Ppo And Hmo Plans Compared: Best Coverage
When navigating the complex world of health insurance, two of the most common types of plans that individuals and families encounter are Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) plans and Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) plans. Each has its own set of benefits, drawbacks, and structural differences that can significantly impact the quality and cost of healthcare for those enrolled. Understanding the nuances of PPO and HMO plans is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with one’s healthcare needs and financial situation.
Introduction to PPO Plans
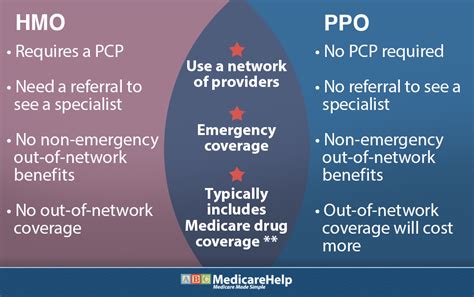
PPO plans are designed to offer a balance between cost and flexibility. They feature a network of healthcare providers who have agreed to provide services to plan members at a discounted rate. One of the hallmark benefits of PPO plans is that they allow members to see any healthcare provider they choose, both in and out of network, without needing a referral. This flexibility, however, comes at a cost, as seeing out-of-network providers typically results in higher out-of-pocket expenses for the member.
Key Features of PPO Plans:
- Network Flexibility: Members can choose to receive care from any doctor or hospital, whether in-network or out-of-network, though out-of-network care is more expensive.
- Referral Requirements: No referrals are needed to see specialists within the network.
- Cost Sharing: Members pay a portion of healthcare costs through deductibles, copays, and coinsurance.
- Premium Costs: Generally higher than HMO plans due to the greater flexibility offered.
Introduction to HMO Plans
HMO plans, on the other hand, prioritize cost savings and coordinated care within a specific network of providers. Members are required to receive medical care and services from the providers within the HMO’s network, except in emergency situations. To see a specialist, a referral from a primary care physician (PCP) is usually necessary. This structured approach aims to control costs by ensuring that all medical care is managed and coordinated, potentially leading to more preventive and less redundant care.
Key Features of HMO Plans:
- Network Restrictions: Care is generally only covered if provided by in-network physicians and hospitals, except in emergency cases.
- Referral Requirements: A referral from a primary care physician is often needed to see a specialist.
- Cost Sharing: Members pay through deductibles, copays, and sometimes coinsurance, though costs are typically lower than PPO plans.
- Premium Costs: Generally lower than PPO plans due to the restricted network and management of care.
Comparative Analysis
Flexibility vs. Cost: The most significant difference between PPO and HMO plans is the flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. PPO plans offer greater flexibility at a higher cost, while HMO plans restrict provider choice in exchange for lower premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
Quality of Care: Both types of plans can offer high-quality care, as the quality of healthcare is more closely related to the individual provider or facility rather than the insurance plan type. However, HMOs often focus on preventive care and coordination, which can lead to better health outcomes for members who follow the plan’s guidelines.
Emergency Care: Both PPO and HMO plans cover emergency care, regardless of whether the emergency room is in-network or out-of-network. This is a federal requirement to ensure that individuals receive necessary emergency care without worrying about network restrictions.
Decision Framework
Choosing between a PPO and an HMO plan depends on several factors, including personal healthcare needs, budget, and preferences regarding provider choice and referrals. The following considerations can help guide the decision:
- Healthcare Needs: Individuals or families with complex or ongoing medical conditions may prefer the flexibility of a PPO plan to ensure access to specialized care without the need for referrals.
- Budget: Those on a tighter budget may find HMO plans more appealing due to lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs.
- Provider Choice: Individuals who value the freedom to choose their healthcare providers without restrictions may prefer PPO plans.
Conclusion
The debate between PPO and HMO plans comes down to individual preferences regarding flexibility, cost, and the management of healthcare. PPO plans offer greater autonomy in choosing healthcare providers but at a higher cost. HMO plans, while more restrictive, can provide comprehensive care at a lower cost, emphasizing preventive measures and coordinated care. Ultimately, the best choice depends on one’s specific healthcare needs, financial situation, and personal comfort with the structures and limitations of each plan type.
What is the main difference between PPO and HMO health insurance plans?
+The main difference between PPO (Preferred Provider Organization) and HMO (Health Maintenance Organization) plans is the level of flexibility in choosing healthcare providers. PPO plans allow members to see any healthcare provider, both in and out of network, without needing a referral, though out-of-network care is more expensive. HMO plans require members to receive care from within the network, except in emergencies, and often need a referral to see a specialist.
Which type of plan is generally more cost-effective for individuals with ongoing medical conditions?
+For individuals with ongoing medical conditions, an HMO plan might be more cost-effective, assuming their healthcare providers are within the network. HMOs focus on managed care, which can lead to more preventive measures and possibly lower out-of-pocket costs over time. However, the need for referrals and the potential limitation on specialist choice must be carefully considered against the cost savings.
Do both PPO and HMO plans cover emergency care?
+Yes, both PPO and HMO plans cover emergency care, regardless of whether the emergency room is in-network or out-of-network. This is mandated by federal law to ensure that individuals receive necessary emergency care without worrying about network restrictions.
In conclusion, while both PPO and HMO plans have their advantages and disadvantages, the choice between them should be based on a thorough evaluation of one’s healthcare needs, financial situation, and personal preferences regarding flexibility and managed care. By understanding the differences and considering these factors, individuals can make an informed decision that ensures they have the best possible coverage for their unique circumstances.


