Cervical Spine Fusion: Restore Neck Mobility
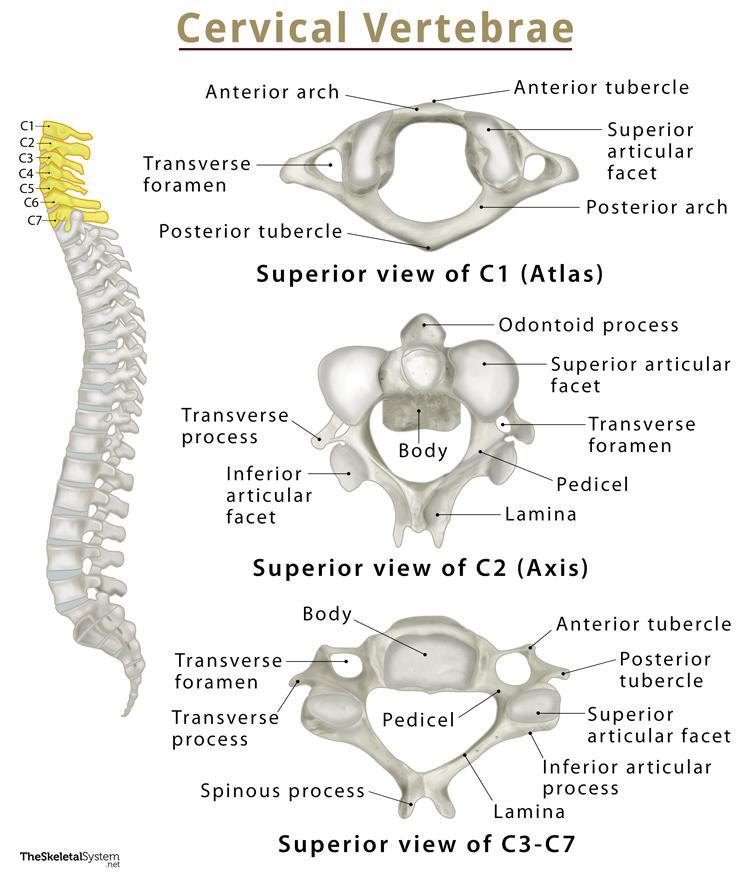
The cervical spine, comprising the seven vertebrae in the neck, plays a crucial role in supporting the head and facilitating a wide range of motion. However, various conditions such as degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, or traumatic injuries can lead to cervical spine instability, resulting in chronic pain, numbness, and limited mobility. Cervical spine fusion is a surgical procedure designed to stabilize the spine, alleviate pain, and restore neck mobility.
Understanding Cervical Spine Fusion
Cervical spine fusion involves the surgical joining of two or more vertebrae in the neck, using bone grafts, instrumentation, or a combination of both. The primary goal of this procedure is to eliminate excessive motion between the vertebrae, reduce pressure on the spinal cord or nerves, and promote the growth of new bone tissue. By stabilizing the spine, cervical spine fusion can help alleviate pain, improve mobility, and enhance overall quality of life.
Types of Cervical Spine Fusion
There are several types of cervical spine fusion procedures, including:
- Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF): This procedure involves the removal of a damaged disc through an incision in the front of the neck, followed by the insertion of a bone graft and instrumentation to stabilize the vertebrae.
- Posterior Cervical Fusion: This approach involves a incision in the back of the neck, allowing the surgeon to access the spine and perform the fusion.
- Cervical Laminectomy and Fusion: This procedure involves the removal of the lamina (a bony plate) to relieve pressure on the spinal cord, followed by the stabilization of the vertebrae using instrumentation and bone grafts.
Benefits and Risks of Cervical Spine Fusion
Cervical spine fusion can offer several benefits, including:
- Pain Relief: By stabilizing the spine and reducing pressure on the spinal cord or nerves, cervical spine fusion can provide significant pain relief.
- Improved Mobility: By eliminating excessive motion between the vertebrae, cervical spine fusion can help restore neck mobility and reduce stiffness.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: By alleviating pain and improving mobility, cervical spine fusion can significantly enhance overall quality of life.
However, as with any surgical procedure, cervical spine fusion also carries some risks, including:
- Infection: As with any surgery, there is a risk of infection with cervical spine fusion.
- Nerve Damage: The proximity of the spinal cord and nerves to the surgical site increases the risk of nerve damage during the procedure.
- Blood Clots: Immobility during the recovery period can increase the risk of blood clots.
Preparation and Recovery
To ensure a successful outcome, it is essential to prepare thoroughly for cervical spine fusion surgery. This includes:
- Pre-Surgical Evaluation: A thorough medical evaluation, including imaging studies and laboratory tests, to assess the underlying condition and overall health.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking can impede the healing process and increase the risk of complications; therefore, it is crucial to cease smoking at least two weeks prior to surgery.
- Medication Management: Certain medications, such as blood thinners, may need to be discontinued or adjusted before surgery.
The recovery period for cervical spine fusion typically involves:
- Hospital Stay: A hospital stay of several days to monitor for potential complications and manage pain.
- Pain Management: A pain management plan, including medication and physical therapy, to alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
- Physical Therapy: A customized physical therapy program to promote mobility, strength, and flexibility.
Future Outlook and Emerging Trends
The field of cervical spine fusion is continually evolving, with emerging trends and technologies aimed at improving outcomes and reducing complications. Some of the future directions include:
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: The development of minimally invasive surgical techniques, such as endoscopic spine surgery, to reduce tissue trauma and promote faster recovery.
- Biologics and Biomaterials: The use of biologics and biomaterials, such as stem cells and nanotechnology, to enhance bone growth and promote spinal fusion.
- Robot-Assisted Surgery: The integration of robotic systems to improve precision, reduce complications, and enhance patient outcomes.
FAQ Section
What are the most common indications for cervical spine fusion?
+The most common indications for cervical spine fusion include degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, traumatic injuries, and tumors. These conditions can cause cervical spine instability, leading to chronic pain, numbness, and limited mobility.
What are the risks and complications associated with cervical spine fusion?
+The risks and complications associated with cervical spine fusion include infection, nerve damage, blood clots, and respiratory problems. Additionally, there is a risk of pseudoarthrosis (failure of the bone to fuse) or adjacent segment disease (degeneration of the adjacent vertebrae).
How long does it take to recover from cervical spine fusion surgery?
+The recovery period for cervical spine fusion surgery can vary depending on the individual and the extent of the procedure. Generally, it can take several weeks to several months to recover fully, with most people returning to normal activities within 3-6 months.
In conclusion, cervical spine fusion is a surgical procedure designed to stabilize the spine, alleviate pain, and restore neck mobility. While it carries some risks and complications, the benefits of cervical spine fusion can be significant, including improved mobility, pain relief, and enhanced quality of life. As the field continues to evolve, emerging trends and technologies aim to improve outcomes and reduce complications, offering new hope for individuals suffering from cervical spine instability.


