Diabetes Blood Sugar Control: Know Your Levels
Understanding blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes. It’s a complex condition that requires careful management to prevent complications. The body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, also known as glucose, is essential for maintaining energy and overall health. In people with diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin, a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, or it can’t effectively use the insulin it produces.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Control
Effective blood sugar control is vital for preventing long-term complications associated with diabetes. High blood sugar levels over an extended period can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to heart disease, kidney damage, and vision problems. On the other hand, low blood sugar levels can cause immediate health issues, including confusion, shakiness, and even loss of consciousness. Therefore, it’s essential to understand how to manage and maintain blood sugar levels within a target range.
Blood Sugar Level Ranges
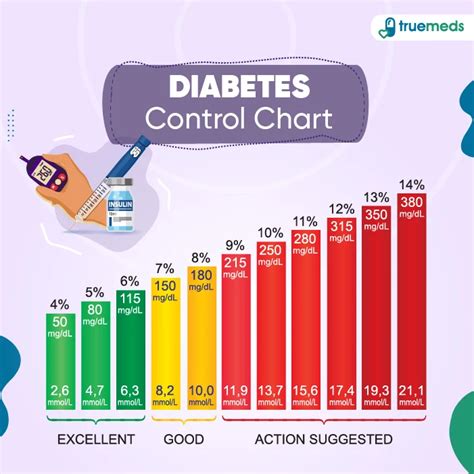
For individuals with diabetes, understanding blood sugar level ranges is critical. The American Diabetes Association recommends the following blood sugar level targets: - Before meals: 80 to 130 mg/dL - After meals: Less than 180 mg/dL
These targets can vary slightly depending on the individual, their age, and other health factors. It’s essential for each person with diabetes to work with their healthcare provider to determine their specific blood sugar goals.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is a fundamental aspect of diabetes management. This can be done using a glucometer, a small device that measures the glucose level in a drop of blood. Additionally, some individuals use continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), which provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night. Monitoring blood sugar levels helps in understanding how different factors such as diet, exercise, and medications affect glucose levels.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including: - Diet: The types and amounts of food consumed can significantly impact blood sugar levels. Foods high in carbohydrates have the most substantial effect. - Exercise: Physical activity can lower blood sugar levels by improving the body’s use of insulin. - Medications: Various diabetes medications can help manage blood sugar levels, including metformin, sulfonylureas, and insulin. - Stress and Illness: Stress and illness can raise blood sugar levels due to the production of stress hormones like cortisol.
Strategies for Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining tight blood sugar control requires a multifaceted approach that includes: - Healthy Eating: Following a balanced diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium. - Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. - Medication Adherence: Taking diabetes medications as prescribed by your healthcare provider. - Regular Monitoring: Checking blood sugar levels frequently to understand how different factors affect them. - Stress Management: Practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
Overcoming Challenges in Blood Sugar Control
Despite the best efforts, challenges in managing blood sugar levels can arise. These challenges might include difficulty in adhering to a diet plan, struggling to maintain a regular exercise routine, or experiencing stress and emotional issues. Overcoming these challenges often requires support from healthcare providers, diabetes educators, family, and friends. Joining a diabetes support group can also provide valuable insights and strategies from others who are managing the condition.
Future Directions in Diabetes Management
Advances in technology and medical research are continually improving diabetes management. The development of smart insulin pens, automated insulin dosing systems, and more sophisticated CGMs are making it easier for individuals with diabetes to manage their condition effectively. Furthermore, research into new medications and therapeutic approaches, such as immunotherapy and stem cell therapy, holds promise for improving blood sugar control and potentially reversing diabetes in some cases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, can cause symptoms such as increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and cuts or wounds that are slow to heal. If left untreated, it can lead to more serious complications.
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the type of diabetes and the treatment plan. Generally, individuals with type 1 diabetes and those with type 2 diabetes who use insulin may need to check their levels more frequently than those who do not use insulin.
Can I still eat sweets if I have diabetes?
+While it's generally recommended to limit sweets and foods high in added sugars, it's not necessary to completely eliminate them from your diet. The key is moderation and balancing the carbohydrate intake from sweets with the rest of your diet and exercise.
How does exercise impact blood sugar levels?
+Exercise can lower blood sugar levels by increasing the body's use of glucose for energy and improving insulin sensitivity. It's essential to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to avoid hypoglycemia and to understand how different types of physical activity affect glucose levels.
Conclusion
Managing diabetes and controlling blood sugar levels is a journey that requires dedication, support, and the right strategies. By understanding the factors that influence blood sugar, incorporating healthy lifestyle habits, and utilizing the latest in diabetes technology and research, individuals with diabetes can lead active, healthy lives. The key to successful blood sugar control lies in a balanced approach that combines medical treatment, diet, exercise, and stress management, all tailored to the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. With the right mindset and support, managing diabetes can become more manageable, allowing individuals to thrive despite the challenges the condition presents.