Difference Between Hmo And Ppo

When navigating the complex world of health insurance, two terms that often come up are HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) and PPO (Preferred Provider Organization). Both HMOs and PPOs are types of health insurance plans, but they have distinct differences in terms of their structure, benefits, and costs. Understanding these differences is crucial for individuals and families to make informed decisions about their healthcare coverage.
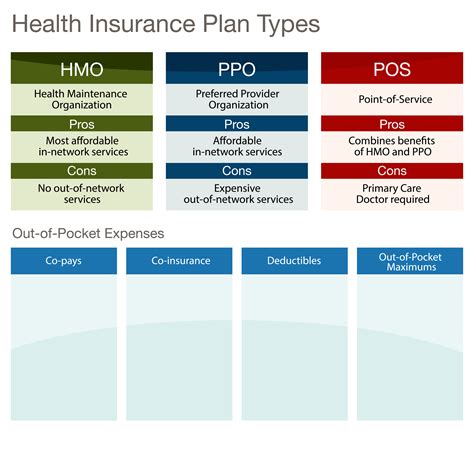
HMO (Health Maintenance Organization)
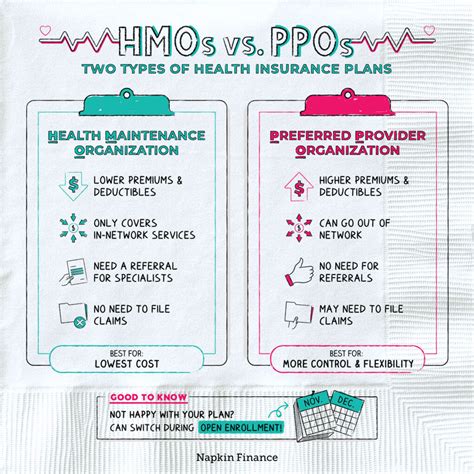
An HMO is a type of health insurance plan that provides healthcare services for a fixed annual fee. It operates on a network basis, where the insured individual must receive medical care and services from providers within the HMO’s network, except in emergency situations. One of the primary goals of an HMO is to provide preventive care to its members, aiming to reduce the need for more costly medical interventions later on.
Key Characteristics of HMOs:
- Network Restrictions: HMOs have a specific network of healthcare providers. Patients must choose a primary care physician from within this network and, in many cases, need a referral from this primary care physician to see a specialist.
- Preventive Care Focus: HMOs emphasize preventive care, offering various screenings and check-ups to help prevent illnesses.
- Lower Out-of-Pocket Costs: Generally, HMOs have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs compared to other types of insurance plans, as long as care is received from within the network.
- Limited Out-of-Network Coverage: HMOs typically do not cover services received outside of their network, except in emergency situations.
PPO (Preferred Provider Organization)
A PPO is another type of health insurance plan that offers a network of healthcare providers from which the insured can choose. Unlike HMOs, PPOs provide more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers, both within and outside of the network, though at different costs.
Key Characteristics of PPOs:
- Flexible Network: While PPOs have a network of preferred providers, patients are not limited to this network for their care. They can choose to see any healthcare provider, both in-network and out-of-network, though out-of-network care usually comes at a higher cost.
- No Primary Care Physician Requirement: In PPO plans, patients do not need to select a primary care physician, and they can see specialists without referrals.
- Higher Out-of-Pocket Costs: PPOs often have higher premiums compared to HMOs, and out-of-pocket costs can be higher, especially for out-of-network care.
- Balance Billing: For out-of-network care, patients may be subject to balance billing, where the healthcare provider charges the patient for the difference between the billed amount and the amount the insurance plan pays.
Comparison Summary
| Feature | HMO | PPO |
|---|---|---|
| Network | Restricted to in-network providers (except emergencies) | Flexible, can choose in-network or out-of-network providers |
| Primary Care Physician | Often required to choose a primary care physician | No requirement to choose a primary care physician |
| Out-of-Pocket Costs | Generally lower for in-network care | Can be higher, especially for out-of-network care |
| Referrals | Often needed for specialist visits | Not required for specialist visits |
| Preventive Care | Strong emphasis on preventive care | May offer preventive care, but not always the focus |
Choosing Between HMO and PPO
When deciding between an HMO and a PPO, consider the following factors: - Cost: If budget is a concern, HMOs might offer lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs. - Flexibility: If the ability to choose any healthcare provider without needing a referral is important, a PPO might be the better choice. - Healthcare Needs: Individuals or families with ongoing healthcare needs might find the preventive focus and lower costs of an HMO beneficial, while those who prefer flexibility in choosing healthcare providers might prefer a PPO. - Provider Network: Check if your preferred healthcare providers are included in the plan’s network before making a decision.
Ultimately, the choice between an HMO and a PPO depends on individual preferences regarding healthcare flexibility, costs, and the importance of having a wide range of provider choices. It’s essential to carefully evaluate the specifics of each plan, including network, costs, and services covered, to make an informed decision that meets one’s healthcare needs and budget.