Gmo Foods: Safe Options For Healthy Eating
The debate surrounding genetically modified organisms (GMOs) has been a longstanding one, with proponents arguing that they offer a solution to global food security and opponents raising concerns about their safety and environmental impact. For individuals seeking to make informed decisions about their diet, navigating the complex landscape of GMO foods can be challenging. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of GMO foods, exploring their safety, benefits, and potential drawbacks, as well as offering guidance on how to make healthy choices in an increasingly complex food environment.
Understanding GMOs
Genetically modified organisms are plants, animals, or microorganisms whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques. This process involves the introduction of genes from one species into the DNA of another species, with the goal of introducing new traits such as pest resistance, improved nutrition, or enhanced durability. GMOs are used in a wide range of applications, from agricultural crops to pharmaceuticals, and their use has become increasingly prevalent in the global food supply.
Safety of GMO Foods
One of the primary concerns surrounding GMO foods is their safety for human consumption. Numerous scientific organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO), the American Medical Association (AMA), and the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), have conducted extensive research on the safety of GMO foods and concluded that they are no more likely to pose health risks than their conventional counterparts. These organizations have found that the genetic modifications made to GMOs do not inherently make them more dangerous and that the rigorous testing and regulatory processes in place are sufficient to ensure their safety.
Benefits of GMO Foods
In addition to their safety, GMO foods offer several potential benefits, including:
- Improved Crop Yields: GMO crops can be engineered to be more resistant to pests and diseases, reducing the need for pesticides and improving crop yields. This can help meet the world’s increasing food demands, especially in regions where food security is a concern.
- Enhanced Nutrition: Genetic modification can be used to enhance the nutritional content of foods. For example, golden rice, a type of rice engineered to contain beta-carotene (a precursor to vitamin A), has the potential to combat vitamin A deficiency in developing countries.
- Drought Tolerance: Scientists are working on developing crops that can thrive in drought conditions, which could be crucial in areas prone to water scarcity.
Potential Drawbacks and Concerns
While GMO foods have numerous benefits, there are also concerns and potential drawbacks to consider:
- Environmental Impact: The introduction of GMOs into the environment can have unintended consequences, such as the development of pesticide-resistant pests or the contamination of non-GMO crops.
- Regulatory Frameworks: The regulation of GMOs varies significantly around the world, with some countries having strict guidelines and others lacking comprehensive frameworks. This disparity can lead to inconsistencies in safety assessments and public trust.
- Labeling and Transparency: The debate over whether GMO foods should be labeled as such continues. Proponents of labeling argue that consumers have the right to know what they are eating, while opponents claim that mandatory labeling could unfairly stigmatize GMO products.
Making Healthy Choices
For consumers looking to make informed decisions about GMO foods, several strategies can be employed:
- Educate Yourself: Stay updated on the latest research and debates surrounding GMOs. Understanding the science behind genetic modification can help demystify the process and its products.
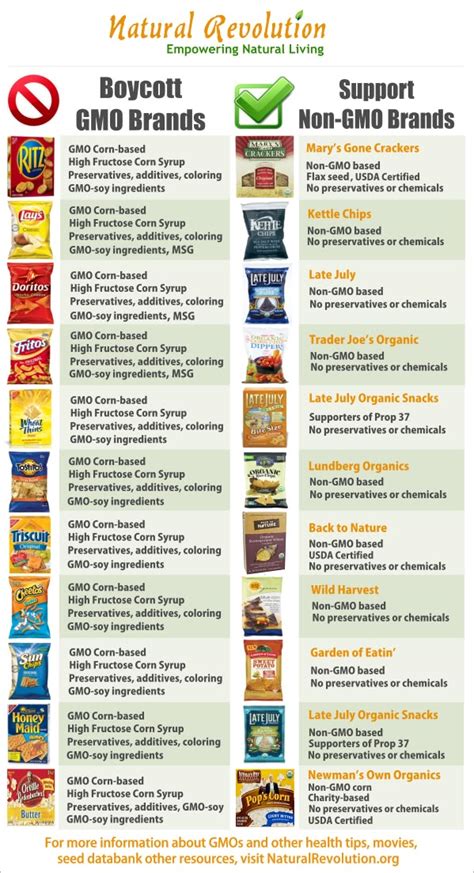
- Check Labels: In countries where GMO labeling is mandatory, check the labels of the products you buy. However, be aware that the absence of a GMO label does not necessarily mean the product is GMO-free, as labeling laws can vary.
- Support Transparent Brands: Choose to support companies that are transparent about their use of GMOs and have clear, non-GMO certified options if that’s your preference.
- Diversify Your Diet: Ensure your diet is varied and includes foods from different sources. This can help minimize exposure to any single type of food, including GMOs.
- Engage in the Conversation: Participate in public discussions and support policies that promote transparency, rigorous safety testing, and sustainable agricultural practices.
Future Perspectives
As technology advances, the potential applications of genetic modification in food production are expected to expand. Techniques like CRISPR/Cas9 offer more precise and efficient ways to edit genes, which could lead to more sophisticated and beneficial GMOs. However, as with any technology, it’s crucial that these advancements are met with careful consideration of their ethical, environmental, and health implications.
Conclusion
GMO foods represent a complex and multifaceted aspect of modern agriculture and food production. While they offer significant benefits in terms of food security, nutrition, and sustainability, they also raise important questions about safety, regulation, and environmental impact. By educating themselves and engaging with the ongoing debate, consumers can make informed choices that align with their values and priorities. Ultimately, a balanced and nuanced approach to GMOs, recognizing both their potential and their challenges, is essential for fostering a healthier and more sustainable food system for all.
Are all GMO foods clearly labeled as such?
+No, the labeling of GMO foods is not standardized worldwide. In some countries, foods containing GMOs must be labeled, while in others, such as the United States, labeling is largely voluntary, although there are moves towards creating a national standard for disclosure.
Can GMOs help address global food security challenges?
+Yes, GMOs have the potential to play a significant role in addressing global food security challenges. By improving crop yields, enhancing nutritional content, and making crops more resilient to pests and environmental stresses, GMOs can help increase food availability and accessibility.
How are GMOs regulated to ensure safety?
+GMOs are regulated by various national and international bodies. The process typically involves a thorough risk assessment that considers the potential impacts on human health and the environment. This includes evaluating the genetic modification process, the characteristics of the GMO, and the conditions under which it will be grown or used.