Healthy Blood Sugar: Control Levels Easily
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is crucial for overall well-being, as it directly impacts energy levels, weight management, and the risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes and heart disease. The human body is designed to regulate blood sugar levels naturally, but with the typical modern diet and lifestyle, this delicate balance can easily be disrupted. Understanding how to control blood sugar levels is not just about managing diabetes; it’s about fostering a healthy metabolism, reducing inflammation, and ensuring that the body’s cells receive the energy they need to function optimally.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Balance
Blood sugar balance is maintained by the body’s internal regulatory system, primarily through the actions of insulin and glucagon, hormones produced by the pancreas. Insulin lowers blood sugar levels by facilitating the entry of glucose into cells, while glucagon raises blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to release stored glucose (glycogen) into the bloodstream. This balance is vital for preventing both hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), conditions that can lead to symptoms ranging from mild (shakiness, hunger) to severe (loss of consciousness, organ damage).
Dietary Strategies for Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
Diet plays a critical role in managing blood sugar levels. Foods that are high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can cause a spike in blood sugar, followed by a crash, which over time can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. Conversely, foods that are rich in fiber, protein, and healthy fats can help slow down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, keeping blood sugar levels stable.
- Whole, Unprocessed Foods: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. These foods are naturally rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals and tend to have a lower glycemic index, meaning they cause a slower and smaller rise in blood sugar levels.
- Glycemic Index (GI): Understanding the GI of foods can be helpful. The GI is a measure of how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. Foods are ranked on a scale of 0 to 100, with higher values given to foods that cause the most rapid increase in blood sugar. Choosing foods with a low GI can help in maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
- Hydration: Adequate hydration is essential for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels. Sometimes, thirst can be mistaken for hunger or cravings for sweets, leading to consuming more calories and sugars than needed.
Lifestyle Interventions
In addition to dietary changes, several lifestyle interventions can significantly impact blood sugar control.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity, including both aerobic exercise and strength training, can improve insulin sensitivity, helping the body to more effectively use insulin and manage blood sugar levels.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can raise blood sugar levels and exacerbate conditions like diabetes. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on blood sugar control.
- Sleep: Getting adequate sleep is crucial. Poor sleep quality and short duration can lead to increased levels of cortisol (a stress hormone), which can disrupt blood sugar balance and contribute to insulin resistance.
Monitoring and Managing Blood Sugar
For individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing it, monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of management. This involves:
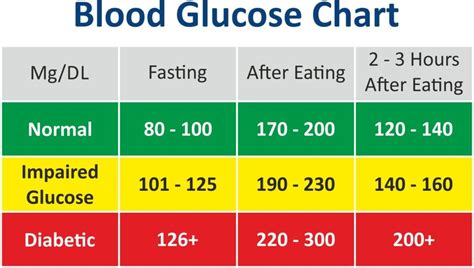
- Regular Testing: Using a glucometer to check blood sugar levels at different times of the day, especially after meals and before bedtime, can provide valuable insights into how diet and activities affect blood sugar.
- Keeping a Diary: Maintaining a diary of food intake, physical activity, stress levels, and sleep patterns alongside blood sugar readings can help identify patterns and triggers of high or low blood sugar levels.
- Adjusting Medications and Lifestyle: Based on the data collected, adjustments can be made to medications (under the guidance of a healthcare provider), diet, and lifestyle to better control blood sugar levels.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is a multifaceted challenge that requires attention to diet, lifestyle, and, when necessary, medical intervention. By understanding how different foods and activities impact blood sugar and by making informed choices, individuals can take proactive steps towards a healthier metabolic profile. Whether the goal is to prevent chronic diseases, manage existing conditions, or simply feel more energized and focused, the strategies outlined above offer a comprehensive approach to achieving and maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on the individual’s health status and the presence of diabetes. For people with type 1 diabetes, it’s common to check blood sugar levels at least four to six times a day. For those with type 2 diabetes, the frequency may vary based on the treatment plan and how well blood sugar is controlled.
Can diet and exercise alone control blood sugar levels?
+For many people, especially those with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, diet and exercise can play a significant role in managing blood sugar levels. A healthy diet that is low in added sugars, saturated fats, and refined carbohydrates, combined with regular physical activity, can improve insulin sensitivity and help keep blood sugar levels within a target range. However, for some individuals, especially those with type 1 diabetes, medication (such as insulin) will also be necessary to control blood sugar levels.