Blood Sugar Range
Maintaining an optimal blood sugar range is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar levels, also known as blood glucose levels, refer to the amount of glucose present in the blood at any given time. Glucose is a type of sugar that serves as the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. When we consume carbohydrates, they are broken down into glucose, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream.
The body naturally regulates blood sugar levels through the release of insulin and glucagon, two hormones produced by the pancreas. Insulin helps to lower blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose by cells, while glucagon raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stored glucose from the liver. In individuals with diabetes, this regulatory mechanism is impaired, leading to abnormally high or low blood sugar levels.
Understanding Blood Sugar Ranges
The following are the general guidelines for blood sugar ranges:
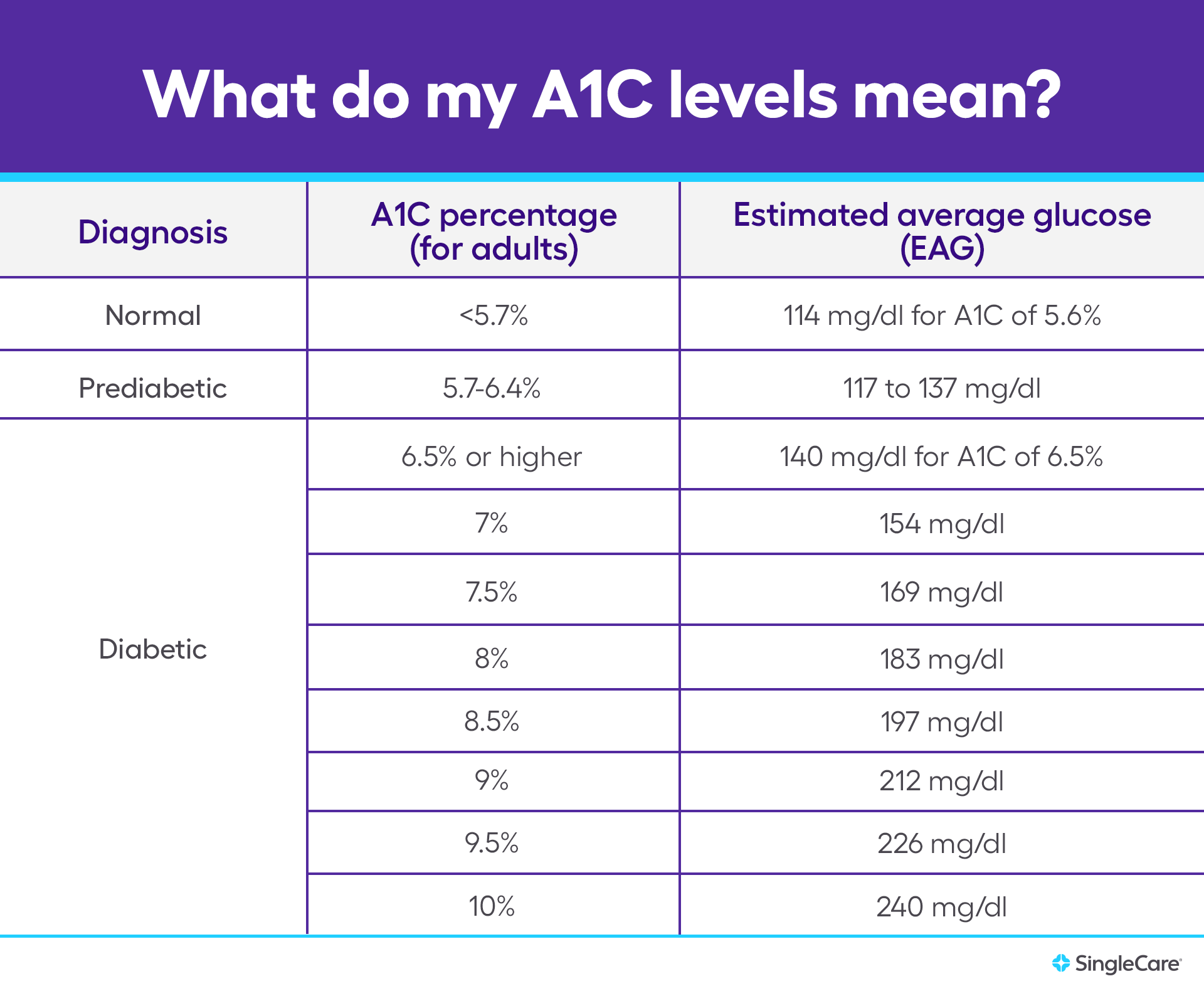
- Normal Blood Sugar Range: For individuals without diabetes, a normal blood sugar range is typically between 70 and 140 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) throughout the day. Levels may rise after meals but should return to normal within a couple of hours.
