Blood Sugar: Know Your Optimal Level
Understanding blood sugar levels is crucial for maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar, also known as blood glucose, is the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the body’s primary source of energy. The body regulates blood sugar levels through a complex process involving the pancreas, liver, and various hormones. In this article, we will delve into the optimal blood sugar levels, the factors that influence blood sugar, and the strategies for managing and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
What are Optimal Blood Sugar Levels?

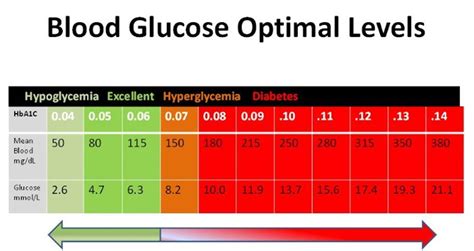
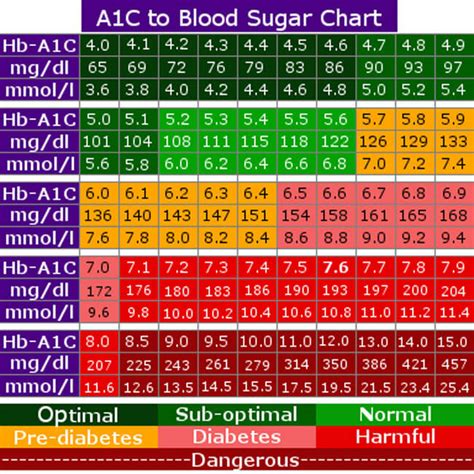
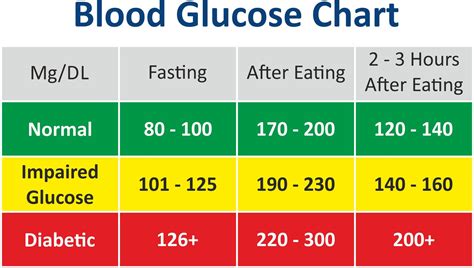
Optimal blood sugar levels vary depending on the individual, their health status, and the time of day. For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 and 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) when fasting (not having eaten for at least 8 hours) and less than 140 mg/dL 2 hours after eating. For people with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following target blood sugar levels:
- Fasting: 80-130 mg/dL
- Before meals: 70-130 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after meals: Less than 180 mg/dL
It’s essential to note that these are general guidelines, and your healthcare provider may set individualized targets based on your specific health needs and conditions.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including:
Diet: The foods you eat, particularly the amount and type of carbohydrates, can significantly affect blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose during digestion, causing blood sugar levels to rise. Foods high in fiber, protein, and healthy fats can help mitigate this effect.
Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can help lower blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, which is the body’s ability to effectively use insulin. This means that with regular activity, the body can more efficiently manage blood sugar levels.
Medications: Certain medications, including diabetes medications, steroids, and some psychiatric medications, can influence blood sugar levels. It’s crucial to discuss the potential effects of any medications with your healthcare provider.
Stress: Stress can cause the body to release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can raise blood sugar levels. Managing stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt hormones that regulate blood sugar, leading to higher blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels
Effective management of blood sugar levels involves a multifaceted approach, including diet, exercise, monitoring, and, when necessary, medication. Here are some strategies to help maintain healthy blood sugar levels:
Dietary Adjustments
- Choose Complex Carbohydrates: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods are rich in fiber, which can slow the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream.
- Portion Control: Be mindful of the portion sizes of carbohydrate-rich foods to avoid spikes in blood sugar levels.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water can help the kidneys flush out excess glucose through urine.
Regular Physical Activity
- Aerobic Exercises: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercises, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercises, or a combination of both, per week.
- Strength Training: Incorporate strength-training activities into your routine at least twice a week to build muscle, which can help improve insulin sensitivity.
Monitoring Blood Sugar
- Use a Glucose Meter: Regularly check your blood sugar levels, especially if you have diabetes, to understand how different factors like food and exercise affect your levels.
- Keep a Log: Record your blood sugar levels, the foods you eat, and your physical activity to identify patterns and make informed decisions about your management plan.
Medication Adherence
If you have diabetes, adhering to your medication regimen as prescribed by your healthcare provider is crucial. This may include oral medications or insulin therapy, depending on the type and severity of your diabetes.
Conclusion
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of overall health, requiring a comprehensive approach that includes dietary adjustments, regular physical activity, monitoring, and, when necessary, medication. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar levels and implementing strategies to manage them, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and its complications. It’s also important to work closely with healthcare providers to set and achieve personalized blood sugar targets, ensuring the best possible health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can cause symptoms such as increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow healing of cuts and wounds. If left untreated, it can lead to more serious complications.
Can blood sugar levels be managed through diet alone?
+For some people, particularly those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, managing blood sugar levels through dietary changes and exercise may be possible. However, for others, especially those with type 1 diabetes, medication or insulin therapy may also be necessary. It's best to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most effective management plan.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on your health status and the presence of diabetes. For individuals with diabetes, checking blood sugar levels at least four times a day (before meals and before bedtime) is common, but your healthcare provider may recommend a different schedule based on your specific needs.
By following the strategies outlined and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers, individuals can effectively manage their blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications and improving overall well-being.