What Is 50 Mcg To Iu? Easy Conversion Guide
Understanding the conversion between micrograms (mcg) and International Units (IU) is crucial in various fields, including nutrition, pharmacology, and biochemistry. The conversion factor between these two units can vary significantly depending on the substance being measured. Here, we’ll delve into the conversion process, using the example of converting 50 micrograms to International Units, and explore how this conversion applies to different substances, focusing on vitamin D as a primary example.
Introduction to Micrograms and International Units
Micrograms (mcg): This is a unit of mass in the metric system, equivalent to one-millionth of a gram. It’s commonly used to measure the amount of substances in pharmaceuticals, nutrition, and chemistry.
International Units (IU): The IU is a unit of measurement for the potency of certain vitamins, hormones, and other biological substances. It was originally defined by the League of Nations and has been adopted by various health organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO).
Conversion Basics
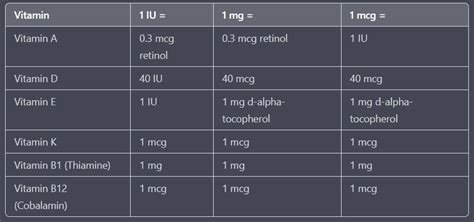
The conversion from micrograms to IU depends on the specific substance being measured. Each substance has its unique conversion factor, which is determined based on its biological activity. For instance, the conversion factor for vitamin D is as follows:
1 microgram of vitamin D = 40 IU
This means that for vitamin D, you multiply the number of micrograms by 40 to get the number of IU.
Converting 50 Mcg to IU for Vitamin D
Using the conversion factor for vitamin D:
50 mcg * 40 IU/mcg = 2000 IU
Therefore, 50 micrograms of vitamin D is equivalent to 2000 IU.
Other Substances
It’s essential to understand that the conversion factor can vary greatly between different substances. For example, for vitamin E, the conversion is:
1 mg (milligram, or 1000 mcg) of dl-alpha-tocopherol (a form of vitamin E) = 22.4 IU
Or, for vitamin A:
1 microgram of retinol (a form of vitamin A) = 3.3 IU
This illustrates how critical it is to know the specific conversion factor for the substance you are working with.
Practical Applications and Considerations
Dietary Supplements: When purchasing dietary supplements, understanding the IU to mcg conversion can help ensure you’re getting the correct dosage, especially if recommendations are given in one unit but the product label lists the other.
Medical Prescriptions: In medical contexts, especially for substances like insulin or heparin, precise conversion between units is critical for effective treatment and to avoid overdose or underdose.
Scientific Research: In research, accurate conversions are essential for interpreting data, comparing results, and drawing meaningful conclusions.
Conclusion
Converting between micrograms and International Units requires knowing the specific conversion factor for the substance of interest. Using vitamin D as an example, we’ve seen how 50 micrograms can be converted to IU. It’s a straightforward process once you have the conversion factor, but the complexity and variety of these factors across different substances necessitate attention to detail and precise knowledge of the conversion rates to ensure accuracy in various applications.