Good Glucose Range: Healthy Blood Sugar Targets
Maintaining a good glucose range is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Blood sugar levels, measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), indicate the amount of glucose present in the blood. Understanding the healthy blood sugar targets can help individuals make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication, ultimately reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day, influenced by factors such as meals, physical activity, and sleep. The body regulates blood sugar levels through the release of insulin and glucagon, hormones produced by the pancreas. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, while glucagon stimulates the release of stored glucose into the bloodstream.
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges
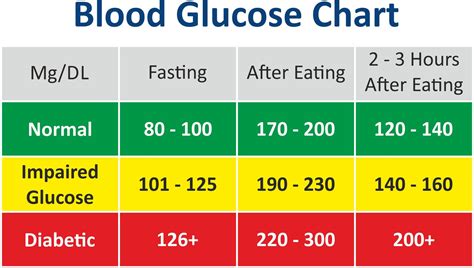
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following blood sugar targets for individuals with diabetes:
- Fasting blood sugar (before eating): 70-130 mg/dL
- Before meals: 70-130 mg/dL
- After meals (1-2 hours): Less than 180 mg/dL
- At bedtime: 100-140 mg/dL
For individuals without diabetes, the normal blood sugar ranges are:
- Fasting blood sugar: 70-99 mg/dL
- After meals: Less than 140 mg/dL
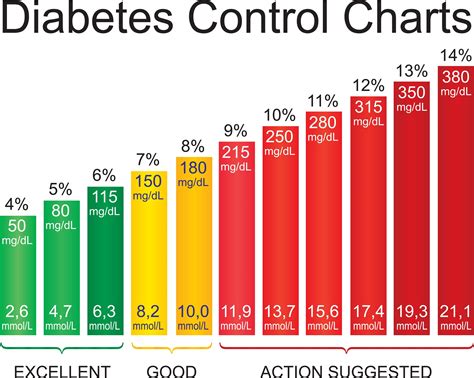
Importance of Blood Sugar Control
Maintaining good glucose ranges is essential for preventing diabetes-related complications, such as:
- Nerve damage (neuropathy): High blood sugar levels can damage nerves, leading to pain, numbness, and tingling sensations in the hands and feet.
- Kidney damage (nephropathy): High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels in the kidneys, impairing their ability to filter waste and excess fluids.
- Eye damage (retinopathy): High blood sugar levels can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision problems and potentially blindness.
- Heart disease and stroke: High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of heart disease and stroke by damaging blood vessels and nerves.
Factors Influencing Blood Sugar Levels

Several factors can influence blood sugar levels, including:
- Diet: Consuming high-carbohydrate foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats can raise blood sugar levels.
- Physical activity: Regular exercise can help lower blood sugar levels by increasing insulin sensitivity.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids and certain antidepressants, can raise blood sugar levels.
- Sleep: Poor sleep quality and duration can disrupt blood sugar regulation.
- Stress: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels by stimulating the release of stress hormones, such as cortisol.
Strategies for Maintaining Healthy Blood Sugar Targets
To maintain good glucose ranges, individuals can follow these strategies:
- Eat a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week.
- Monitor blood sugar levels: Regularly check blood sugar levels to identify patterns and make adjustments to diet and exercise.
- Get enough sleep: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night to help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Manage stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
Conclusion
Maintaining a good glucose range is crucial for overall health, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. By understanding the healthy blood sugar targets, factors that influence blood sugar levels, and implementing strategies for maintaining healthy blood sugar targets, individuals can reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes and promote overall well-being.
Additional Resources
For more information on blood sugar management and diabetes prevention, consult the following resources:
- American Diabetes Association (ADA): www.diabetes.org
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): www.cdc.gov/diabetes
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes
What are the normal blood sugar ranges for individuals without diabetes?
+For individuals without diabetes, the normal blood sugar ranges are: Fasting blood sugar: 70-99 mg/dL, and After meals: Less than 140 mg/dL.
How can I maintain healthy blood sugar targets?
+To maintain healthy blood sugar targets, individuals can follow these strategies: Eat a balanced diet, Exercise regularly, Monitor blood sugar levels, Get enough sleep, and Manage stress.
What are the risks of high blood sugar levels?
+High blood sugar levels can increase the risk of complications, such as nerve damage, kidney damage, eye damage, heart disease, and stroke.



