Blood Sugar Measurement
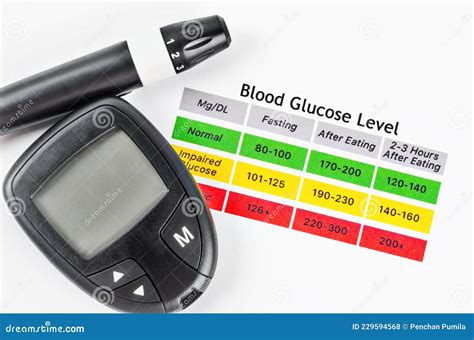
Measuring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin, a hormone that regulates blood glucose levels. The importance of blood sugar measurement cannot be overstated, as it provides individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers with vital information necessary for making informed decisions about treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and prevention of complications.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the body’s primary source of energy. Under normal circumstances, the body maintains blood glucose levels within a narrow range through the actions of insulin and glucagon, hormones produced by the pancreas. In individuals with diabetes, this balance is disrupted, leading to elevated blood glucose levels.
Methods of Blood Sugar Measurement
There are several methods for measuring blood sugar levels, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Fingerstick Method: This is the most common method of blood sugar measurement. It involves pricking the skin, typically on the fingertip, with a small needle (lancet) to collect a drop of blood, which is then placed on a test strip and read by a blood glucose meter. The fingerstick method provides immediate results and is widely used for daily glucose monitoring.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Systems: CGMs are small devices that are worn on the body and measure glucose levels throughout the day and night. They use a small sensor inserted under the skin to measure interstitial glucose levels, providing real-time data on glucose trends and patterns. CGMs are particularly beneficial for individuals who experience significant glucose fluctuations or have difficulties managing their blood sugar levels.
Laboratory Tests: Blood glucose levels can also be measured through laboratory tests, such as the fasting plasma glucose test or the oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT). These tests are typically used for diagnosing diabetes or prediabetes and are conducted in a healthcare setting.
Importance of Accurate Blood Sugar Measurement
Accurate blood sugar measurement is vital for several reasons:
Treatment Adjustment: Blood glucose readings help individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers adjust medication, diet, and exercise regimens to achieve optimal glucose control.
Prevention of Complications: Chronic high blood sugar levels can lead to serious complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Regular monitoring and management of blood glucose levels can significantly reduce the risk of these complications.
Improved Quality of Life: By maintaining blood sugar levels within a target range, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of symptoms such as fatigue, frequent urination, and blurred vision, thereby improving their overall quality of life.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the importance of blood sugar measurement, there are challenges and considerations to be aware of:
Accuracy and Reliability: The accuracy of blood glucose meters and test strips can be affected by various factors, including the quality of the device, user technique, and environmental conditions.
Cost and Accessibility: The cost of blood glucose monitoring supplies can be a barrier for some individuals, particularly in areas with limited access to healthcare resources.
Psychological Impact: Frequent blood sugar monitoring can have a psychological impact, contributing to stress, anxiety, and feelings of burnout among individuals with diabetes.
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of blood sugar measurement is continually evolving, with innovations aimed at improving accuracy, convenience, and accessibility. Some of the future trends and developments include:
Non-Invasive Monitoring Technologies: Research into non-invasive glucose monitoring technologies, such as devices that use optical or electrical signals to measure glucose levels, could significantly reduce the burden of daily fingerstick testing.
Advanced CGM Systems: Next-generation CGMs are expected to offer improved accuracy, longer sensor durability, and enhanced user interfaces, further integrating into daily life and improving glucose management.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Data Analytics: The integration of AI and data analytics with glucose monitoring data has the potential to provide personalized insights and predictive models, helping individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers make data-driven decisions.
In conclusion, blood sugar measurement is a cornerstone of diabetes management, offering valuable insights into glucose control and guiding therapeutic decisions. As technology continues to advance and innovations emerge, the future of blood sugar measurement promises to be more accurate, accessible, and integrated into the daily lives of individuals with diabetes.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 to 140 mg/dL, though these can vary slightly depending on the time of day and when you last ate. For those with diabetes, the target range may vary based on age, other health conditions, and the presence of complications, but generally, the aim is to keep levels between 80 to 180 mg/dL.
How often should I measure my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of blood sugar measurement depends on the type of diabetes you have, your treatment plan, and how well your blood sugar levels are controlled. Generally, individuals with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes may need to test their blood sugar levels several times a day. It's best to consult with your healthcare provider to determine the testing schedule that's right for you.
Can blood sugar levels be managed without medication?
+Yes, for some individuals, particularly those with prediabetes or early-stage type 2 diabetes, it may be possible to manage blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes alone, including diet, exercise, and weight loss. However, this should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as medication may still be necessary to achieve and maintain target blood glucose levels.
In the realm of diabetes management, the ability to accurately and conveniently measure blood sugar levels stands as a significant advancement, contributing to better health outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals worldwide. As research and technology continue to evolve, the hope is for even more sophisticated, user-friendly, and accessible methods of blood glucose monitoring, further empowering those living with diabetes to take control of their health.



