Flu And Covid Test
The advent of the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly altered the landscape of respiratory illness diagnosis and management. Among the key challenges has been differentiating between COVID-19 and other common respiratory infections, such as influenza (the flu), due to overlapping symptoms. This complexity necessitates the development and deployment of accurate diagnostic tests to guide clinical decision-making and public health interventions. In this context, the role of flu and COVID-19 tests cannot be overstated, as they provide critical information needed to manage individual cases and control the spread of these diseases within communities.
Understanding the Symptoms
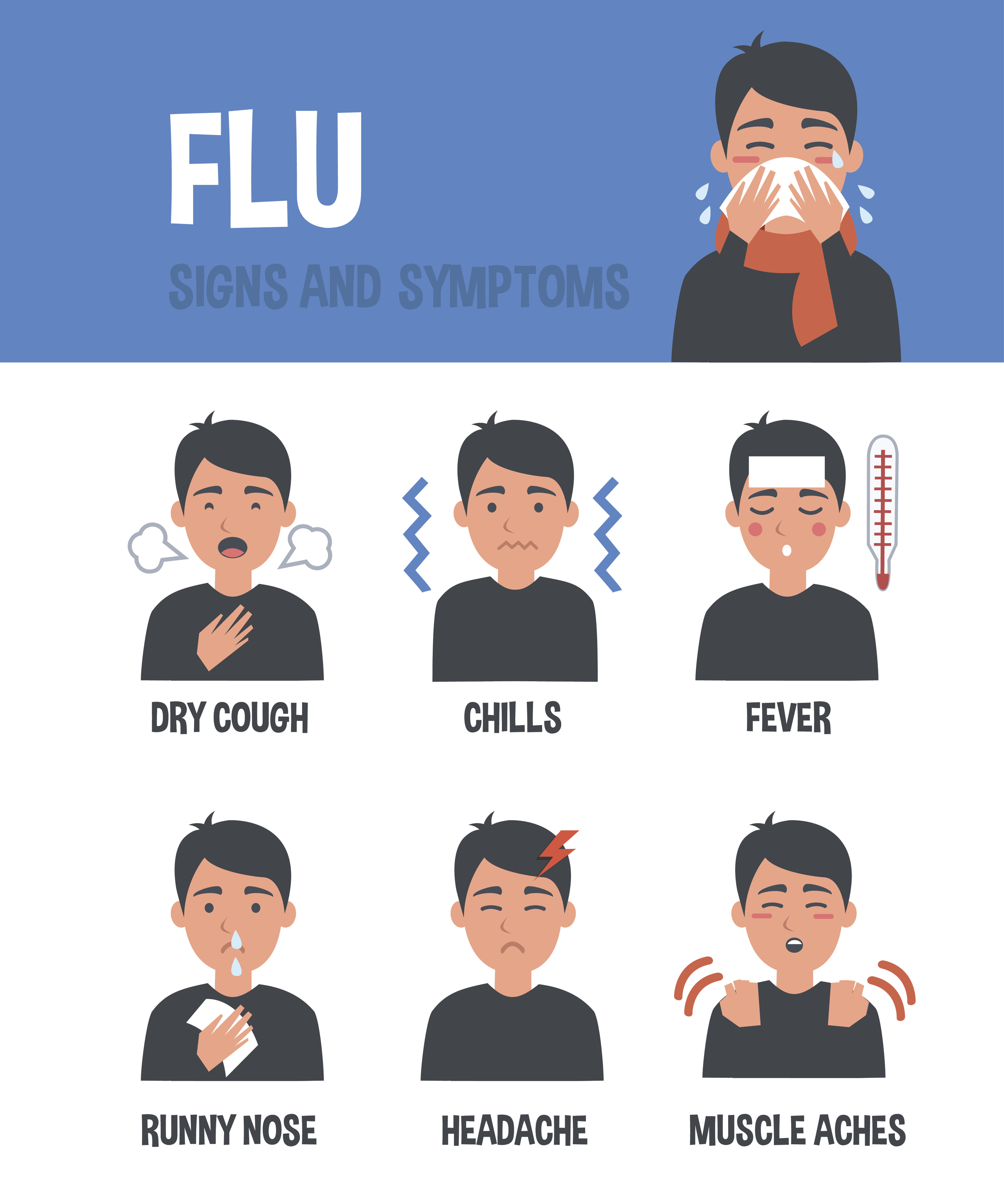
Both influenza and COVID-19 can present with similar symptoms, including fever, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, and sore throat. However, COVID-19 is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus and has a broader range of symptoms and potential complications, including loss of taste or smell, and in severe cases, pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome. The similarity in symptoms underscores the need for specific diagnostic testing to distinguish between these two conditions.
