Diabetic Sugar Levels Explained
Understanding diabetic sugar levels is crucial for individuals living with diabetes, as well as for those who are at risk of developing the condition. Diabetes, a chronic health condition, affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose), which is a vital source of energy for the body’s cells. The key to managing diabetes lies in maintaining blood sugar levels within a target range to prevent complications.
What are Normal Blood Sugar Levels?
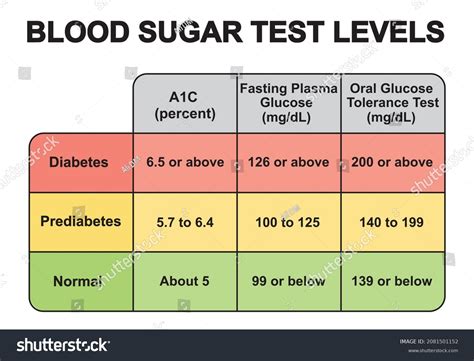
For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 to 99 mg/dL when fasting (not having eaten for at least 8 hours) and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. These levels can vary slightly depending on the laboratory or testing method but generally fall within these ranges.
Blood Sugar Levels in Diabetes
In diabetes, the body either doesn’t make enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or can’t effectively use the insulin it produces (Type 2 diabetes), leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar can lead to heart disease, nerve damage, kidney disease, and other serious health problems.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. People with Type 1 diabetes must take insulin daily to control their blood sugar levels. The target blood sugar ranges for individuals with Type 1 diabetes can vary, especially in children, but generally aim for levels between 70 to 180 mg/dL.
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, the most common form of diabetes, results from a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, including obesity, physical inactivity, and an unhealthy diet. Initially, the pancreas may produce extra insulin to compensate for its decreased effectiveness, but over time, it may not be able to keep up with the body’s demand, leading to high blood sugar levels. Treatment includes lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin therapy. The target blood sugar levels for those with Type 2 diabetes also aim to keep fasting levels below 130 mg/dL and post-meal levels below 180 mg/dL, though these targets can be adjusted based on individual factors.
Monitoring Blood Sugar
Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is essential for managing diabetes. This can be done through:
- Fingerstick Tests: Using a glucometer to check blood sugar levels at different times of the day.
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): Small devices that track blood sugar levels throughout the day and night.
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) Tests: Regular blood tests that measure average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
Managing High Blood Sugar Levels
High blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) can lead to serious complications if left untreated. Symptoms may include increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, and fatigue. Managing high blood sugar involves:
- Medications: Insulin and/or oral medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Lifestyle Changes: Eating a healthy diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep.
- Stress Management: Stress can raise blood sugar levels; practices like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help.
Managing Low Blood Sugar Levels
Low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) are equally dangerous and can occur suddenly. Symptoms include shakiness, sweating, hunger, dizziness, and confusion. Immediate treatment involves consuming fast-acting carbohydrates like glucose tablets or fruit juice, followed by a snack with protein to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing diabetic sugar levels is crucial for the health and well-being of individuals with diabetes. By maintaining target blood sugar ranges through a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, individuals can reduce their risk of complications and lead active, healthy lives. It’s essential for everyone, regardless of their diabetes status, to understand the importance of healthy blood sugar levels and the steps they can take to prevent or manage this condition.
What are the normal blood sugar levels for someone without diabetes?
+For individuals without diabetes, normal blood sugar levels are typically between 70 to 99 mg/dL when fasting and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
How do I manage high blood sugar levels?
+Managing high blood sugar involves taking medications as prescribed, making lifestyle changes such as eating a healthy diet, staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and getting enough sleep, and managing stress through practices like yoga or meditation.
What are the symptoms of low blood sugar, and how is it treated?
+Symptoms of low blood sugar include shakiness, sweating, hunger, dizziness, and confusion. Immediate treatment involves consuming fast-acting carbohydrates like glucose tablets or fruit juice, followed by a snack with protein to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Understanding diabetic sugar levels and taking proactive steps towards their management is not only a matter of personal health but also a critical component of preventing long-term complications and improving the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.