening exercises: Progressing to strengthening exercises to restore muscle function and stability.
- Functional activities: Gradually returning to functional activities, such as walking, climbing stairs, and cycling.
Future Directions
The field of arthroscopic knee surgery is constantly evolving, with advancements in technology and surgical techniques expanding the scope of minimally invasive procedures. Some of the future directions include:
- Robotic-assisted arthroscopy: The use of robotic systems to enhance precision and accuracy during arthroscopic procedures.
- Biologic therapies: The use of biologic agents, such as stem cells and platelet-rich plasma, to promote healing and tissue regeneration.
- Minimally invasive osteotomies: The development of minimally invasive techniques for osteotomies, which involve cutting and realigning bones to correct deformities.
In conclusion, arthroscopic knee surgery has revolutionized the treatment of knee conditions, offering a minimally invasive alternative to traditional open surgery. With its numerous benefits, including reduced recovery time, less post-operative pain, and minimal scarring, arthroscopic knee surgery has become a popular choice among patients and orthopedic surgeons alike. As the field continues to evolve, we can expect to see further advancements in technology and surgical techniques, expanding the scope of minimally invasive procedures and improving patient outcomes.
What is the typical recovery time for arthroscopic knee surgery?
+The typical recovery time for arthroscopic knee surgery can vary depending on the individual and the specific procedure. However, most patients can expect to return to their normal activities within 2-6 weeks.
What are the potential risks and complications of arthroscopic knee surgery?
+Potential risks and complications of arthroscopic knee surgery include infection, nerve damage, bleeding, and reactions to anesthesia. However, these complications are rare and can be minimized with proper surgical techniques and post-operative care.
Can arthroscopic knee surgery be performed on an outpatient basis?
+How long does the arthroscopic procedure typically take?
+The length of the arthroscopic procedure can vary depending on the specific procedure and the individual patient. However, most arthroscopic procedures can be completed within 30-60 minutes.
What are the benefits of arthroscopic knee surgery compared to traditional open surgery?
+The benefits of arthroscopic knee surgery compared to traditional open surgery include reduced recovery time, less post-operative pain, and minimal scarring.