Diagnostic Testing for Flu and COVID-19
Several types of tests are available for diagnosing influenza and COVID-19, each with its own set of advantages and limitations.
Molecular Tests (RT-PCR): These are considered the gold standard for diagnosing both flu and COVID-19. RT-PCR (Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction) tests detect the genetic material of the viruses, providing highly sensitive and specific results. They can take several hours to produce results and require specialized equipment.
Rapid Antigen Tests: These tests detect proteins on the surface of the viruses. They are quicker and more convenient than RT-PCR but may be less sensitive, potentially leading to false-negative results.
Serology Tests: These tests look for antibodies in the blood, indicating past infection. While useful for epidemiological studies and understanding immune responses, they are not as helpful for diagnosing current infections.
Point-of-Care Tests: Designed for use at the point of care, these tests can provide quick results and are crucial in settings where rapid diagnosis is necessary for immediate patient management decisions.
Combined Testing for Flu and COVID-19
Given the overlapping symptomatology of influenza and COVID-19, combined testing has emerged as a practical approach. This involves using a single test or platform that can detect both influenza viruses (A and B) and SARS-CoV-2. Such multiplex assays simplify the diagnostic process, reduce the need for multiple tests, and can provide quicker turnaround times for results. This efficiency is particularly valuable during peak respiratory virus seasons when healthcare resources may be stretched thin.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the advancements in diagnostic testing, several challenges persist. These include access to testing, particularly in resource-limited settings, the potential for false-negative results, especially with rapid antigen tests, and the ongoing evolution of SARS-CoV-2, which can affect test sensitivity. The development of more efficient, accessible, and reliable testing technologies remains an urgent priority.
Moreover, the integration of diagnostic testing with other public health strategies, such as vaccination programs, contact tracing, and non-pharmaceutical interventions, is crucial for effectively controlling the spread of both influenza and COVID-19. As the global community continues to navigate the complexities of the COVID-19 pandemic and prepares for future influenza seasons, the importance of robust, adaptable, and Accessible diagnostic testing cannot be overstated.
Practical Application Guide: When to Get Tested
- If You’re Experiencing Symptoms: Seek testing if you have symptoms of COVID-19 or the flu, especially if you’re at higher risk for severe disease.
- After Exposure: Consider testing if you’ve been in close contact with someone who has COVID-19 or the flu, even if you don’t have symptoms.
- Before Procedures: Some medical procedures may require COVID-19 testing beforehand to ensure safety.
- For Travel: Check the latest travel advisories, as some destinations may require proof of a negative COVID-19 test.
What is the difference between flu and COVID-19 tests?
+Flu tests typically detect influenza A and B viruses, while COVID-19 tests detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Combined tests can detect both.
How long do COVID-19 test results take?
+Results can take anywhere from 15 minutes to several hours or even days, depending on the type of test and where it's processed.
Can I get a false-negative result from a COVID-19 test?
+Yes, false-negative results can occur, especially with rapid antigen tests. This is why repeat testing may be recommended in some cases.
How often should I get tested for COVID-19?
+The frequency of testing depends on your exposure risk, symptoms, and local health guidelines. It's best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Can I use at-home COVID-19 tests?
+Yes, at-home tests are available and can provide quick results. However, their accuracy may vary, and a healthcare provider may still recommend a laboratory test for confirmation.
In conclusion, the ability to accurately diagnose and differentiate between influenza and COVID-19 is crucial for managing these illnesses and controlling their spread. As diagnostic technologies continue to evolve, it’s essential for healthcare professionals and the public to stay informed about the latest testing options, their uses, and their limitations. By leveraging these tools effectively, we can work towards mitigating the impact of these significant public health challenges.