Covid Strain Now
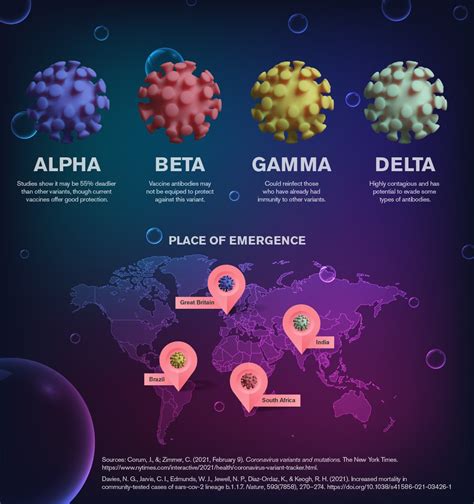
The COVID-19 pandemic has been a relentless global health crisis, with the SARS-CoV-2 virus continuously evolving and mutating. One of the most pressing concerns in the ongoing fight against COVID-19 is the emergence of new strains, which can potentially evade immunity, increase transmissibility, or enhance severity. As the world continues to navigate this pandemic, understanding the latest COVID strain is crucial for developing effective public health strategies, updating vaccines, and optimizing treatment protocols.
Origin and Spread of New Strains
New strains of a virus emerge due to mutations in the viral genome. These mutations can occur randomly during the replication process of the virus within a host. The COVID-19 virus, like other RNA viruses, has a high mutation rate, which facilitates the generation of new strains. Some of these mutations may confer advantages to the virus, such as increased transmissibility or the ability to partially evade the immune system, leading to their proliferation.
The spread of new COVID strains is influenced by various factors including human behavior, travel, and public health measures. In areas with high rates of vaccination, the spread of the virus and the emergence of new strains can be significantly reduced. However, in regions with lower vaccination rates, the virus has more opportunities to spread and mutate.
Impact of New Strains on Public Health
The emergence of new COVID strains pose several challenges to public health. Firstly, there’s the concern that new strains may reduce the effectiveness of existing vaccines. Although the current vaccines have shown a remarkable ability to protect against severe disease and death from COVID-19, there is always a possibility that future mutations could necessitate updates to vaccine formulations.
Secondly, new strains can impact the severity and presentation of the disease. Some strains may cause milder symptoms, while others could lead to more severe outcomes, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly and those with underlying health conditions.
Lastly, the detection and tracking of new strains require continuous genomic surveillance. This involves sequencing the viral genome from patient samples to identify new mutations and understand their potential impact. Advanced technologies and international collaboration have been instrumental in monitoring the evolution of the virus and providing critical information for public health responses.
Current Response and Future Directions
The response to new COVID strains involves a multifaceted approach. Vaccination remains a cornerstone of COVID-19 prevention, with ongoing efforts to update vaccines to match circulating strains. Booster shots, which can enhance immunity and broaden protection against different strains, are being recommended for various segments of the population based on factors such as age, health status, and occupational risk.
Besides vaccination, non-pharmacological interventions (NPIs) such as mask-wearing, physical distancing, and improved ventilation continue to play a vital role in reducing the spread of the virus. The development of effective antiviral treatments and monoclonal antibody therapies also offers hope for managing COVID-19 cases and preventing severe disease.
Looking ahead, the global community must remain vigilant and adaptive. This includes investing in surveillance and sequencing capabilities, supporting vaccine development and distribution, and promoting behaviors that reduce the risk of transmission. International cooperation and data sharing are essential for staying ahead of the virus and mitigating the impact of future strains.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of preparedness, innovation, and global solidarity in the face of emerging health threats. As new strains of the virus continue to emerge, our responses must be guided by the latest scientific evidence, a commitment to equity, and a recognition of the interconnectedness of our world. By working together and leveraging advances in technology and public health, we can navigate the challenges posed by COVID-19 and build a more resilient future for all.
How often do new COVID strains emerge?
+New COVID strains can emerge frequently due to the high mutation rate of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The exact timing and characteristics of new strains are unpredictable and depend on various factors, including the rate of transmission, the extent of viral replication, and the immune pressure exerted by vaccination and previous infections.
Can current vaccines protect against new COVID strains?
+Current vaccines have been highly effective in protecting against severe disease and death from COVID-19, including from many of the new strains. However, the level of protection can vary depending on the specific strain and the individual’s immune response. Booster shots and updated vaccine formulations are being developed to ensure ongoing protection against evolving strains.
What can individuals do to protect themselves from new COVID strains?
+Individuals can protect themselves by getting vaccinated, including receiving booster shots as recommended, practicing good hygiene such as frequent hand washing, wearing masks in crowded areas or during travel, maintaining physical distancing, and staying informed about local health guidelines and the prevalence of COVID-19 in their community.