Pill I 10

The realm of pill development has undergone significant transformations over the years, driven by advancements in pharmaceutical technology, changing patient needs, and the quest for more effective and safer medications. One of the fascinating areas of innovation is in the creation of smart pills, which are designed to be more than just a vehicle for delivering drugs; they are sophisticated devices that can monitor health metrics, ensure adherence to medication regimens, and even provide real-time feedback to both patients and healthcare providers.
Introduction to Smart Pills
At the heart of the smart pill revolution is a convergence of pharmacology, nanotechnology, and information technology. These pills are equipped with miniature sensors, cameras, or other diagnostic tools that can perform a variety of functions once inside the body. For instance, some smart pills are designed to monitor the pH levels of the stomach and intestines, which can help in diagnosing gastrointestinal disorders. Others can capture images of the digestive tract, aiding in the early detection of diseases like cancer.
The journey of these pills from concept to reality involves overcoming several challenges, including ensuring they can withstand the harsh conditions of the digestive system, developing materials that are both biocompatible and capable of housing sophisticated electronics, and addressing privacy and ethical concerns related to the collection and transmission of personal health data.
Technical Breakdown: How Smart Pills Work
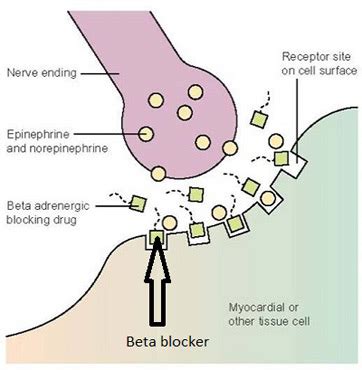
Sensors and Diagnostics: Smart pills contain tiny sensors that can measure various health indicators such as temperature, pH, and pressure. These sensors are crucial for diagnosing conditions within the body that are hard to detect through traditional methods.
Data Transmission: Once the sensors collect data, it is transmitted to an external device such as a smartphone or a computer via wireless communication technologies like Bluetooth or Wi-Fi. This allows for real-time monitoring and swift action in case of any anomalies.
Power Source: Given their small size, smart pills must be powered by a compact, long-lasting power source. Innovations in battery technology, such as bio-batteries that can harness energy from bodily fluids, are addressing this challenge.
Material and Design: The outer casing of smart pills must be made from materials that are not only safe for human consumption but also capable of protecting the internal electronics from the corrosive environment of the stomach and intestines.
Historical Evolution: From Concept to Reality
The concept of smart pills has been around for several decades, but significant advancements have been made in the 21st century. Early versions were often large, cumbersome, and limited in their capabilities. However, with advancements in miniaturization, nanotechnology, and software development, smart pills have become more sophisticated and practical for use in medical settings.
Expert Insight
According to Dr. Maria Rodriguez, a leading researcher in the field of pharmaceutical technology, “The future of medicine is closely tied to the development of smart pills. These devices have the potential not only to improve drug delivery systems but also to revolutionize how we diagnose and treat diseases. The challenge now is to ensure that these technologies are accessible to all who need them, regardless of their economic or geographical background.”
Comparative Analysis: Traditional Pills vs. Smart Pills
| Feature | Traditional Pills | Smart Pills |
|---|---|---|
| Drug Delivery | Limited to the release of the active ingredient | Can monitor and adjust drug release based on body conditions |
| Diagnosis | No diagnostic capability | Can diagnose conditions in real-time |
| Adherence | Relies on patient compliance | Ensures adherence through real-time monitoring |
| Feedback | No real-time feedback to patient or healthcare provider | Provides immediate feedback for personalized healthcare |

Future Trends Projection
As technology continues to advance, we can expect smart pills to become even more integrated into healthcare systems. Future developments may include pills that can adapt their drug release based on the patient’s genetic profile, lifestyle, and current health status. Additionally, there is potential for smart pills to be used not just for treatment but also for prevention, by monitoring health metrics and identifying potential health risks before they manifest as diseases.
Decision Framework for Adopting Smart Pill Technology
For healthcare providers and patients considering the adoption of smart pill technology, several factors should be considered: - Effectiveness: Does the smart pill offer significant improvements over traditional treatment methods? - Safety: Are there any known side effects or risks associated with the use of smart pills? - Cost: Is the technology affordable, and are there any long-term cost savings? - Privacy: How is personal health data collected, stored, and protected?
Myth vs. Reality: Addressing Concerns About Smart Pills
There are several myths and misconceptions about smart pills, ranging from concerns about privacy and data security to beliefs about their invasiveness and potential for abuse. In reality, smart pills are designed with safety and privacy in mind, using end-to-end encryption and secure data storage practices. They are also non-invasive, designed to be swallowed and then either pass harmlessly out of the body or dissolve, releasing their payload in a controlled manner.
Resource Guide: Further Reading and Exploration
For those interested in delving deeper into the world of smart pills and their applications, several resources are available: - Scientific Journals: Publications such as the Journal of Controlled Release and Nature Medicine often feature articles on the latest advancements in smart pill technology. - Healthcare Forums: Online forums where patients and healthcare providers share their experiences and insights can provide valuable perspectives on the practical applications of smart pills. - Pharmaceutical Industry Reports: These reports offer detailed analyses of market trends, upcoming technologies, and challenges facing the development and adoption of smart pills.
Conclusion
Smart pills represent a significant leap forward in the integration of technology and medicine, promising to make healthcare more personal, effective, and accessible. As this technology continues to evolve, it’s crucial to address the ethical, privacy, and accessibility concerns that arise, ensuring that these innovations benefit humanity as a whole. The future of smart pills holds tremendous potential, not just as tools for delivering medication, but as gateways to a new era of preventive, personalized, and precision healthcare.
What are smart pills, and how do they work?
+Smart pills are innovative, swallowable devices that combine drug delivery with diagnostic capabilities. They can monitor health metrics, ensure medication adherence, and provide real-time feedback to both patients and healthcare providers.
What are the potential benefits of using smart pills over traditional medication?
+The potential benefits include improved drug delivery, enhanced diagnostic capabilities, better adherence to medication regimens, and the provision of real-time feedback for personalized healthcare plans.
Are smart pills safe, and what about privacy concerns?
+Smart pills are designed to be safe and non-invasive. Concerns about privacy are addressed through the use of secure data storage and transmission practices, ensuring that personal health information is protected.
How do smart pills contribute to the future of healthcare?
+Smart pills are poised to revolutionize healthcare by enabling preventive, personalized, and precision medicine. They offer a potential solution for improving drug efficacy, reducing healthcare costs, and enhancing patient outcomes.
What are the challenges facing the widespread adoption of smart pill technology?
+Challenges include ensuring affordability and accessibility, addressing ethical and privacy concerns, and overcoming regulatory hurdles. Additionally, there is a need for further research and development to expand the capabilities and applications of smart pills.