Signs Of Strep Throat
Strep throat, also known as streptococcal pharyngitis, is a bacterial infection caused by Group A Streptococcus (GAS). It’s a common and highly contagious illness that can affect people of all ages, but it’s most prevalent among children and adolescents. Recognizing the signs of strep throat is crucial for prompt diagnosis and treatment to prevent potential complications. In this article, we’ll delve into the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of strep throat, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this condition.
Symptoms of Strep Throat
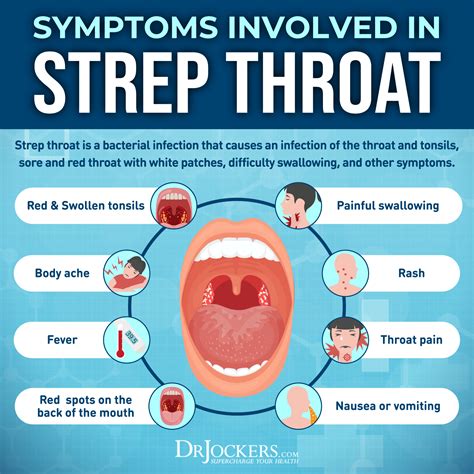
The symptoms of strep throat can vary from person to person, but common signs include: - Sudden and severe sore throat - Painful swallowing - Fever, usually above 101°F (38.3°C) - White or yellow patches on the tonsils - Swollen, tender lymph nodes in the neck - Headache - Stomachache - Rash (in some cases, particularly in children) - Loss of appetite - General feeling of being unwell
It’s essential to note that not all sore throats are caused by strep bacteria. Viruses are responsible for the majority of sore throats, but strep throat infections require antibiotic treatment to prevent complications.
Causes and Risk Factors
Strep throat is caused by Group A Streptococcus bacteria. It spreads through: - Direct contact with mucus or saliva from an infected person - Indirect contact, such as sharing utensils, drinks, or personal items - Airborne transmission when an infected person coughs or sneezes
Risk factors for developing strep throat include: - Age: Children between 5 and 15 years old are at the highest risk - Time of year: Strep throat is more common during the winter and early spring - Exposure: Being in close proximity to someone with strep throat - Poor hygiene: Not practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing
Diagnosis of Strep Throat
Diagnosing strep throat involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers may perform: - A rapid strep test (RST): A quick test that can detect strep antigens within minutes - A throat culture: A more accurate test that involves sending a sample to a lab for analysis
Treatment for Strep Throat
The primary treatment for strep throat is antibiotics, which help reduce the risk of complications and the duration of the illness. Commonly prescribed antibiotics include: - Penicillin - Amoxicillin - Azithromycin (for those allergic to penicillin)
It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before finishing the medication. Additionally, over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help manage pain and fever.
Complications of Untreated Strep Throat
If left untreated, strep throat can lead to several complications, including: - Acute rheumatic fever (ARF): A rare but serious disease that can cause heart damage - Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis (PSGN): A kidney disease - Abscesses around the tonsils or in the neck - Sinusitis or ear infections
Prevention of Strep Throat
While it’s not possible to completely eliminate the risk of getting strep throat, several measures can help reduce the chance of infection: - Practice good hygiene: Wash hands frequently, especially after coughing or sneezing - Avoid close contact with someone who has strep throat - Do not share utensils, drinks, or personal items - Stay home from work or school when sick to prevent spreading the infection - Cover the mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
What are the first signs of strep throat?
+The first signs of strep throat often include a sudden and severe sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and a fever. These symptoms can develop quickly, sometimes within a few hours.
How long does it take for strep throat symptoms to appear after exposure?
+The incubation period of strep throat, which is the time between exposure to the bacteria and the onset of symptoms, typically ranges from 2 to 5 days.
Can strep throat be treated without antibiotics?
+No, strep throat is a bacterial infection that requires antibiotic treatment to prevent complications and reduce the risk of transmission to others. While supportive care, such as rest and hydration, can help manage symptoms, antibiotics are necessary for a full recovery.
How can I prevent spreading strep throat to others?
+To prevent spreading strep throat, practice good hygiene by washing your hands frequently, avoid close contact with others, do not share personal items, and stay home from work or school until you have been on antibiotics for at least 24 hours and your symptoms have improved.
Can strep throat recur?
+Yes, it is possible for strep throat to recur, especially if the initial infection was not fully treated or if there is ongoing exposure to the bacteria. Recurring strep throat can indicate a carrier state, where the bacteria are present in the throat without causing symptoms but can still be transmitted to others.
Strep throat is a serious infection that requires medical attention to prevent potential complications. By understanding the signs, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage the condition and reduce the risk of transmission. If you suspect you or a family member has strep throat, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, prompt and appropriate treatment is key to recovering from strep throat and preventing long-term health issues.