Chemical Burn On Skin
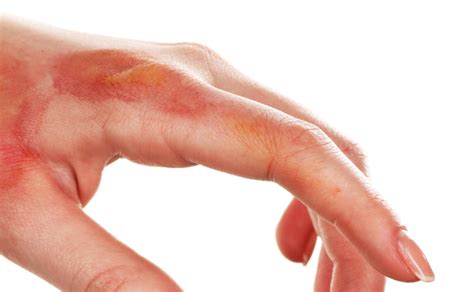
Chemical burns on the skin, also known as caustic burns, occur when the skin comes into contact with a corrosive substance, leading to tissue damage and potentially severe injuries. These types of burns can be caused by a wide range of substances, including strong acids, bases, and other chemicals commonly found in household products, industrial settings, and laboratories. The severity of a chemical burn can vary greatly depending on the type of chemical involved, the concentration of the substance, the duration of exposure, and the area of the body affected.
Understanding Chemical Burns
Chemical burns can be categorized based on the type of chemical involved. Acidic substances, such as sulfuric acid, nitric acid, and hydrochloric acid, can cause severe burns by coagulating proteins in the skin, leading to cell death. Basic substances, such as sodium hydroxide (lye) and calcium hydroxide, can also cause significant damage by liquefying tissues. Other chemicals, like phenol and white phosphorus, can penetrate deep into tissues, causing systemic toxicity and further complicating treatment.
Symptoms and Signs
The symptoms of a chemical burn can vary, but common signs include:
- Pain: The most immediate symptom, which can range from mild to severe.
- Redness and Irritation: The affected area may become red, swollen, and inflamed.
- Blistering: Blisters may form as the skin reacts to the chemical.
- Skin Discoloration: The skin may turn white or black, indicating tissue death.
- Breathing Difficulty: If the chemical is inhaled, it can cause respiratory distress.
Treatment and First Aid
The treatment of chemical burns involves several critical steps:
- Neutralization: If the chemical is an acid, a base can be used to neutralize it, and vice versa. However, water should be used cautiously as it can activate some chemicals.
- Flush with Water: Rinsing the affected area with plenty of cool or lukewarm water for at least 20 minutes to remove the chemical. Cold water should be avoided as it can cause hypothermia, while hot water can activate certain chemicals.
- Remove Contaminated Clothing: Any clothing that has come into contact with the chemical should be carefully removed to prevent further skin contact.
- Cover the Burn: After flushing, the burn should be covered with a sterile, non-stick dressing or cloth. Do not apply any ointments or creams.
- Seek Medical Attention: Even if the burn seems minor, it’s crucial to seek medical help. Chemical burns can lead to long-term damage and may require specialized care.
Prevention
Preventing chemical burns involves handling chemicals with caution and taking appropriate safety measures:
- Wear Protective Gear: Gloves, goggles, and protective clothing can prevent skin contact.
- Read Labels: Always read the labels of household and industrial chemicals to understand their potential hazards.
- Use in Well-Ventilated Areas: This can reduce the risk of inhaling chemical fumes.
- Keep Out of Reach: Store chemicals in a safe place, inaccessible to children and pets.
Complications and Long-Term Effects
Chemical burns can lead to several complications, including infection, scarring, and long-term skin damage. In severe cases, they can also lead to systemic poisoning if the chemical is absorbed into the bloodstream, affecting internal organs. Psychological trauma may also occur, especially if the burn results in significant disfigurement.
Conclusion
Chemical burns are serious injuries that require immediate attention. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing the appropriate first aid and treatment can significantly reduce the risk of long-term damage. Prevention, through safe handling and storage of chemicals, is also crucial. Given the potential severity of chemical burns, it’s essential for everyone to be aware of the risks associated with chemicals and to take proactive steps to avoid such injuries.
What are the immediate steps to take if someone suffers a chemical burn?
+The first step is to remove any contaminated clothing and jewelry, then flush the affected area with plenty of cool or lukewarm water for at least 20 minutes to neutralize the chemical. It's also crucial to seek medical attention immediately after the initial first aid.
Can all chemical burns be prevented?
+While not all chemical burns can be completely prevented, the risk can be significantly reduced by handling chemicals with caution, wearing protective gear, reading and following the instructions on chemical labels, and storing chemicals in a safe and secure manner.
How can one tell if a chemical burn is severe?
+A severe chemical burn may cause intense pain, significant blistering, charred or white skin, and difficulty breathing if the chemical was inhaled. Any burn that covers a large area of the body or is deep should be considered severe and requires immediate medical attention.
Chemical burns underscore the importance of safety and caution when dealing with any potentially hazardous substances. By understanding the risks and taking proactive measures, individuals can protect themselves and others from these potentially devastating injuries.