High Blood Sugar Numbers
The concern about high blood sugar numbers is a common issue for many individuals, particularly those diagnosed with diabetes. High blood sugar, also known as hyperglycemia, occurs when the body has too much glucose (sugar) in the bloodstream. This condition can lead to a variety of complications, including damage to organs such as the kidneys, heart, and nerves, as well as increased risk of infections and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
The Impact of High Blood Sugar on the Body
High blood sugar numbers can affect various parts of the body, leading to a range of symptoms and potential health issues. Some of the common effects include:
- Increased urination: When there is too much glucose in the blood, the kidneys try to remove it by increasing urine production. This can lead to frequent urination and dehydration if not enough fluids are consumed.
- Excessive thirst: As the body loses water through increased urination, it can cause feelings of thirst and dry mouth.
- Blurred vision: High blood sugar levels can cause the lens in the eye to swell, leading to blurred vision.
- Fatigue: The body’s cells are not getting the energy they need, leading to feelings of tiredness and weakness.
- Slow healing of cuts and wounds: High blood sugar levels can affect the body’s ability to heal wounds, making them more susceptible to infection.
Understanding Blood Sugar Numbers
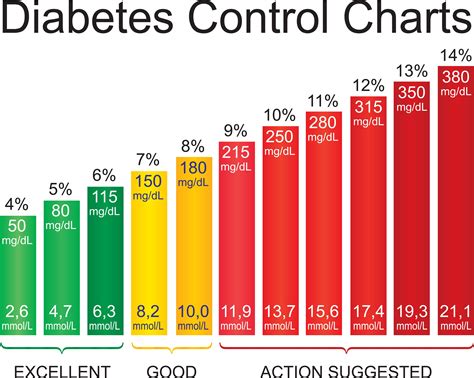
To manage high blood sugar, it’s essential to understand what the numbers mean. Blood sugar levels are measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) and are typically categorized as follows:
- Normal: Less than 100 mg/dL (fasting) or less than 140 mg/dL (after eating)
- Prediabetes: 100-125 mg/dL (fasting) or 140-199 mg/dL (after eating)
- Diabetes: 126 mg/dL or higher (fasting) or 200 mg/dL or higher (after eating)
Managing High Blood Sugar
There are several ways to manage high blood sugar numbers, including:
- Medication: Taking medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider can help regulate blood sugar levels.
- Diet: Eating a healthy, balanced diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates can help manage blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can help the body use insulin more efficiently and lower blood sugar levels.
- Monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels can help identify patterns and make adjustments to treatment plans as needed.
Preventing High Blood Sugar
While some cases of high blood sugar may be unavoidable, there are steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing the condition. These include:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight, particularly around the waist, can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Eating a balanced diet: Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help the body regulate blood sugar levels.
- Getting regular check-ups: Regular health check-ups can help identify any potential issues before they become major problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of high blood sugar?
+Common symptoms include increased urination, excessive thirst, blurred vision, fatigue, and slow healing of cuts and wounds.
How can I prevent high blood sugar?
+Prevention strategies include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and getting regular check-ups.
What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
+Normal blood sugar levels are typically less than 100 mg/dL (fasting) or less than 140 mg/dL (after eating).
How often should I check my blood sugar levels?
+The frequency of checking blood sugar levels depends on individual circumstances and should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Can high blood sugar be managed without medication?
+In some cases, high blood sugar can be managed through lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, but this should be done under the guidance of a healthcare provider.