Blood Sugar: Know Your Normal Limit
Maintaining a healthy blood sugar level is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts energy levels, weight, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. Blood sugar, also known as glucose, is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, and its levels are regulated by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Understanding what constitutes a normal blood sugar level and how to manage it is essential for preventing complications and ensuring optimal health.
What is Normal Blood Sugar?
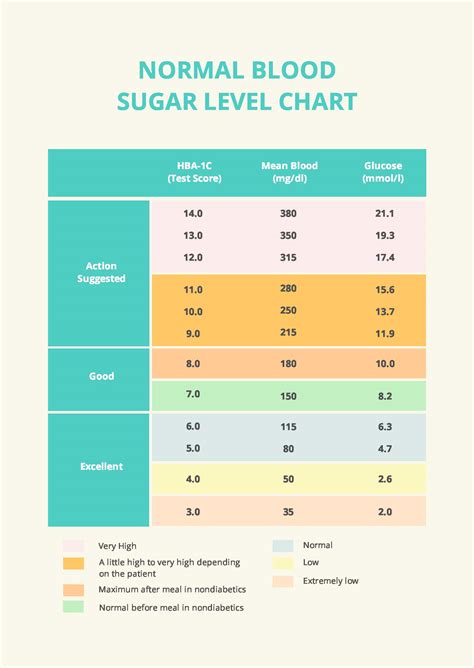
Normal blood sugar levels vary throughout the day, depending on factors such as the time of day, what and when you last ate, and your physical activity level. Generally, a normal fasting blood glucose level is between 70 and 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter). After eating, blood sugar levels typically rise but should remain below 140 mg/dL. It’s also important to note that blood sugar levels can fluctuate due to various factors, including stress, certain medications, and hormonal changes.
Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, especially for individuals with diabetes or those at risk, is vital. This can be done through self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) using a glucometer or by having regular HbA1c tests, which measure average blood glucose control over the past 2-3 months.
Understanding Blood Sugar Measurement
Blood sugar measurements are typically taken in two contexts: fasting and postprandial (after eating).
- Fasting Blood Sugar: This measurement is taken after an overnight fast of at least 8 hours. It reflects the body’s ability to manage blood glucose levels when not influenced by recent food intake. A fasting blood glucose level of 100-125 mg/dL indicates impaired fasting glucose (prediabetes), while a level of 126 mg/dL or higher suggests diabetes.
- Postprandial Blood Sugar: This is measured 1-2 hours after eating to see how the body manages glucose after a meal. Levels should ideally be below 140 mg/dL to minimize the risk of vascular complications.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming high amounts of simple carbohydrates and sugars can cause blood sugar spikes. A diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats is beneficial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, reducing blood sugar levels. Both aerobic exercises and strength training are beneficial.
- Stress: Stress can cause the release of hormones like cortisol, which can increase blood sugar levels. Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night.
- Medications: Certain medications, including steroids and some psychiatric drugs, can raise blood sugar levels. It’s crucial to discuss medication effects with your healthcare provider.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Effective management of blood sugar involves a combination of dietary changes, regular physical activity, stress management, and, if necessary, medication as prescribed by a healthcare provider. Here are some practical tips:
- Keep Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps the kidneys flush out excess glucose through urine.
- Eat Regular Meals: Skipping meals can lead to low blood sugar, while eating too much can cause high blood sugar. Finding a balance is key.
- Be Mindful of Carbohydrates: Focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, which are rich in fiber and digest slowly, preventing sudden spikes in blood sugar.
- Limit Processed and Sugary Foods: These foods are high in simple carbohydrates and added sugars, contributing to blood sugar spikes.
- Stay Active: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
The Importance of Monitoring and Maintenance
For individuals with diabetes or prediabetes, regularly monitoring blood sugar levels and adjusting treatment plans as necessary is crucial. This can involve working closely with a healthcare provider to set realistic goals, understanding how different factors affect blood sugar levels, and making lifestyle adjustments to maintain healthy levels.
Steps to Healthy Blood Sugar Management:
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Discuss your risk factors, current health status, and any concerns about blood sugar levels.
- Undergo Necessary Tests: Regular blood glucose tests and HbA1c tests can provide valuable insights into your blood sugar control.
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Focus on a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and stress management.
- Monitor Progress: Keep track of your blood sugar levels, diet, and physical activity to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
- Seek Support: Connect with support groups, either in-person or online, to share experiences and learn from others managing similar conditions.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is a multifaceted process that involves understanding what constitutes normal levels, being aware of the factors that influence these levels, and implementing effective management strategies. By adopting a holistic approach to health, individuals can not only maintain healthy blood sugar levels but also reduce the risk of chronic diseases and improve overall quality of life.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels after eating?
+After eating, blood sugar levels should ideally remain below 140 mg/dL to minimize the risk of vascular complications. However, this can vary slightly from person to person based on factors such as the type of meal consumed, physical activity level, and individual metabolic factors.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on your health status and the presence of any diabetes or prediabetes diagnosis. For those with diabetes, checking levels might be necessary multiple times a day, while for those without diabetes, an annual check during a routine health exam may suffice. Consult with your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate frequency for your specific situation.
What are the signs of high blood sugar?
+Common signs of high blood sugar include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, cuts or wounds that are slow to heal, and recurrent skin, gum, or bladder infections. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.