- Diabetes Blood Sugar Range: For individuals with diabetes, the target blood sugar range may vary depending on factors such as age, other health conditions, and the type of diabetes. Generally, the American Diabetes Association recommends the following target blood sugar levels:
- Before meals: 80 to 130 mg/dL
- After meals (1-2 hours): Less than 180 mg/dL
- Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar): Blood sugar levels below 70 mg/dL are considered low and can lead to symptoms such as shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, or even loss of consciousness if left untreated.
- Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar): Levels above 180 mg/dL can lead to symptoms like thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and in severe cases, ketoacidosis, a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: The types and amounts of carbohydrates consumed can significantly affect blood sugar levels. Foods with a high glycemic index can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar.
- Physical Activity: Exercise can lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body’s sensitivity to insulin.
- Medications: Certain medications, including those for diabetes, can impact blood sugar levels.
- Stress and Illness: Stress and illness can raise blood sugar levels due to the release of stress hormones like cortisol, which can increase glucose production in the liver.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can affect blood sugar control and insulin sensitivity.
Management and Monitoring
For individuals with diabetes, managing blood sugar levels involves a combination of medication (if prescribed), diet, exercise, and regular monitoring. Blood glucose meters are commonly used for self-monitoring, providing instant readings of blood sugar levels. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are also available, offering real-time data on glucose levels throughout the day and night.
Prevention Strategies
Even for those without diabetes, maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is important for preventing the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Strategies include:
- Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen, can increase the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
- Stress Management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels and insulin sensitivity.
Understanding and managing blood sugar ranges is a critical aspect of maintaining metabolic health and preventing complications associated with diabetes. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and, if necessary, working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can keep their blood sugar levels within a healthy range and reduce their risk of diabetes-related complications.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+The symptoms of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and in severe cases, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. If left untreated, hyperglycemia can lead to more serious complications, including diabetic ketoacidosis, which requires immediate medical attention.
How can I lower my blood sugar levels naturally?
+Natural ways to lower blood sugar levels include increasing physical activity, such as brisk walking, to improve insulin sensitivity. Dietary changes, like reducing carbohydrate intake, increasing fiber consumption, and choosing foods with a low glycemic index, can also help. Additionally, staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water and managing stress through techniques like yoga or meditation can contribute to better blood sugar control.
Can blood sugar levels be too low?
+Yes, blood sugar levels can be too low, a condition known as hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia occurs when blood glucose drops below 70 mg/dL and can be caused by skipping meals, taking too much diabetes medication, or engaging in intense physical activity without adequate food intake. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include shakiness, dizziness, hunger, irritability, confusion, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. Prompt treatment with fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or juice, is essential to raise blood sugar levels back to a safe range.
Conclusion:
Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is essential for health and can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle modifications, including diet, exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep. For individuals with diabetes, self-monitoring of blood glucose levels, adherence to medication regimens, and regular check-ups with healthcare providers are crucial for managing the condition effectively. By adopting healthy habits and being aware of the factors influencing blood sugar levels, individuals can reduce their risk of developing diabetes and its complications, improving overall quality of life.