Healthy A1c Level
Maintaining a healthy A1c level is crucial for individuals with diabetes, as it reflects the average blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 months. The A1c test measures the percentage of hemoglobin in red blood cells that has been glycated, or bound to glucose. A healthy A1c level indicates that blood sugar levels are well-controlled, reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
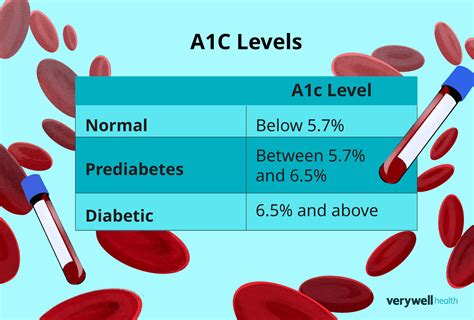
For individuals without diabetes, the normal A1c range is typically below 5.7%. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends an A1c goal of less than 7% for most adults. However, this target may vary depending on factors such as age, comorbidities, and duration of diabetes. Tighter control, such as an A1c level below 6.5%, may be beneficial for some individuals, but it can also increase the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Achieving a healthy A1c level requires a multifaceted approach that incorporates lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring. A well-balanced diet that emphasizes whole, unprocessed foods, such as vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity, including aerobic exercise and strength training, can improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake.
In addition to diet and exercise, medication plays a critical role in managing A1c levels. For individuals with type 2 diabetes, metformin is often the first-line medication, as it has been shown to reduce A1c levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Other medications, such as sulfonylureas, meglitinides, and DPP-4 inhibitors, may also be prescribed to help control blood sugar levels. For those with type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is essential to regulate A1c levels.
Regular monitoring of A1c levels is crucial to assess the effectiveness of treatment plans and make adjustments as needed. The frequency of A1c testing depends on individual factors, such as the severity of diabetes, medication regimens, and lifestyle changes. Generally, A1c levels are checked every 3-6 months, but more frequent testing may be necessary for those with unstable or poorly controlled diabetes.
Several factors can influence A1c levels, including:
- Hemoglobin variants: Certain genetic disorders, such as sickle cell anemia or thalassemia, can affect hemoglobin and alter A1c results.
- Kidney function: Impaired kidney function can lead to inaccurate A1c readings, as the kidneys play a crucial role in filtering and removing excess glucose from the blood.
- Anemia: Iron deficiency anemia or other forms of anemia can affect hemoglobin levels and A1c results.
- Pregnancy: A1c levels may be lower during pregnancy due to changes in red blood cell turnover and hemoglobin production.
To illustrate the importance of maintaining a healthy A1c level, consider the following scenario:
Meet Jane, a 45-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes. Jane’s A1c level is 8.5%, indicating poor blood sugar control. Her healthcare provider recommends lifestyle modifications, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, and prescribes metformin to help regulate her blood sugar levels. After 3 months of adhering to her treatment plan, Jane’s A1c level decreases to 7.2%, indicating improved blood sugar control. As a result, Jane reduces her risk of developing complications associated with diabetes, such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems.
In conclusion, maintaining a healthy A1c level is essential for individuals with diabetes to reduce the risk of complications and improve overall health outcomes. A comprehensive treatment plan that incorporates lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, and regular monitoring can help achieve and maintain a healthy A1c level.
What is a healthy A1c level for individuals with diabetes?
+The American Diabetes Association recommends an A1c goal of less than 7% for most adults with diabetes. However, this target may vary depending on individual factors, such as age, comorbidities, and duration of diabetes.
How often should I get my A1c level checked?
+The frequency of A1c testing depends on individual factors, such as the severity of diabetes, medication regimens, and lifestyle changes. Generally, A1c levels are checked every 3-6 months, but more frequent testing may be necessary for those with unstable or poorly controlled diabetes.
Can lifestyle modifications alone help maintain a healthy A1c level?
+Lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve A1c levels. However, for many individuals with diabetes, medication is also necessary to achieve and maintain a healthy A1c level.
By understanding the importance of maintaining a healthy A1c level and implementing a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of complications and improve their overall health outcomes.



