Complete Blood Count
The complete blood count (CBC) is a fundamental diagnostic tool used in medicine to evaluate the overall health of an individual. It is a widely used test that provides valuable information about the different components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. In this comprehensive overview, we will delve into the intricacies of the CBC, exploring its various components, the process of conducting the test, and the significance of its results.
Introduction to Blood Components
Blood is a complex fluid that performs multiple vital functions in the body, including transporting oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to cells and removing waste products. It is composed of several key components, each with distinct roles:
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): These cells are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues. They contain the protein hemoglobin, which binds to oxygen, allowing it to be transported.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs): Also known as leukocytes, these cells are an essential part of the immune system, playing a crucial role in defending the body against infections and diseases.
- Platelets: These small, irregularly-shaped cells are vital for blood clotting, helping to prevent excessive bleeding when a blood vessel is injured.
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) Test
The CBC test is a straightforward procedure that involves drawing a sample of blood from a vein, typically in the arm. The blood sample is then sent to a laboratory for analysis, where various parameters are measured to provide a comprehensive picture of the blood’s composition.
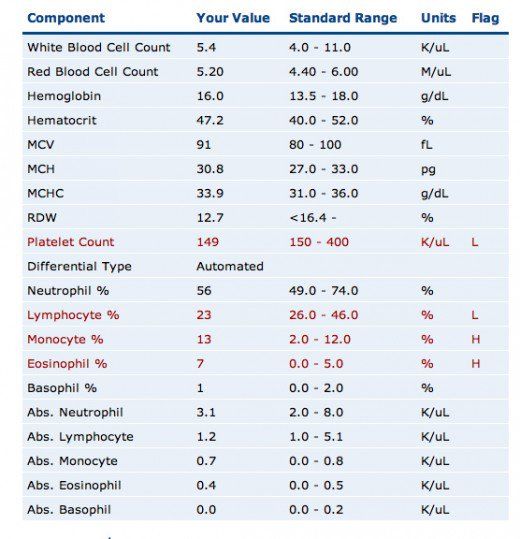
A typical CBC test evaluates several key parameters, including:
- Red Blood Cell Count: The total number of RBCs in the blood.
- Hemoglobin (Hb): The amount of hemoglobin in the blood, which is essential for oxygen transport.
- Hematocrit (Hct): The proportion of blood volume that is occupied by RBCs.
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV): The average size of RBCs, which can help diagnose conditions such as anemia.
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin (MCH): The average amount of hemoglobin in each RBC.
- Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration (MCHC): The average concentration of hemoglobin in each RBC.
- White Blood Cell Count: The total number of WBCs in the blood.
- Differential Count: The proportion of different types of WBCs, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, and basophils.
- Platelet Count: The total number of platelets in the blood.
Interpreting CBC Results
The results of a CBC test can provide valuable insights into an individual’s health, helping to diagnose a range of conditions, from anemia and infection to blood disorders and cancer. When interpreting CBC results, healthcare professionals consider several factors, including the individual’s medical history, symptoms, and physical examination findings.
Abnormal CBC results can indicate a variety of conditions, such as:
- Anemia: A decrease in RBC count, hemoglobin, or hematocrit.
- Infection: An increase in WBC count, particularly neutrophils.
- Bleeding Disorders: A decrease in platelet count or function.
- Blood Cancers: Abnormalities in WBC or RBC counts, such as leukocytosis (high WBC count) or thrombocytopenia (low platelet count).
Clinical Significance of CBC Results
The CBC test is an essential diagnostic tool in clinical practice, helping healthcare professionals to:
- Diagnose and Monitor Diseases: CBC results can aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of various conditions, including anemia, infection, and blood cancers.
- Evaluate Response to Treatment: Regular CBC tests can help assess the effectiveness of treatments, such as chemotherapy or antibiotics.
- Screen for Blood Disorders: CBC results can help identify individuals at risk of blood disorders, such as thrombocytopenia or leukopenia.
- Guide Transfusion Decisions: CBC results can inform decisions regarding blood transfusions, helping to ensure that patients receive the necessary blood components.
The CBC test is a powerful diagnostic tool that provides valuable information about an individual's blood composition. By interpreting CBC results in the context of medical history, symptoms, and physical examination findings, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management of various conditions.
Comparison of CBC with Other Diagnostic Tests
While the CBC test is a widely used and valuable diagnostic tool, it is often used in conjunction with other tests to provide a more comprehensive picture of an individual’s health. Some of these tests include:
- Blood Chemistry Tests: These tests evaluate various components of blood, such as electrolytes, enzymes, and hormones.
- Urinalysis: This test analyzes the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of urine to detect abnormalities.
- Imaging Studies: Techniques such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide valuable information about internal organs and structures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the complete blood count (CBC) test is a fundamental diagnostic tool that provides essential information about an individual’s blood composition. By understanding the various components of the CBC test and interpreting results in the context of medical history and physical examination findings, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about diagnosis, treatment, and management of various conditions. As a crucial component of clinical practice, the CBC test continues to play a vital role in promoting patient health and well-being.
What is the purpose of a complete blood count (CBC) test?
+The purpose of a CBC test is to evaluate the overall health of an individual by measuring various components of blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
What are the different components of a CBC test?
+A CBC test typically evaluates red blood cell count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, mean corpuscular volume (MCV), mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH), mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC), white blood cell count, differential count, and platelet count.
What do abnormal CBC results indicate?
+Abnormal CBC results can indicate a range of conditions, including anemia, infection, bleeding disorders, and blood cancers. Healthcare professionals consider various factors, including medical history, symptoms, and physical examination findings, when interpreting CBC results.