Flu Symptoms 2024
As the world continues to navigate the complexities of various viruses and their impacts on public health, understanding the symptoms of flu, also known as influenza, remains crucial. The flu is a contagious respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses that can cause mild to severe illness. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of flu symptoms, particularly focusing on the 2024 flu season, and offer insights into prevention, diagnosis, and treatment.
Introduction to Influenza
Influenza viruses are constantly evolving, which is why each flu season can bring different strains and varying levels of severity. The symptoms of flu can sometimes be confused with those of the common cold, but they are generally more severe. Understanding these symptoms is the first step in managing and treating the flu effectively.
Common Symptoms of Flu
The symptoms of flu can vary from person to person, but common signs include:
- Fever: This is often one of the first symptoms, although not everyone with flu will have a fever.
- Cough: This can range from a mild, dry cough to a more severe, productive cough that brings up mucus.
- Sore Throat: Inflammation of the throat due to the virus.
- Runny or Stuffy Nose: Similar to the common cold, but in the context of flu, these symptoms can be more pronounced.
- Headache: Often described as a severe headache, which can be debilitating.
- Fatigue: Extreme tiredness that can interfere with daily activities.
- Muscle or Body Aches: Pain and stiffness in the back, arms, and legs.
- Diarrhea and Vomiting: More common in children than adults, but these symptoms can occur.
- Chest Discomfort: Coughing can sometimes lead to discomfort in the chest area.
Differences Between Flu and Common Cold
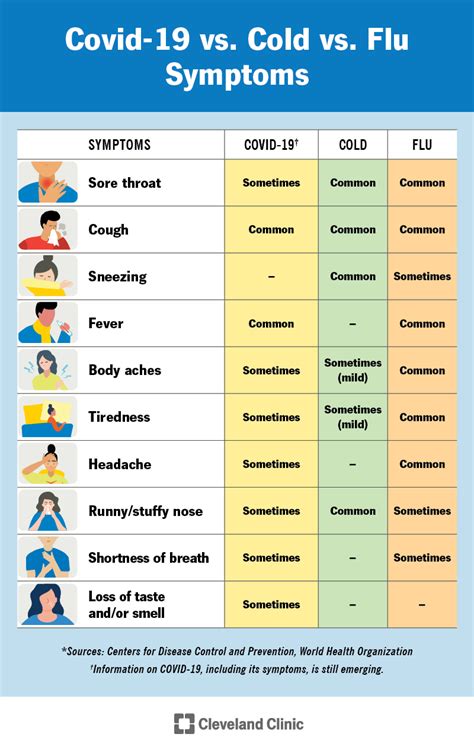
It’s essential to differentiate between flu and the common cold. While both share some symptoms, such as cough and runny or stuffy nose, flu symptoms are typically more severe and come on suddenly. People with colds are more likely to have a runny or stuffy nose, and their symptoms tend to develop gradually.
High-Risk Groups
Certain groups of people are at a higher risk for complications from flu. These include:
- Older Adults: People 65 years and older.
- Young Children: Especially those under 5 years, and particularly those under 2 years.
- Pregnant Women: Influenza can cause severe illness in pregnant women and their developing babies.
- People with Certain Chronic Health Conditions: Conditions like heart disease, lung disease, and diabetes can increase the risk of flu complications.
Prevention and Vaccination
Prevention is key when it comes to managing the flu. The most effective way to prevent flu is by getting vaccinated each year. The flu vaccine is updated annually to protect against the influenza viruses that research suggests will be most common during the upcoming season. Good health habits can also help prevent the spread of flu, including:
- Frequent Handwashing: With soap and water for at least 20 seconds.
- Avoiding Close Contact: With people who are sick.
- Avoiding Touching Your Eyes, Nose, and Mouth: As these are common ways for the virus to enter the body.
- Staying Home When Sick: To prevent spreading the flu to others.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing flu involves a physical exam, a review of symptoms, and sometimes additional tests such as a throat swab or a rapid influenza diagnostic test. For most people, the flu will resolve on its own with rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to manage symptoms. However, in some cases, especially for those at high risk for complications, antiviral drugs may be prescribed. These drugs can help make the illness milder and shorten the time you are sick.
Future Outlook and Ongoing Research
The landscape of influenza is constantly evolving, driven by the virus’s ability to mutate and the global connectivity that facilitates its spread. Ongoing research focuses on developing more effective vaccines, including universal flu vaccines that could protect against multiple strains without needing annual updates. Additionally, the development of new antiviral drugs is a critical area of research to help manage and treat flu infections effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and managing flu symptoms is a critical aspect of maintaining public health. By recognizing the common symptoms, understanding who is at risk, and adopting prevention strategies such as vaccination and good hygiene practices, individuals can play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of flu. As research continues to advance our understanding of influenza and develop new tools for its prevention and treatment, staying informed and proactive is key to navigating each flu season effectively.
What are the typical symptoms of flu, and how do they differ from the common cold?
+The typical symptoms of flu include fever, cough, sore throat, runny or stuffy nose, headache, fatigue, and muscle or body aches. While the common cold shares some of these symptoms, flu symptoms are generally more severe and sudden in onset. The common cold tends to cause more nasal congestion and less fever and body ache than the flu.
How can I prevent the flu, and is the flu vaccine effective?
+Preventing the flu involves getting vaccinated each year, practicing good hygiene such as frequent handwashing, avoiding close contact with people who are sick, and avoiding touching your eyes, nose, and mouth. The flu vaccine is the most effective way to prevent flu and is updated annually to protect against the most common strains. While no vaccine is 100% effective, the flu vaccine significantly reduces the risk of getting and spreading flu.
What are the high-risk groups for flu complications, and how can they be protected?
+High-risk groups for flu complications include older adults, young children, pregnant women, and people with certain chronic health conditions. These groups can be protected by ensuring they receive the flu vaccine, encouraging those around them to get vaccinated to prevent spread, and promptly seeking medical care if they develop flu symptoms.
In the ever-evolving landscape of public health, staying vigilant and informed about flu symptoms and preventive measures is crucial. As research and medical science continue to advance, so too does our understanding of how to combat influenza effectively. Whether through vaccination, good hygiene practices, or the development of new treatments, managing the flu requires a multifaceted approach that involves individuals, communities, and healthcare systems working together.