Co2 Blood Test Low: Improve Your Results Now
Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in the blood are a critical indicator of respiratory and metabolic function. A low CO2 blood test result can signal various health issues, ranging from mild to severe. Understanding the implications of low CO2 levels and how to improve them is essential for maintaining overall well-being.
Introduction to CO2 in the Blood

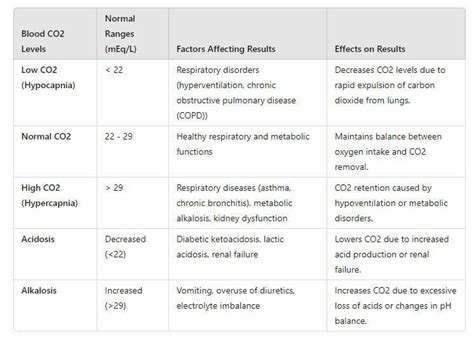
Carbon dioxide is a byproduct of cellular metabolism, where the body breaks down nutrients to produce energy. The lungs expel CO2 through exhalation, and the kidneys help regulate its levels in the blood by adjusting the amount of bicarbonate (a base) produced. The balance between CO2 and bicarbonate is crucial for maintaining the body’s acid-base equilibrium.
Causes of Low CO2 Blood Levels
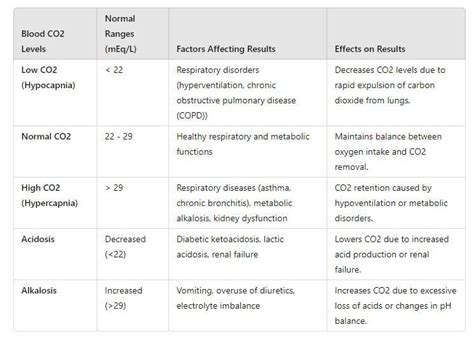
Several factors can lead to low CO2 levels in the blood, including:
- Respiratory Alkalosis: This condition occurs when the lungs remove too much CO2 from the bloodstream, often due to hyperventilation. Anxiety, panic attacks, and high-altitude environments can trigger hyperventilation.
- Metabolic Acidosis: Although this condition involves an excess of acid in the body, it can sometimes lead to decreased CO2 levels as the body tries to compensate for the imbalance.
- Diarrhea and Vomiting: Loss of bicarbonate through gastrointestinal secretions can reduce CO2 levels.
- Kidney Diseases: Certain kidney diseases can affect the body’s ability to regulate electrolytes and acid-base balance, potentially leading to low CO2 levels.
Symptoms of Low CO2 Levels
Individuals with low CO2 levels may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Dizziness and Lightheadedness: Reduced CO2 can lead to vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), potentially decreasing blood flow to the brain.
- Confusion and Disorientation: Severe cases can affect cognitive function.
- Numbness or Tingling: Especially in the extremities, due to altered nerve function.
- Rapid Breathing: The body may try to compensate for the imbalance by increasing respiratory rate.
Improving Low CO2 Blood Test Results
To address low CO2 levels, it’s crucial to identify and treat the underlying cause. Here are some steps and considerations:
Medical Evaluation
Consulting with a healthcare provider is the first step. They will perform a thorough medical evaluation, including a physical exam, medical history, and possibly additional blood tests to determine the cause of the low CO2 levels.
Treatment of Underlying Conditions
- Respiratory Issues: Addressing respiratory alkalosis may involve treating the underlying cause, such as anxiety, and practicing breathing exercises to normalize respiratory rate.
- Gastrointestinal Losses: Managing conditions like diarrhea and vomiting is crucial. This may involve medication to control symptoms and oral rehydration solutions to replace lost fluids and electrolytes.
- Kidney Diseases: Treatment depends on the specific disease but may include dietary changes, medications to control electrolyte imbalances, and in severe cases, dialysis.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Making certain lifestyle adjustments can help improve CO2 levels and overall health:
- Breathing Exercises: Practices like deep breathing can help normalize respiratory patterns and reduce hyperventilation.
- Dietary Changes: Consuming a balanced diet that includes foods rich in bicarbonate (such as fruits and vegetables) can help regulate acid-base balance.
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake is essential, especially in cases of gastrointestinal loss.
Monitoring Progress
- Regular Check-ups: Schedule follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor CO2 levels and assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
- Symptom Tracking: Keep a journal of symptoms to identify any changes or patterns.
- Adjusting Treatment: Be prepared to make adjustments to the treatment plan based on progress and any new developments.
Conclusion

Low CO2 blood test results indicate a potential health issue that requires prompt attention. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and taking proactive steps to improve CO2 levels, individuals can work towards restoring their body’s delicate acid-base balance. It’s essential to approach this condition with a comprehensive strategy that includes medical evaluation, treatment of underlying conditions, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing monitoring.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the normal range for CO2 levels in the blood?
+The normal range for CO2 levels in the blood, measured as bicarbonate (HCO3), is typically between 22 and 28 milliequivalents per liter (mEq/L). However, this range can slightly vary depending on the laboratory and the individual's health status.
Can low CO2 levels be life-threatening?
+In severe cases, yes, low CO2 levels can be life-threatening. They can lead to significant disturbances in the body's acid-base balance, affecting vital organs such as the brain and heart. Prompt medical attention is necessary if symptoms persist or worsen.
How long does it take to improve CO2 levels in the blood?
+The time it takes to improve CO2 levels can vary significantly depending on the underlying cause and the effectiveness of the treatment plan. Mild cases may resolve within days to weeks with appropriate treatment, while more severe or chronic conditions may require longer-term management and monitoring.
Addressing low CO2 blood test results requires a tailored approach that considers the individual’s overall health, the severity of the condition, and the root cause of the imbalance. With the right medical care, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing monitoring, it’s possible to improve CO2 levels and regain a healthy balance.


