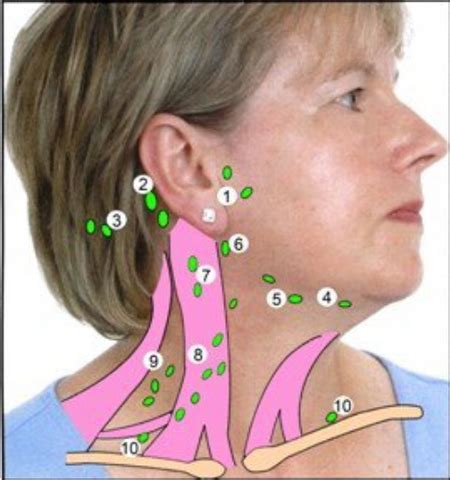
Goiter Disease Causes Revealed
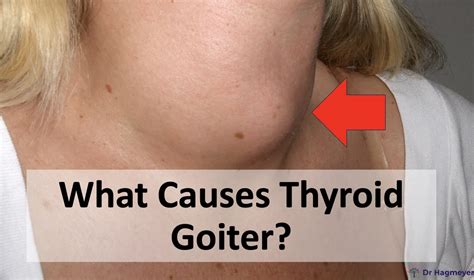
The prevalence of goiter disease, a condition characterized by the enlargement of the thyroid gland, has been a significant health concern worldwide. The thyroid gland, a vital endocrine gland situated in the neck, plays a pivotal role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development. When the thyroid gland becomes enlarged, it can lead to a range of complications, including difficulty swallowing, breathing, and even cancer. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of goiter disease, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options, as well as providing insights into the latest research and advancements in the field.
Understanding Goiter Disease
Goiter disease, also known as thyromegaly, can be caused by a variety of factors, including iodine deficiency, thyroid nodules, thyroiditis, and thyroid cancer. Iodine deficiency is the most common cause of goiter worldwide, particularly in areas where the diet lacks sufficient iodine. The thyroid gland requires iodine to produce thyroid hormones, and a deficiency can lead to an enlargement of the gland as it attempts to capture more iodine from the bloodstream.
Iodine Deficiency: A Global Health Concern
Iodine deficiency is a significant public health concern, affecting over 2 billion people worldwide. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that nearly 30% of the global population is at risk of iodine deficiency, with the majority residing in developing countries. Iodine deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including goiter, cretinism, and hypothyroidism. The WHO recommends a daily intake of 150 micrograms of iodine for adults, which can be achieved through a balanced diet that includes iodized salt, seafood, and dairy products.
Thyroid Nodules: A Common Cause of Goiter
Thyroid nodules are another common cause of goiter disease. These nodules are growths that form on the thyroid gland, and they can be either benign or cancerous. Benign thyroid nodules are non-cancerous and are often asymptomatic, while cancerous nodules can lead to thyroid cancer. According to the American Thyroid Association, thyroid nodules affect approximately 68% of the population, with the majority being benign.
Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the Thyroid Gland
Thyroiditis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can lead to goiter disease. There are several types of thyroiditis, including Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, De Quervain’s thyroiditis, and subacute thyroiditis. Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack the thyroid gland, leading to inflammation and damage. De Quervain’s thyroiditis is a rare condition caused by a viral infection, while subacute thyroiditis is a temporary condition that resolves on its own.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing goiter disease typically involves a physical examination, thyroid function tests, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scans. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause of the goiter. For example, iodine supplementation can help alleviate iodine deficiency, while surgery or radiation therapy may be necessary for thyroid cancer.
Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy
Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is a common treatment option for goiter disease caused by hypothyroidism. This involves taking synthetic thyroid hormones to replace the missing hormones produced by the thyroid gland. According to the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, thyroid hormone replacement therapy is effective in managing hypothyroidism, with over 90% of patients experiencing significant improvement in symptoms.
Latest Research and Advancements
Research into goiter disease is ongoing, with scientists exploring new treatments and diagnostic techniques. For example, a recent study published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism found that a new thyroid hormone replacement therapy, called tiratricol, was effective in managing hypothyroidism in patients with goiter disease. Another study published in the journal Thyroid found that a novel imaging technique, called thyroid elastography, was able to accurately diagnose thyroid cancer in patients with goiter disease.
Conclusion
Goiter disease is a complex condition with multiple causes and symptoms. Understanding the underlying causes of goiter disease is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. By exploring the intricacies of goiter disease, we can gain a deeper understanding of the condition and develop more effective treatment options. As research continues to advance our knowledge of goiter disease, we can expect to see improved outcomes for patients affected by this condition.
What are the symptoms of goiter disease?
+The symptoms of goiter disease can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common symptoms include swelling in the neck, difficulty swallowing, breathing difficulties, and hoarseness. In some cases, goiter disease can also cause fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance.
How is goiter disease diagnosed?
+Diagnosing goiter disease typically involves a physical examination, thyroid function tests, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scans. In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of the goiter.
What are the treatment options for goiter disease?
+Treatment options for goiter disease vary depending on the underlying cause. Iodine supplementation can help alleviate iodine deficiency, while surgery or radiation therapy may be necessary for thyroid cancer. Thyroid hormone replacement therapy is also a common treatment option for goiter disease caused by hypothyroidism.
In conclusion, goiter disease is a complex condition that requires a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the underlying causes of goiter disease and exploring the latest research and advancements, we can develop more effective treatment options and improve outcomes for patients affected by this condition. As we continue to advance our knowledge of goiter disease, we can expect to see improved patient outcomes and a reduction in the global burden of this condition.