Co2 Blood Levels: Manage Symptoms
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a naturally occurring gas in the human body, essential for various physiological processes. However, abnormal CO2 blood levels can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Managing these symptoms requires a comprehensive understanding of the underlying causes and implementing effective strategies to regulate CO2 levels.
Understanding CO2 Blood Levels
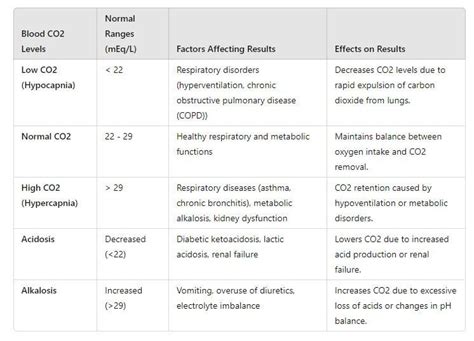
CO2 is a byproduct of cellular respiration, where the body’s cells convert glucose into energy. The lungs expel excess CO2 through exhalation, while the kidneys help regulate CO2 levels by adjusting the amount of bicarbonate in the blood. Normal CO2 blood levels typically range from 23 to 29 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). However, factors such as respiratory or metabolic disorders, certain medications, or environmental conditions can disrupt this balance, leading to abnormal CO2 levels.
Symptoms of Abnormal CO2 Blood Levels
Hypercapnia, or elevated CO2 blood levels, can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing
- Headaches or confusion
- Fatigue or weakness
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Numbness or tingling in the extremities
- Chest pain or tightness
On the other hand, hypocapnia, or low CO2 blood levels, can lead to symptoms such as:
- Rapid breathing or hyperventilation
- Lightheadedness or fainting
- Nausea or vomiting
- Muscle cramps or spasms
- Anxiety or panic attacks
Strategies for Managing CO2 Blood Levels
Managing symptoms of abnormal CO2 blood levels requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and respiratory therapies. Some effective strategies include:
- Breathing Exercises: Practicing deep, controlled breathing can help regulate CO2 levels and alleviate symptoms. Techniques such as diaphragmatic breathing, box breathing, or holotropic breathwork can be beneficial.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help improve respiratory function and increase CO2 tolerance. However, it’s essential to avoid overexertion, which can worsen symptoms.
- Dietary Changes: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help maintain healthy CO2 levels. Avoiding processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats can also be beneficial.
- Stress Management: Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or tai chi can help mitigate symptoms of abnormal CO2 blood levels.
- Medical Interventions: In some cases, medical treatment may be necessary to regulate CO2 levels. This can include oxygen therapy, respiratory medications, or surgical interventions.
Case Study: Managing CO2 Blood Levels in Chronic Respiratory Disease
A 65-year-old male patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) experienced frequent episodes of hypercapnia, leading to severe shortness of breath and fatigue. Through a combination of breathing exercises, pulmonary rehabilitation, and oxygen therapy, the patient was able to manage his CO2 blood levels and improve his overall quality of life.
| Intervention | Frequency | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Breathing Exercises | 3 times a day | 10-15 minutes |
| Pulmonary Rehabilitation | 2 times a week | 6 weeks |
| Oxygen Therapy | As needed | Ongoing |

Future Trends in CO2 Blood Level Management
Advances in medical technology and research are expected to revolutionize the management of CO2 blood levels. Some emerging trends include:
- Personalized Medicine: Tailoring treatment plans to individual genetic profiles and health status.
- Remote Monitoring: Using wearable devices and mobile apps to track CO2 levels and symptoms in real-time.
- Respiratory Therapies: Developing new treatments such as inhaled carbon dioxide therapy or respiratory muscle training.
What are the normal CO2 blood levels in a healthy individual?
+Normal CO2 blood levels typically range from 23 to 29 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L).
What are the symptoms of hypercapnia?
+Hypercapnia can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, headaches, fatigue, dizziness, and numbness or tingling in the extremities.
How can I manage my CO2 blood levels through lifestyle changes?
+Lifestyle changes such as practicing deep breathing exercises, engaging in regular physical activity, and eating a balanced diet can help manage CO2 blood levels.
In conclusion, managing CO2 blood levels requires a comprehensive approach that incorporates lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and respiratory therapies. By understanding the underlying causes of abnormal CO2 levels and implementing effective strategies, individuals can alleviate symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. As research and technology continue to evolve, we can expect to see new and innovative approaches to managing CO2 blood levels emerge.