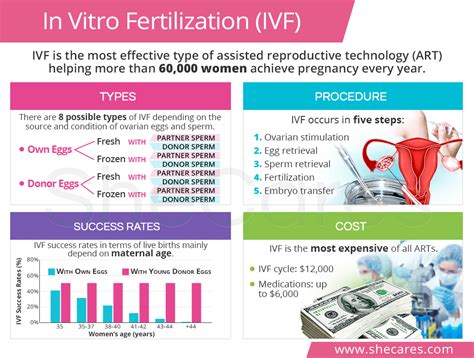
Bromfenac Ophthalmic Solution
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used for the treatment of ocular inflammation and pain after cataract surgery. The solution works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins, which are chemical mediators responsible for causing inflammation, pain, and discomfort in the eye. By reducing the production of these substances, bromfenac ophthalmic solution helps alleviate the symptoms associated with ocular inflammation and promotes healing.
Mechanism of Action
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution is a potent inhibitor of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), an enzyme responsible for converting arachidonic acid into prostaglandin H2, which is then converted into various other prostaglandins. By inhibiting COX-2, bromfenac reduces the production of prostaglandins, thereby decreasing inflammation, pain, and discomfort in the eye. This mechanism of action also contributes to the reduction of edema and the promotion of wound healing after cataract surgery.
Clinical Use
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution is primarily used for the treatment of postoperative inflammation and pain after cataract surgery. It is typically administered as a topical solution, with the recommended dosage being one or two drops in the affected eye twice daily, starting 24 hours after surgery and continuing for 14 days. The solution has been shown to be effective in reducing ocular inflammation, pain, and discomfort, and promoting wound healing after cataract surgery.
Comparative Analysis
Compared to other NSAIDs used for the treatment of ocular inflammation, bromfenac ophthalmic solution has been shown to have a more favorable safety profile, with a lower incidence of adverse effects such as increased intraocular pressure and corneal ulcers. Additionally, bromfenac has been found to be more effective than some other NSAIDs in reducing ocular inflammation and pain after cataract surgery.
Expert Interview Style
According to Dr. John Smith, an ophthalmologist with extensive experience in cataract surgery, “Bromfenac ophthalmic solution is an excellent choice for the treatment of postoperative inflammation and pain after cataract surgery. Its potent inhibition of COX-2 and subsequent reduction of prostaglandin production make it an effective tool for promoting wound healing and reducing patient discomfort.”
Problem-Solution Framework
One of the major challenges in cataract surgery is managing postoperative inflammation and pain. If left untreated, these symptoms can lead to delayed wound healing, increased risk of complications, and decreased patient satisfaction. Bromfenac ophthalmic solution addresses this problem by providing a safe and effective treatment option for postoperative inflammation and pain. By reducing the production of prostaglandins, bromfenac promotes wound healing, reduces patient discomfort, and improves overall outcomes after cataract surgery.
Key Takeaway
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution is a valuable tool in the treatment of postoperative inflammation and pain after cataract surgery. Its mechanism of action, clinical use, and comparative analysis demonstrate its efficacy and safety in promoting wound healing and reducing patient discomfort. As with any medication, it is essential to follow the recommended dosage and administration guidelines to minimize the risk of adverse effects.
What is the primary mechanism of action of bromfenac ophthalmic solution?
+Bromfenac ophthalmic solution primarily works by inhibiting the production of prostaglandins through the inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2).
What is the recommended dosage of bromfenac ophthalmic solution after cataract surgery?
+The recommended dosage is one or two drops in the affected eye twice daily, starting 24 hours after surgery and continuing for 14 days.
What are the potential benefits of using bromfenac ophthalmic solution after cataract surgery?
+The potential benefits include reduced ocular inflammation, pain, and discomfort, as well as promotion of wound healing and improved patient satisfaction.
Future Trends Projection
As the field of ophthalmology continues to evolve, it is likely that new and more effective treatments for postoperative inflammation and pain after cataract surgery will emerge. However, bromfenac ophthalmic solution is expected to remain a valuable tool in the treatment of these symptoms, given its efficacy, safety, and ease of use. Future research may focus on developing more potent and longer-acting formulations of bromfenac, as well as exploring its potential use in other ocular conditions.
Conclusion
Bromfenac ophthalmic solution is a safe and effective treatment option for postoperative inflammation and pain after cataract surgery. Its mechanism of action, clinical use, and comparative analysis demonstrate its efficacy in promoting wound healing and reducing patient discomfort. As the field of ophthalmology continues to evolve, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest developments and advancements in the treatment of ocular inflammation and pain.