Blood Diabetic Levels: Manage Your Numbers
The complexity of managing blood sugar levels is a challenge many individuals with diabetes face on a daily basis. The meticulous balancing act between diet, exercise, medication, and lifestyle adjustments can be overwhelming, yet mastering this equilibrium is crucial for maintaining optimal health and preventing the onset of complications associated with diabetes. At the heart of this management is the understanding and control of blood diabetic levels, which serve as a critical indicator of how well the body is regulating blood glucose.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
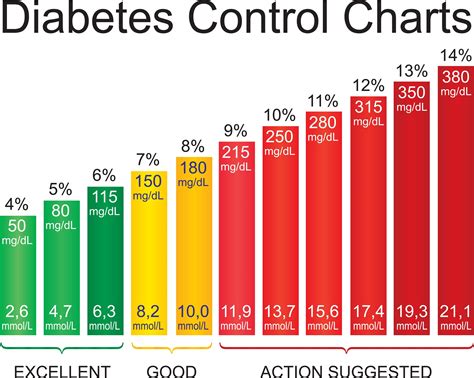
Blood sugar levels, measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), indicate the amount of glucose present in the blood. For individuals without diabetes, the body naturally regulates these levels, ensuring they remain within a narrow, healthy range. However, for those with diabetes, whether Type 1, Type 2, or gestational, the body either cannot produce enough insulin (a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels) or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which, if left unmanaged, can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
The Importance of Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a cornerstone of diabetes management. By regularly checking these levels, individuals can understand how different factors, such as food, physical activity, and medications, affect their blood sugar. This information is invaluable for making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication adjustments to keep blood sugar levels within a target range. The American Diabetes Association recommends the following target blood sugar levels for most adults with diabetes: - Before meals: 80 to 130 mg/dL - After meals (1 to 2 hours after beginning of meal): Less than 180 mg/dL
Strategies for Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Dietary Adjustments
Diet plays a pivotal role in managing blood sugar levels. Eating a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium, and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar. The concept of glycemic index (GI) is also important; choosing foods with a low GI means they are less likely to cause a spike in blood sugar levels. Additionally, meal planning and carbohydrate counting can help manage the amount of glucose entering the bloodstream.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another crucial component of managing diabetes. Exercise not only helps the body use insulin more efficiently but also reduces blood sugar levels and improves heart health. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent choices, and it’s recommended to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.
Medication and Insulin Therapy
For many with diabetes, medication or insulin therapy is necessary to help manage blood sugar levels. Oral medications and insulin work in different ways to lower blood sugar, and the type of medication prescribed depends on the type of diabetes, the severity of the condition, and other health factors. It’s essential to follow the medication regimen as prescribed by a healthcare provider and to monitor blood sugar levels to adjust the dosage or type of medication as needed.
Stress Management
Stress can have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. When under stress, the body releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can cause blood sugar levels to rise. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises, can help mitigate this effect and contribute to better blood sugar management.
Advanced Technologies for Diabetes Management
The advent of advanced technologies has revolutionized the way individuals manage their diabetes. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, insulin pumps, and mobile applications designed to track food, activity, and medications offer real-time insights and personalized feedback. These tools can help identify patterns and trends in blood sugar levels, enabling more precise management and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Living with Diabetes: Lifestyle Adjustments
Living with diabetes requires a holistic approach that encompasses not just medical management but also lifestyle adjustments. This includes getting enough sleep, staying hydrated, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and maintaining a healthy weight. By adopting these habits and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes can lead active, healthy lives.
Conclusion
Managing blood diabetic levels is a multifaceted challenge that requires dedication, knowledge, and the right support system. By understanding the intricacies of blood sugar regulation, utilizing monitoring and management strategies, and embracing lifestyle adjustments, individuals with diabetes can navigate their condition effectively. Remember, diabetes management is a journey, and with the right mindset, tools, and professional guidance, it’s possible to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent complications, ultimately enhancing the quality of life.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels in individuals without diabetes?
+For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL when fasting and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels if I have diabetes?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes, the treatment plan, and how well the diabetes is controlled. Generally, individuals with Type 1 diabetes and some with Type 2 diabetes may need to check their blood sugar levels several times a day.
What are the potential risks of high blood sugar levels if left unmanaged?
+High blood sugar levels, if left unmanaged, can lead to serious health issues, including heart disease, kidney damage (nephropathy), nerve damage (neuropathy), and vision problems (including blindness). Additionally, unmanaged diabetes increases the risk of infections and can lead to conditions like gastroparesis and foot damage.
Can diet and exercise alone manage diabetes, or is medication always necessary?
+For some individuals, particularly those with prediabetes or newly diagnosed Type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes including diet and exercise can be enough to manage blood sugar levels. However, many people with diabetes will require medication or insulin therapy in addition to lifestyle changes to achieve target blood sugar levels.
How does stress affect blood sugar levels, and what are some effective stress management techniques?
+Stress can raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Effective stress management techniques include deep breathing exercises, yoga, meditation, and engaging in physical activity. These practices can help reduce stress and contribute to better blood sugar management.