The realm of mental health is complex and multifaceted, with various medications available to manage symptoms of anxiety and depression. One such medication is buspirone, a non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic that has been used for decades to treat generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). While buspirone is generally considered safe and effective, it is crucial to understand its potential risks and benefits to minimize adverse effects and optimize treatment outcomes.
Introduction to Buspirone
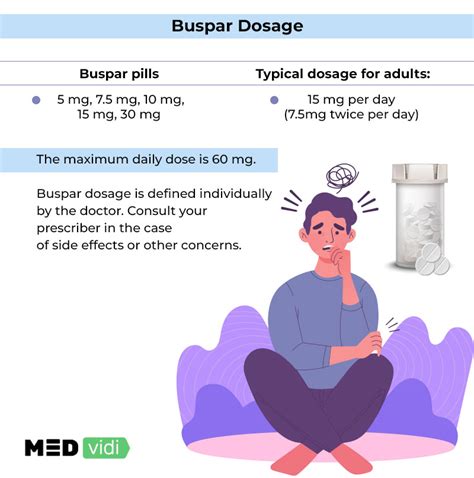
Buspirone, sold under the brand name BuSpar, is a psychotropic medication that belongs to the azapirone class. It is primarily used to treat GAD, a condition characterized by excessive and persistent worry about everyday things, even when there is no apparent reason to worry. Unlike benzodiazepines, buspirone does not exhibit sedative, muscle relaxant, or anticonvulsant activities, which makes it a preferred choice for patients who require anxiolytic therapy without the risk of dependence or withdrawal symptoms.
Mechanism of Action
The exact mechanism of action of buspirone is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve the modulation of serotonin and dopamine neurotransmission in the brain. Buspirone acts as a partial agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor, which is thought to contribute to its anxiolytic effects. Additionally, buspirone has been shown to exhibit some affinity for dopamine D2 and D3 receptors, although the clinical significance of this is not well established.
Benefits of Buspirone
Buspirone has several benefits that make it a valuable treatment option for patients with GAD. These benefits include:
- Efficacy: Buspirone has been shown to be effective in reducing symptoms of anxiety, such as worry, fear, and tension, in patients with GAD.
- Safety: Buspirone is generally considered safe and well-tolerated, with a low risk of dependence, withdrawal symptoms, and sedation.
- Lack of interactions: Buspirone has a relatively low potential for drug interactions, which makes it a good choice for patients taking multiple medications.
Risks and Side Effects
While buspirone is generally considered safe, it can cause some side effects and interact with other medications. Common side effects of buspirone include:
- Dizziness: Buspirone can cause dizziness or lightheadedness, especially when standing up from a sitting or lying down position.
- Nausea: Some patients may experience nausea or vomiting when taking buspirone.
- Headache: Buspirone can cause headaches, which are usually mild and temporary.
- Fatigue: Buspirone can cause fatigue or drowsiness, although this is less common than with benzodiazepines.
Minimizing Risks
To minimize the risks associated with buspirone, patients should:
- Follow dosing instructions: Patients should take buspirone exactly as prescribed by their doctor, without exceeding the recommended dose.
- Monitor side effects: Patients should report any side effects or concerns to their doctor, who can adjust the dose or switch to a different medication if necessary.
- Avoid interactions: Patients should inform their doctor about all medications they are taking, including over-the-counter medications and supplements, to minimize the risk of interactions.
- Attend follow-up appointments: Regular follow-up appointments with a doctor can help monitor the effectiveness of buspirone and minimize the risk of adverse effects.
Special Considerations
Buspirone may not be suitable for all patients, particularly those with certain medical conditions or taking specific medications. For example:
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Buspirone should be used with caution in pregnant or breastfeeding women, as its safety in these populations has not been well established.
- Liver or kidney disease: Patients with liver or kidney disease may require dose adjustments or closer monitoring when taking buspirone.
- Elderly patients: Elderly patients may be more susceptible to the side effects of buspirone, such as dizziness or cognitive impairment.
FAQ Section
What is the typical dose of buspirone for anxiety?
+The typical dose of buspirone for anxiety is 15-30 mg per day, divided into two or three doses. However, the dose may be adjusted based on individual response and tolerability.
Can buspirone be taken with other medications?
+Buspirone can be taken with other medications, but it is essential to inform your doctor about all medications you are taking to minimize the risk of interactions. Certain medications, such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), may interact with buspirone and increase the risk of adverse effects.
How long does it take for buspirone to start working?
+Buspirone may take several weeks to start working, with some patients experiencing improvements in anxiety symptoms within 1-2 weeks. However, it may take up to 4-6 weeks to achieve the full therapeutic effect.
Conclusion
Buspirone is a valuable treatment option for patients with generalized anxiety disorder, offering a relatively safe and effective alternative to benzodiazepines. By understanding the potential risks and benefits of buspirone, patients and healthcare providers can work together to minimize adverse effects and optimize treatment outcomes. Regular monitoring, dose adjustments, and open communication can help ensure that buspirone is used safely and effectively to improve mental health and well-being.